- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
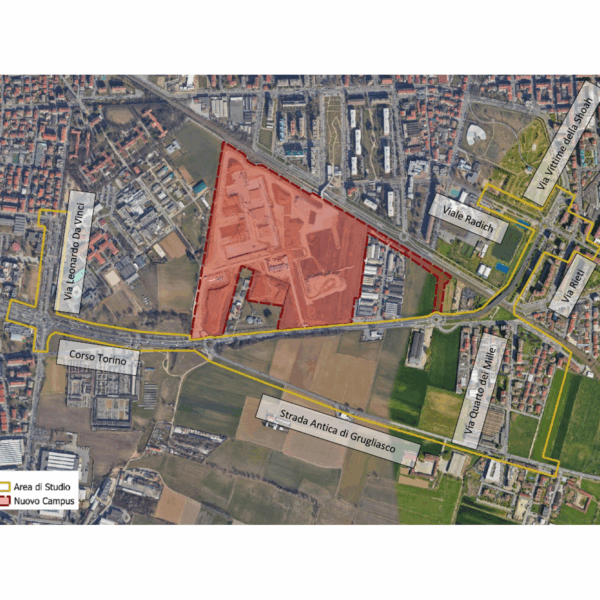
- Assessment of the impact on traffic of the opening of the new campus of the University of Turin, ‘Città delle Scienze e dell’Ambiente’ (City of Science and Environment), located in Grugliasco, Metropolitan City of Turin TRT was chosen by Zona Ovest di Torino srl to provide modelling support in defining the impact of the new campus of the University of Turin, ‘Città delle Scienze e dell’Ambiente’ (City of Science and Environment), in the municipality of Grugliasco. The new campus includes facilities for the Chemistry and Biology Departments, spaces for research, teaching and ancillary services for students, covering a total of approximately 90.000 m2 and is expected to double the university population (from the current 5,000 to approximately 10,000). The study begins with the VISUM model developed by TRT on behalf of Zona Ovest and the Municipality of Grugliasco as part of the support assignment for the evaluation of the PGTU, further refining its calibration through a traffic detection campaign. The macroscopic model was used for the municipal-scale assessment of the opening of the new campus, while the local impact assessment was carried out using a dynamic microscopic simulation model in the VISSIM environment. The study took into account various data sources, in addition to ad hoc surveys, of a demographic and statistical nature on the student population and university staff involved in the transfer (keeping teachers separate from researchers, research fellows, scholarship holders, technical and administrative staff, etc.) as well as information on the current travel habits of people who already gravitate towards Grugliasco (where the veterinary, agrovet, agricultural and “agrinnova” facilities are located), including modes of transport, weekly campus attendance, the number of years students are behind in their studies, and the location of their domicile or residence. The analyses carried out have made it possible to identify the configuration and adaptation measures for the road network that are most effective in mitigating the impact of the opening of the university campus.
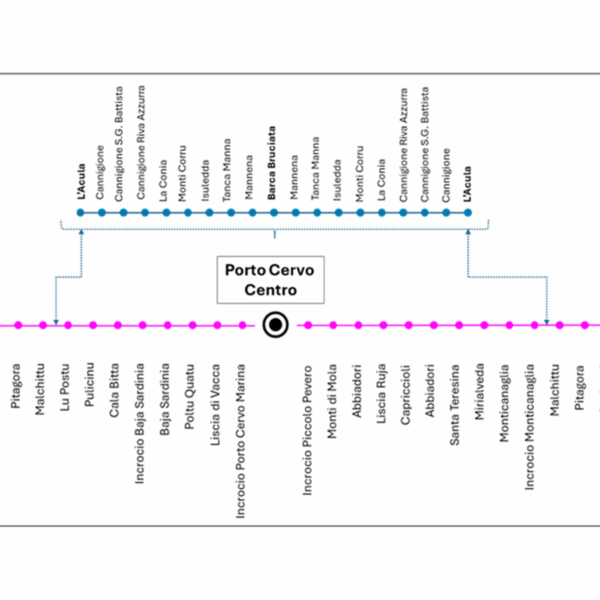
- Design and technical assistance for the award of the Local Public Transport service of the Municipality of Arzachena The Municipality of Arzachena entrusted TRT with the service of “Design and technical assistance for the award of the Local Public Transport service of the Municipality of Arzachena”. The assignment involves activities aimed at the design and assistance for the awarding of the Local Public Transport (LPT) service contract for the Municipality of Arzachena. The work is structured into three main phases: •Preliminary territorial and transport analysis, aimed at understanding the territorial dynamics and the characteristics of the existing service; •Planning and design of the public transport service, consisting of the definition of the characteristics of the proposed public transport service; •Technical assistance to the procedures for the selection and award of the service, consisting of technical support to the Municipality for the preparation of the tender documents and for all phases of the award procedure. The first phase of analysis aims to reconstruct the current framework of local mobility, considering the settlement, demographic and tourist characteristics of the municipal area, as well as analysing transport demand through specific investigations. The second phase is based on the results of the knowledge framework reconstruction to develop a new transport offer configuration, consistent with the mobility needs of the different user groups, both in summer (tourists) and winter (residents), distinguishing between annual service, seasonal summer service and any flexible services. The activities also include technical assistance to the Municipality of Arzachena in the preparation of the special tender specifications, the tender rules and the service contract scheme. To date, TRT has completed the preliminary territorial and transport analysis.
- Municipality of Fermo, Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan Following a tender procedure, the Municipality of Fermo entrusted TRT, together with local experts, with drafting the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (PUMS) and the related Preliminary Environmental Report – Screening procedure for Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA).The drafting of the PUMS is structured in three phases. The first phase is related to the definition of guidelines, including the knowledge framework of the mobility system and the SWOT analysis, leading to the formulation of objectives and strategies. The planning-programming framework was defined at regional, provincial, and local levels, along with the territorial and socio-economic context of the planning area, the supply of transport networks and services, mobility demand, and the social (accidents) and environmental impacts generated by the mobility system. The second phase includes the drafting of the preliminary PUMS report, which builds on the knowledge framework to identify planning scenarios and related actions. This document allows the initiation of the SEA screening procedure, providing the essential information to assess the environmental impact of the Plan. In parallel with the first and during the second phase, a participation process was developed involving local stakeholders: initially to identify the critical issues of the mobility system and later to critically review the system of actions forming the Plan’s scenario. The feedback received helped refine the definition of scenarios based on comments and suggestions. The third phase is the drafting of the final Plan document, which includes not only the contents of the second phase but also the results of the MOMOS model application, as well as cost estimates and target indicators.
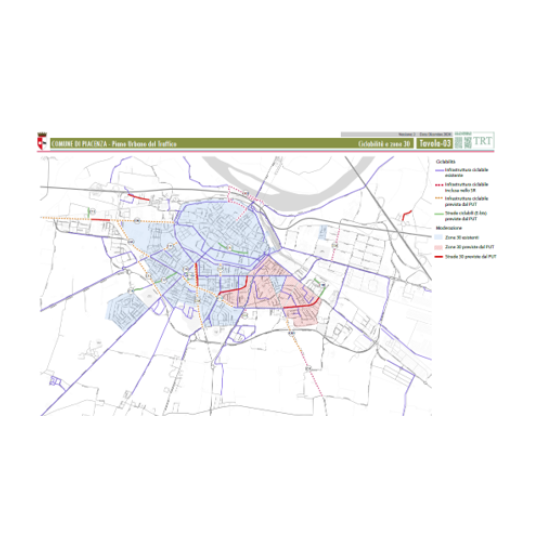
- Update of the Urban Traffic Plan (UTP) of the Municipality of Piacenza, a short-term (two-year) implementation tool of the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan The Municipality of Piacenza has commissioned TRT to draft the monitoring report for the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (SUMP) (document submitted and registered on 10/08/2023) and to update the Urban Traffic Plan (UTP). The UTP is a short-term implementation plan (covering a two-year period) aimed at carrying out the interventions foreseen in the Short-Term Scenario of the SUMP. The development of Piacenza’s UTP follows the guidelines set out in the Ministerial Directives of 1995 and the most recent updates to the Italian Highway Code. The monitoring of the SUMP lays the foundation for selecting the interventions that define the scenarios of the UTP. In fact, the document reports on the updated state of urban mobility in Piacenza, assessing the progress and impacts of the actions taken since the approval of the SUMP in December 2020. Based on this evidence, the most consistent interventions with the SUMP’s short-term scenario (2–3 years) have been selected. This selection also considered existing planning tools, such as the 2024–2026 Three-Year Public Works Program, the Cycling Plan (approved on 17/04/2023), the Smart City Plan (October 2019), the Environmental Noise Action Plan, and other strategic documents. The UTP was developed in three main phases: With Municipal Resolution No. 23 of 11 February 2025, the Draft Plan was adopted. Following the 30-day period dedicated to public consultation, and the related replies/amendments, the Plan was definitely approved by the Municipal Council with Resolution No. 25 of 22/09/2025.
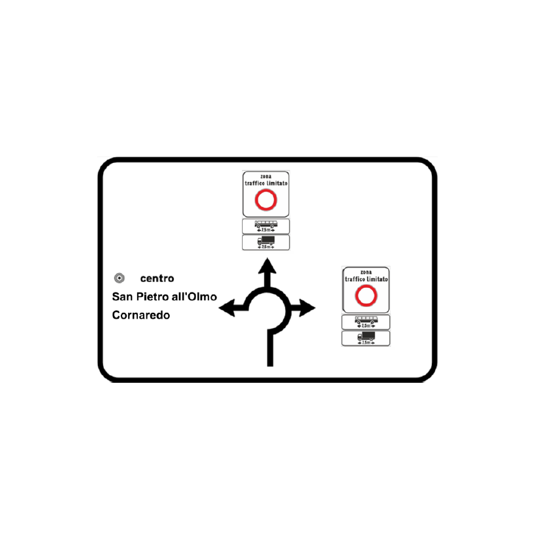
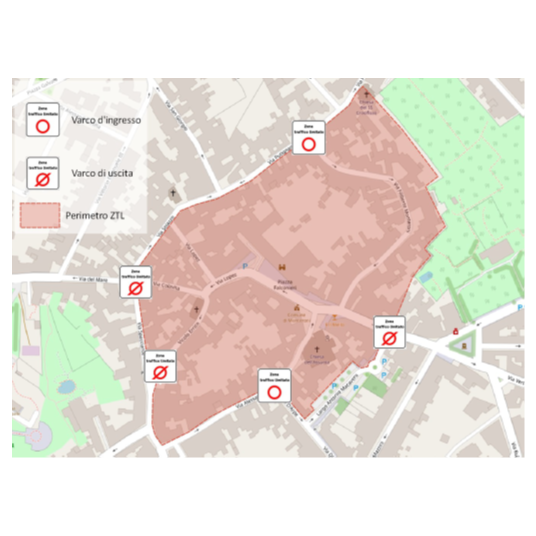
- Study to identify the perimeter of a Restricted Traffic Zone within the inhabited area of Cusago (Milan) TRT was commissioned to carry out a study aimed at identifying the correct perimeter of a Restricted Traffic Zone (ZTL) for commercial vehicle traffic to be placed within the inhabited area of Cusago, a municipality of the Metropolitan City of Milan. The implementation of the ZTL for heavy vehicles is intended to solve the problem of heavy vehicles crossing residential areas, where today a ban on access is in force, which is frequently not respected. The study included: Photographic overview of planned access points location
- Drafting of the Urban Plan of Sustainable Mobility of the Municipality of Monteroni di Lecce(LE) accompanied by verification of subjection to strategic environmental assessment (SEA) The Municipality of Monteroni di Lecce (LE) has entrusted TRT Trasporti e Territorio with the service of drafting the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (PUMS). The Plan is financed by the Apulia Region as part of the authority’s commitment to provide municipalities with strategic planning tools for the urban mobility and transport sector. TRT was chosen by the Administration in continuity with the recent work carried out for the elaboration of the General Urban Traffic Plan (PGTU), approved by the City Council in April 2024.Starting from the knowledge of the territory acquired thanks to the previous PGTU, TRT has drafted the PUMS, a Pano document of a strategic nature with a 10-year time horizon, which represents a medium-long term guide capable of orienting the Administration’s decisions in the field of mobility.The drafting of the PUMS developed through two phases. The first consisted in drafting the Plan’s Guidelines, containing the cognitive framework, the SWOT analysis and, consequently, the Plan’s objectives and strategies, including the description of indicators. The cognitive framework included the superordinate planning framework, the analysis of mobility demand, infrastructure and services endowment, the position of traffic attractors as well as information related to mobility impacts (pollutants, accidents, motorisation rate, etc.).The second phase included the identification of alternative Plan scenarios, monitoring, cost estimation, the results of the Plan Scenario assessment through the implementation of the strategic model MOMOS (MOdello per la MObilità Sostenibile) with the consequent extraction of transport, environmental, social and economic sustainability indicators. MOMOS was applied to assess, in an aggregate way, the impact of the mobility policies introduced, such as the expansion of the bicycle network, new public transport services, the ZTL, speed moderation, etc.. A screening report was also prepared to accompany the second phase, in order to evaluate the exclusion of the Plan from the SEA process by the competent authority. Monteroni SUMP was adopted with resolution n. 136 in the 8th on November 2024 by the Town Government Council and approved with resolution n. 6 in the 12th February 2025 by the Town Council.
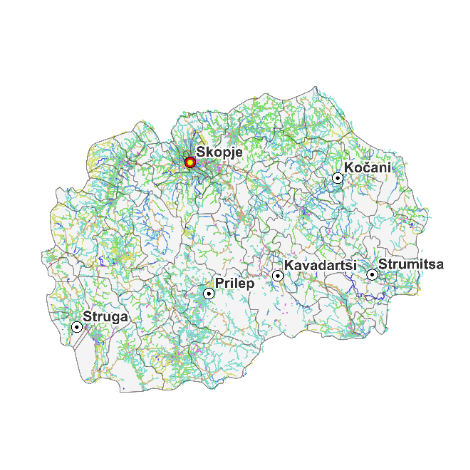
- Technical Assistance for Development of Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans for five Municipalities and providing training on developing and implementation of Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans North Macedonia faces significant challenges in managing its extensive local road network, which spans approximately 9,000 kilometers and falls under the jurisdiction of decentralized municipalities. Many of these municipalities lack the capacity and resources necessary for effective infrastructure maintenance, resulting in deteriorating road conditions that limit access to essential services and opportunities, ultimately affecting citizens’ quality of life. Developing a well-structured Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (SUMP) is crucial to addressing these challenges and achieving the aforementioned objectives. The primary objective of this project, financed by the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development – World Bank, is to develop the SUMPs for the municipalities of Kavadarci, Kochani, Struga, Strumica, and Prilep by enhancing accessibility, promoting health and safety, supporting economic growth, and mitigating environmental impacts. This will be achieved through the promotion of sustainable transport modes, and the adoption of low-carbon initiatives aimed at reducing emissions and optimizing traffic flow. The SUMP development process aligns with European guidelines and is divided into two macro-activities:
- Technical secretariat of the coordination platform to support Member States in implementing requirements for urban nodes in the revised TEN-T Regulation The European Commission’s Sustainable and Smart Mobility Strategy outlines a roadmap for achieving a sustainable, smart, and resilient transport system, with cities playing a central role in this transition. By 2030, all cities are expected to develop Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMPs) to drive this transformation. The New Urban Mobility Framework further emphasizes the importance of integrating cities and regions into the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) by improving first and last-mile connections for both passengers and freight. Ensuring better coordination among local authorities is key to achieving this goal. To support these efforts, the revised TEN-T Regulation designates 432 urban nodes and establishes key requirements to be met by 31 December 2027. These include: To facilitate the implementation of these requirements, a coordination platform is being established. This platform serves as the main forum for exchange and collaboration among EU Member States, supporting the rollout of SUMPs and urban mobility indicators (UMI). By fostering knowledge-sharing and cross-border cooperation, it aims to ensure a consistent and high-quality approach to urban mobility across Europe. The platform’s technical secretariat is coordinated by PwC, with TIS, TRT, and ICLEI integrating the consortium. TRT leads Task 2, a pivotal component of the project that focuses on providing expert advice for implementing the urban node requirements. Key responsibilities include:
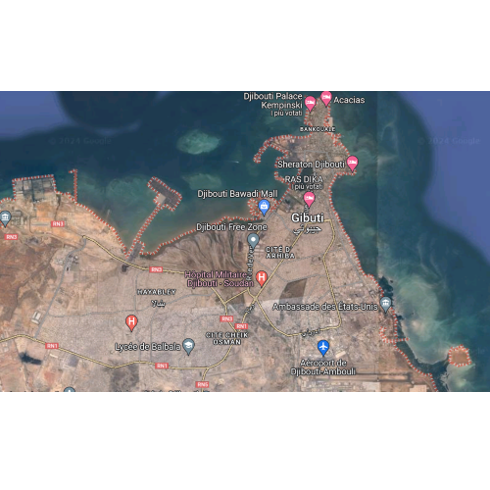
- The Djibouti authorities have appointed the consortium led by IDEA Consult to develop a long-term vision for urban mobility and an action plan for the short, medium and long term, taking into account climate change and its impact on transport networks. The aim of the project is to address the problems of the capital’s transport system, which are undermining its functionality. The study will be carried out in three phases An initial diagnostic phase of the urban transport system, which includes analysing demand, surveying the current state of the road infrastructure and constructing a macro and micro model. A second phase consisting of two main activities: a short-term priority investment programme providing rapid responses to problems, and the development of a shared long-term strategic vision for the urban transport system. Finally, a third phase will be the definition of the master plan for the urban road system. Within the consortium TRT will be responsible for: