- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
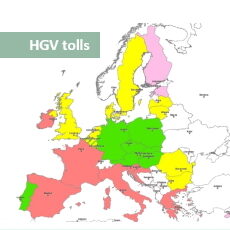
- Assessment of infrastructure costs calculation, tolls calculation and variation for heavy goods vehicles in Member States Directive 1999/62/EC and following amendments provide the legal framework for the application of toll charges to heavy vehicles in the EU, stipulating that road infrastructure charging shall be based on the recovery of infrastructure costs and of traffic-related externalities. Before implementing or amending tolling arrangements, Member States must provide the Commission with a detailed description of the new system. As contractor of the FWC, TRT verifies whether the tolling arrangement notified to the Commission fully respects the provisions of the Directive. The methodology applied for the assessment includes: determination of the scope of the tolling scheme notified by the Member State; identification of costs eligible to be recovered through tolls; allocation of infrastructure costs across vehicles categories; calculation of the weighted average tolls and cost recovery rate. In its assessment reports, TRT provides sound and evidence‐based analyses of the methodology used for infrastructure costs calculation, assessment of compliancy with the Directive’s core principles, as well as recommendations for possible modifications and improvements. Thus far TRT has assessed nine cases, including tolling arrangements from Italy, Spain, France, Bulgaria, Poland and Hungary.
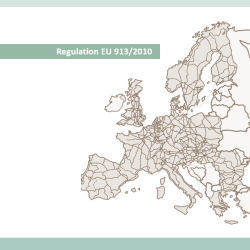
- Evaluation of Regulation (EU) No 913/2010 concerning a European rail network for competitive freight The evaluation support study covered all the provisions of the Regulation, all the European countries participating in a Rail Freight Corridor (RFC) and addressed the period from the establishment of the RFCs until 2020. The key overall challenge addressed by the Regulation is the need to improve the competitiveness of rail freight compared to other transport modes. The starting point of the Regulation is that the quality of the rail freight capacity provided by the infrastructure managers to the operators of international rail freight services needs to improve in order to make it happens. The study identified the impact of the Regulation by comparing the actual developments in the rail freight sector, i.e. with the Regulation in place, with respect to a baseline situation describing the likely developments that would have occurred without this policy intervention. The study also took into account the activities related to the RFCs going beyond the provisions of the Regulation, addressing for instance technical and operational interoperability along the RFCs. Furthermore, the study covered the activities of the rail sector undertaken in the period of analysis and contributing to the objectives of the Regulation. Practically, the study examined the relevance, effectiveness, efficiency, coherence and EU added value of the Regulation. The analysis was based on data collected from a range of primary and secondary sources and direct input from concerned stakeholders, collected using interviews and surveys with national authorities, the rail industry and the Commission’s open public consultation. The study has found that the Regulation has been implemented as far as the designation, the governance and the investment and management of the RFCs are concerned. The concerned stakeholders have fulfilled the provisions of the Regulation in a formal sense and within their actual scope. Viewed on its own, however, the Regulation has had a relatively limited impact in achieving the general, specific and operational objectives and has not led to a broad adoption of the tools, which have produced the intended effects only to a limited extent. TRT acted as leader of the study team built in partnership with M-Five (DE), MC-Vienna (AT) and TEPR (UK). TRT was responsible for (i) the design of the evaluation, (ii) the definition of an evaluation baseline, (iii) the analysis of the stakeholders consultation, (iv) the analysis of the effectiveness and efficiency of the Regulation and (v) the estimation of costs and benefits from the implementation. For more information Evaluation of EU regulation on TEN-T rail freight corridors, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication
- Evaluation of the White Paper ‘Roadmap to a single European transport area – towards a competitive and resource efficient transport system’ The 2011 Transport White Paper “Roadmap to a Single European Transport Area – Towards a competitive and resource efficient transport system” is the document with which the European Commission has outlined the strategy on the future EU transport system and which defines the political agenda for the next decades. The main objectives of the strategy are (i) reduce carbon dioxide emissions in transport to a level that is 60 % below that of 1990; (ii) reduce the transport sector’s dependence on oil; (iii) reduce congestion growth. The strategy is articulated through 40 action points and 132 initiatives aimed at achieving 10 operational targets at different time horizons (2030 and 2050). TRT, member of the consortium led by Ricardo NL and participated by M-Five, E3Modelling and TEPR is responsible for carrying out the mid-term evaluation of the effectiveness of the strategy in order to support the European Commission in identifying any proposals for revising the document. The purpose of the evaluation is to provide a robust evidence-based assessment of the White Paper and the actions following from it since its adoption in 2011. It examines the effectiveness, efficiency, coherence, relevance and EU added value of the White Paper in line with the Better Regulation Guidelines. The evaluation looks at the identified needs for transport policy, the objectives and goals set in the White Paper, the proposed initiatives, reached outcomes and their results, as well as the overall impact of the strategy since it was put in place. The results of the evaluation are intended to inform subsequent decisions of the Commission on possible priorities for the future agenda of EU transport policy. For more information Evaluation of the White Paper ‘Roadmap to a single European transport area – towards a competitive and resource efficient transport system’. Final report, March 2021
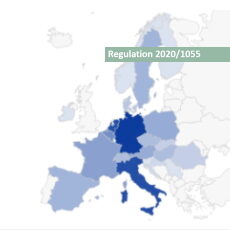
- Data gathering and analysis of the impacts of cabotage restrictions on combined transport road legs: support study for the evaluation of Regulation 2020/1055 (Mobility Package 1) Regulation 2020/1055 will allow Member States to apply the so-called cabotage restrictions to road legs of international combined transport operations if those road legs do not cross a border. The objective of the study was to provide the Commission with an analysis on the market impacts of the new restrictions. To that end, TRT conducted a survey among major combined transport organisers and terminal operators, covering all modal combinations and a wide range of Member States. The survey focused on the collection of data and information on combined transport road legs, and on the compliance strategies and impacts foreseen by the respondents. Based on the results of the survey, the study evaluated the quantitative impacts of cabotage restrictions on the European combined transport market, including estimates of the expected change in combined transport volumes, market share, modal shift and other transport activity indicators. According to the results, the rail-road segment would suffer more than the other modes considered (short sea shipping and inland navigation) mainly because of the tighter competition of the road only carriage. Relevance of the various compliance measures for CTOs (% of CT operations concerned by each measure) For more information Mobility Package 1 and impacts on combined transport sector, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication
- Nantes Debat Publique – Nantes Atlantique airport, traffic forecasts due diligence On January 2018, the French Prime Minister announced the decision to abandon the project for the construction of the new airport of Notre‐Dame‐des‐Landes and develop the existing Nantes‐Atlantique airport under the management of the Direction Générale de l’Aviation Civile (DGAC). The development of the Nantes‐Atlantic airport by 2040 was subject to prior consultation of the Commission Nationale du Débat Publique (CNDP), in order to inform in a transparent way the participants and discuss mobility needs, protection issues populations, environmental issues, socio‐economic impacts as well as territorial integration of the project. This consultation was envisaged to gather the opinions, stakeholder expectations and proposals for the development of the existing airport, and the options studied by the DGAC to meet needs in short (2025), medium (2030) and long (2040) terms. The objective of the analysis was to assess the solidity of the traffic forecast, taking into account the stakeholders’ opinions that evaluated the projections either underestimating the traffic potential or overestimating it due to taxation, stabilisation of the economic growth and climate change related regulations. The analysis of the traffic forecast was based on documents and studies related provided by the CNDP. Additional documentation was gathered in relation to air transport market development and transport demand projections at different geographical levels. The study identified the following factors as potentially influencing air traffic growth at the airport in the future. Operating airlines and networks. The penetration of low cost airlines in the air market of the region significantly supported the development of the airport traffic during the past. Relationship between airlines networks, travellers profile and socioeconomic context of the region. The network, especially for the international segment, is reflected by the profile of the travellers identified according to the surveys carried out. Competition with other French airports, although it was found low due the small size of the closest airport (Rennes) and negligible interaction with other comparable regional airports. Competition with high-speed trains and long-distance buses. The extensions of the TGV network might divert some air demand at 2030 (LGV Bretagne‐Pays de la Loire) and 2050 (Ligne nouvelle Ouest Bretagne Pays de la Loire). Policies for internalisation of external costs, because the French Government announced an environmental tax levied on airlines flying out of the country. The political scenario (i.e., Brexit) and macro‐economic (e.g., increase the oil price). The study found that the forecast of 2019 did not overestimate the development of the airport at 2030. At 2030‐2050, the growth seem less likely to happen, because the offer of connections could reach the saturation. For more information, please check Debat public website
- Financial and economic analysis of the new metro line Afragola AV-Napoli and of a moving walkways at Colli Aminei station The project consists of an evaluation of two transport infrastructure projects: the new metro line Afragola-Napoli (LAN) and of a moving walkways at the Colli Aminei metro station (CAM). Respectively, these projects have been planned by the regional administration to connect the Afragola high-speed rail station with Naples inner city, and to improve the accessibility of the (sloping) Colli Aminei metro station. Based on a detailed traffic analysis, TRT carried out a financial and economic evaluation (cost benefit analysis) of the projects, considering on the one hand the project investment and operating costs, and on the other hand the impacts expected from the induced modal shift (lower road traffic levels, travel time savings, reduction of traffic externalities, etc.). The evaluation took into consideration different project layouts of LAN and CAM, contributing to identify the best alternative from a cost-benefit point of view. As provided by the national guidelines on transport project evaluation, a risk analysis was also developed including a qualitative risk analysis, a quantitative risk analysis, a sensitivity analysis.
- Evaluation of noise differentiated track access charges schemes: Support study to the evaluation of Implementing Regulation 2015/429 The Regulation 2015/429 establishes rules for Noise Differentiated Track Access Charge (NDTAC) schemes. The purpose of the study is to provide insight on the performance of the Regulation and its impacts in the EU. To that end, it answers 19 evaluation questions grouped under the evaluation criteria of effectiveness, efficiency, relevance, sustainability, coherence and EU added value. The primary geographical scope of the evaluation is the three Member States were the Regulation has been applied (AT, DE, NL), along with Switzerland (the first country to create a NDTAC scheme aiming at reducing rail noise by incentivising the retrofitting of noisy wagons with composite brake blocks). The wider EU is also considered, in order to understand the impacts that the NDTAC schemes in these four countries have had in countries that did not implement such schemes. The analysis is based on data collected from a range of primary and secondary sources including data on the freight wagons fleet and direct input from relevant stakeholders collected using interviews and surveys with rail industry, authorities and a public consultation.
- Flex-Rail – Paradigm shifts for railway – Technology uptake strategies for a lean, integrated and flexible railway system Shift2Rail (S2R, shift2rail.org) develops the building blocks for the future rail system, as envisaged in the Multi‐Annual Action Plan (MAAP). However, S2R’s work programmes need to be continuously monitored and updated to ensure that they optimally make use of the potential of new technological innovations and developments rising in the society, other industries and specifically within the rail sector. The Flex‐Rail project has the objective of identifying and assessing technological possibilities and innovative concepts that can shape rail operating and business models, aiming to contribute to the formulation of required paradigm shifts for the rail sector. In this view, Flex-Rail has the vision to target a lean, integrated and flexible railway system to stimulate further innovation of the rail sector and ensure that rail the services can address the future user needs. In particular, the Flex-Rail project addresses the following aspects: forecast the evolution of key fundamental technologies and identification of technical risks and potential blocking points; analysis of possible achievement of future impacts, through the definition and implementation of an impact assessment framework and modelling tool for rail scenario and transition pathways; formulation of technological concepts for a future rail system scenario developed on a participatory process involving the users of the rail system. Also, the scenarios build on the analysis of trends and innovations happening in other transport sectors; assessment of business feasibility and analysis of the current safety requirements. The Flex-Rail project develops an in‐depth overview of the state of the art of ideas and technological trends related to innovations of the transport industry and non‐transport sector technologies. As such, it constitutes a knowledge basis for subsequent activities focussed on (i) the definition of key performance indicators, which are key assessment components, (ii) the identification of gaps and development of future (rail system) transition pathways and (iii) the impact assessment of these transition pathways and scenarios. A dedicate interactive website has been created to explore technological trends an innovations relevant for rail transport(*). On these basis, a dedicated assessment framework has been designed to determine the impact of innovation packages and transition pathways on a number of key performance indicators for rail transport and per System Platform Demonstrator (SPD), as defined in S2R’s MAAP. A gap analysis for each SPD has been developed, considering the fulfilment of user’s requirements of rail and modal competitors and for different market segments. This has allowed to identify potential market segments and rail modal share growth. By evaluating such possible paradigm solutions, with aligning or enabling trends and technologies, future scenarios have been developed and assessed on the basis of an open-innovation process for collecting additional future requirements. Among its activities, Flex-Rail mapped projects, studies, initiatives and experts’ groups outputs related to new technologies and trends within and outside the transport sectors that may directly and indirectly have an influence on the rail transport sector. Mapping such these activities ensured coherence with the worldwide […]
- Modal shift in European transport: a way forward The study, developed for the TRAN committee of the European Parliament for the Year of Multimodality (2018), provides a comprehensive analysis of the progress and potential of modal shift in the EU from road to more sustainable transport modes, with respect to the policy objectives set in the 2011 White Paper on transport. The study focuses both on passenger and freight transport, highlighting the main barriers and factors that are hampering a more effective modal shift at EU level, providing policy recommendations for the way forward. The analysis carried out highlights that, at EU level, a modal shift from road to more sustainable transport means (rail, inland waterways, public transport) is taking place at a lower pace, compared to the objectives previously set. The relevant measures proposed, besides broadly confirming the actions so far undertaken, include the increase of investments on multimodal projects, the improvement of multimodal access and connectivity of all the EU regions and to enhance the use of ITS technologies. [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]