- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
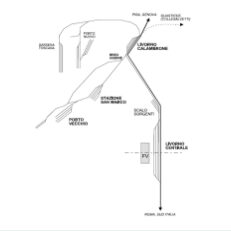
- Feasibility study and preliminary design of the railway network of the Northern Tyrrhenian sea port system TRT, with Vega Engineering, was in charge of the feasibility project for the development of railway network of the ports of Livorno and Piombino. The objective of the work is to quantify the transport demand observed in the past, with reference to the movement of goods and passengers and, at the same time, to estimate the future freight flows, also using the transport simulation model –TRUST, developed by TRTv that works at European scale. The project proposals envisage the improvement of the capacity of the existing terminals and their progressive adaptation to international standards. On the basis of the proposed project alternatives, a specific study was made of the railway capacity of the system in terms of the number of trains that can be operated by the two ports, verifying that the long-term demand forecasts can be met by the planned planning schemes, while also maintaining residual capacity . The transport performance of the railway system, together with the design characteristics (costs, construction times, etc.), constitute the database that has allowed the development of a Multicriteria Analysis that has compared the different design alternatives. A Cost Benefit Analysis was conducted, to assess the advantages and disadvantages of the project for the community.
- Impact assessment on measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail The impact assessment study is intended to provide evidence-based support for developing a new initiative implementing: Action 19: Measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including – if necessary – through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail Action 24: EU 2021 Rail Corridor Initiative – Revise the Rail Freight Corridor Regulation of the European Commission’s Smart Mobility Strategy (COM/2020/789 final) for achieving the objectives of the EU Green Deal (COM/2019/640 final). In the Green Deal and the Strategy vision for the future EU transport system, a substantial part of the 75% of inland freight carried today by road should shift onto rail and inland waterways. Moreover, rail freight traffic is projected to increase by 50% by 2030 and double by 2050; by 2030, rail and waterborne-based intermodal transport will be able to compete on equal footing with road-only transport in the EU.
- Impact assessment support study for the new proposal addressing the development of multimodal digital mobility services and a cost-benefit analysis for the revision of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/1926 on multimodal travel information services Maximising multimodality and intermodality in passenger mobility is a key element in reducing transport’s contribution to climate change while ensuring that transport systems operate efficiently, both within Member States and also across the EU’s internal borders. Multimodal digital mobility services (MDMS) are, in turn, crucial to foster multimodality as they promote comparability, transparency, and the selling of products across operators and modes. MDMS bring direct benefits to users: they help people to navigate and access an increasingly complex and diverse range of transport offerings, including a range of shared mobility services, as well as to understand the role and benefits of active modes, that will help them meet their mobility needs in different, more sustainable ways. This can also help to increase accessibility more generally, and so help to reduce social exclusion, by enabling those most in need to access the mobility services that enable them to participate more fully in society. Services that support multimodal transport also help to make transport more efficient and sustainable by increasing the utilisation of the various transport services, improving their operation, and nudging users towards the more sustainable options. The study is crucial in informing the scope and focus of the actions that are necessary at the EU level to ensure that MDMS can fully contribute to the aims of the Smart Mobility Strategy and the Green Deal and, more importantly, bring their associated benefits to users and the environment.
- Analysis accompanying the Impact Assessment for the revision of Directive 92/106/EEC (Combined Transport Directive) The project aims to provide a robust evidence-based analysis to develop an impact assessment on the possible revision of the Combined Transport Directive. The objective of the revision is to increase the share of rail, SSS and IWW in the EU freight transport, reducing GHG emissions as well as other transport externalities such as congestion and accidents. The impact assessment should inform the specific measures to be included and the level of ambition of the revised Directive, including the following tasks: Task 1: analysis of the main problems and policy objectives identified by the Commission Task 2: Assessment of the policy measures according to their legal, political and technical feasibility Task 3: Analysis of the baseline scenario, including both the status-quo and the likely evolution of the problem drivers Task 4: Assessment of the economic, social and environmental impacts of each policy option Task 5 and 6: comparison of options and selection of the preferred policy options TRT is involved mainly in Task 3 and 4, providing among others EU scale modelling (ASTRA) for estimations of key variables (transport activity, modal share, fuel consumption, emissions, etc.) for the baseline and policy scenarios, and tailored cost models to quantify the economic impacts of the proposed measures and combination of measures.
- Strada-dei-Parchi: Traffic study and cost benefit analysis of A24-A25 motorway The objective of the project was the traffic study, the cost-benefit and risk analysis of different of A24 and A25 motorways’ layout alternatives. The AIMSUN traffic simulation model was used to evaluate the impacts of the different route design variants, with special focus on travel times and accessibility. The Cost-Benefit Analysis of the alternative scenarios was combined with the sensitivity analysis of the main variables (e.g. investment costs, maintenance, etc.) and the risk analysis to evaluate the effects of uncertain variables (eg traffic demand, investment costs, incidence of weather conditions) represented with different probability distributions of occurrence. The Cost-benefit Analysis provided the economic indicators: Net Present Value – NPV and Economic Internal. Particular attention was paid to the assessment of the weather conditions impact on traffic and travel times in the various design alternatives.
- Study on costs and benefits of the sustainable urban mobility transition The study had the objective to assess the impacts of different sustainable urban mobility transition scenarios, producing a quantitative analysis of their costs and benefits for European cities by 2030 and 2050. The calculation is based on an improvement and extension of the MOMOS model, which allows to calculate the costs and benefits of the transition through a set of indicators. To take into account differences among 779 European cities, the quantification of results has been applied to 12 city prototypes, which considered different dimensions (small, medium, and large cities) and geographic areas (southern, central/western, northern, and eastern Europe). The project considered three potential scenarios, based on a combination of policy measures taken from key EU initiatives: Promote and regulate, based on changing behaviour and promotion; Plan and build, focused on investments in technology and infrastructure; Mixed, which combines policies from the previous two scenarios. The three scenarios were built on specific combinations and applications of policy measures, belonging to six different policy groups: Shared Mobility and Demand Management; Innovative Services; Green Public Transport and Logistics Fleets & Charging Infrastructure; Pricing Schemes; Transport Infrastructure; Traffic management and control. The outputs of the study consisted in a series of indicators from three domains: transport (modal split, car ownership), environment (CO2 emissions, fatalities), and economic (city costs, revenues, and externalities). Also, a policy effectiveness comparison determined the best policy measures, in terms of associated cost/revenues and CO2 reduction, according to different city sizes. For more information: Full results of the study can be explored with this interactive tool. The study’s Full Report can be downloaded here. Additional info can also be found on the EIT Urban Mobility website For more information: New contract Interactive tool to explore results of 2021 study 2021 study’s Full Report EIT Urban Mobility website on 2021 study
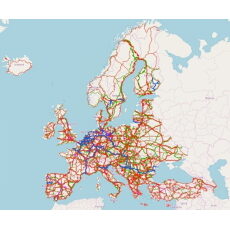
- Impact assessment for the revision of regulation (eu) n° 1315/2013 on union guide-lines for the development of the trans-european transport network The European Union with the Green Deal (proposal EC COM(2019) 640 final) has agreed to implement the Paris Climate Agreement leading the EU towards climate neutrality in 2050. In a more detailed communication in 2020 the European Commission proposed to step-up the climate policy ambition for 2030 and reduce GHG emissions of the EU by 55% compared to 1990 (EC COM(2020) 562). For the transport sector the EC published a new smart and sustainable mobility strategy in December 2020 (EC COM(2020) 789) presenting the strategic policy framework that would deliver the GHG reductions required by the transport sector for 2030 and until 2050. As part of this highly dynamic policy framework the EC has foreseen the revision of several existing transport regulations. The revision of the TEN-T guidelines is one of the major transport related policies besides the revision of the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure and the Intelligent Transport System directives and the planned revision of the Rail Freight Corridors regulation. This study carries out the analysis accompanying the impact assessment for the revision of Regulation (EU) N° 1315/2013 on Union Guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network. Supported by two European scale modelling tools ASTRA and TRUST, the study provides the assessment of three alternative policy options in terms of their transport, economic, social and environmental impacts and identifies the most promising one. The report is available on the website of the “Publications Office of the European Union” at this link.
- Analysis of docks’ capacity in concession to Arcelor Mittal Spa in the port of Taranto TRT has been contracted to carry out an assessment of the actual capacity of the docks taking into account the current production level of the steel plant. The need for the analysis was expressed by the AdSP Management Committee in agreement with the local authorities. Due to the significant reduction that affected the plant’s production capacity in recent years with the main consequence of the inevitable decline in port traffic, the analysis was conducted with the main objective of responding to the need for rationalization and efficiency of the logistics and port infrastructure organization. During the study, statistical data and potential future scenarios for the relaunch of the plant were considered, highlighting the existing oversizing of the docks intended for raw materials and products handling, with respect to the actual operational needs. At the end of the analysis, strategies to promote the efficient use of the docks and the functional and environmental progress of the freight handling have been included. The need for solutions with reduced environmental impact, in line with the requirements and expected performance, was also stressed.
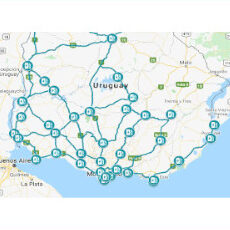
- Technical Assistance to Develop a Business Model to Finance and Scale-up E-Mobility in Uruguay Uruguay has an emerging electric vehicle sector, with good growth prospects and a strong policy agenda on fleet electrification. The country has committed to several mitigation measures in the transport sector, such as the introduction of electric vehicles in public transport, of utility electric vehicles and the installation of the first electrical route of Latin America connecting Colonia-Montevideo-Chui. The main objective of this project is to provide a policy and regulatory guide for a smooth transition to e-mobility in Uruguay and help the country to achieve an efficient and sustainable transport decarbonisation, through: Diagnosis of the current infrastructure and regulatory situation of e-mobility; Assessment of the several pilot projects already developed; Identification of desired business models and financing scheme for e-buses and private EVs; Propose a policy and regulatory guide to achieve overall e-mobility expansion targets in a time-line consistent with Uruguayan Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to the Paris Agreement objectives; Propose a consistent and sustainable body of fiscal incentives and subsidies to favour and promote the previous e-mobility targets. The project is carried out by an international consortium led by MRC Consultants and Transaction Advisers (ES) and composed by TRT (IT) and SEG Ingeniería (UY). TRT is specifically involved in the project component related to private e-mobility, as well as in the fiscal impact assessment to proposed measures and policies. The project will provide a set of outputs including: E-bus financing alternative sschemes with estimated cost impact, timeframe, and impact on rolling stock; Assessment of long-term fiscal impact and ways to ensure efficiency and sustainability of alternative schemes; Regulatory and fiscal incentive schemes to sustainably increase use of private e-vehicles; Long-term fiscal impact analysis of incentives and tax revenues from foregone taxes, and elaborate recommendations; Two public workshops and related materials available for knowledge sharing.