- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
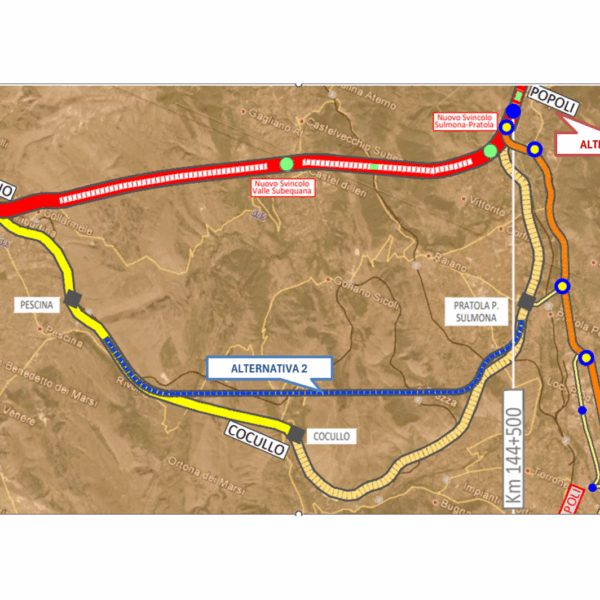
- Comparative analysis of costs and savings of two alternative routes As part of the feasibility study for the structural and functional upgrade of the A25 motorway, with particular attention to the section known as the “Cerchio-Popoli Variant,” TRT was tasked with preparing a comparative analysis of the costs and savings between two possible route alternatives. The currently operational highway section between Cerchio and Popoli presents significant infrastructure challenges related to both the age of the structures and the morphological conditions of the terrain it crosses. In this context, Strada dei Parchi S.p.A. and Italferr have submitted design modification proposals aimed at improving the safety, functionality, and sustainability of the infrastructure. Alternative 1 envisions the construction of three new tunnels, two viaducts, and new junctions, along with the demolition of the existing section between Cucullo, Pratola Peligna, and Sulmona. The new route would extend from the municipality of Cerchio to Popoli and would save approximately 17 km compared to the current situation. Alternative 2 envisions the construction of a new tunnel and the simultaneous demolition of the same existing section between Cucullo, Pratola Peligna, and Sulmona. This solution would save approximately 7.5 km compared to the current situation. For Alternatives 1 and 2, costs and savings were estimated over a 34-year timeframe, including the four years of construction of Alternative 1 (the first to enter into operation) and the 30 years of operation from its opening date. Based on the demand data provided by the traffic study (carried out by Plinomia Srl, and including accidents’ costs estimation as well), three growth scenarios were defined: Precautionary, Optimistic, and Pessimistic. For each scenario, the construction and maintenance costs of the works, the residual value taking into account the useful life of the various components, the time savings, the environmental benefits, and the accident costs of the two alternatives were compared.
- Application of the TRUST model to support the resilience analysis of the Alpine crossing system The aim of the study was to analyse the resilience of the Alpine crossing system, that is, to evaluate how much the complex of crossings can guarantee an adequate level of service in case of “breakdown” events. For this purpose, the TRUST model, which is a strategic model at European scale, was used to simulate the functioning of the entire range of crossings with respect to the different hypothesized scenarios. The definition of the scenarios considered the fact that, from the point of view of their modelling, it is not the nature of the event that generates a certain variation of the inputs that is significant, but the extent of the variation that is determined in the functioning of the transport system. The scenarios have been translated into variations of one or more input elements of the model itself, namely: availability of some arcs to the modelled vehicle categories, capacity of the road links, travel speed on the links for the modelled vehicle categories. The application of the TRUST model produced, for each scenario, the following results compared to the reference situation:
- Assess the degree of the implementation of the ‘user pays’ and the ‘polluter pays’ principles in the transport field in the EU Member States and other developed countries The objective of the study is to assess the extent to which the “user pays” and the “polluter pays” principles are implemented in the transport field. This allows the European Commission to observe the progress of Member States towards the goal of full internalisation of external and infrastructure costs of transport and to identify options for further internalisation. This study is an update of previous studies published in the years 2019 and 2014. The scope of the current study is extended to cover all external costs, all transport modes and, geographically, EU27 plus UK, Norway, Switzerland, Turkey, Western Balkans, Iceland, USA (2 States), Canada (2 provinces), Japan, Australia, New Zealand. Specific objectives concern: Provide estimations of total, average and marginal infrastructure and external costs for all relevant modes/vehicle categories and countries. Provide a detailed and transparent overview of the transport-related taxes and charges, including their structure and revenues, for all relevant modes/vehicle categories and countries. Assess the application for the different transport modes in the relevant countries of both the user-pays and polluter-pays principles. The update of the Handbook on External costs The objectives of the study are achieved through a comprehensive data collection on infrastructure costs (i.e., investment, renewal and operating), transport charges, earmarking of tax revenues and user charges. Appropriate methodologies are applied to estimate external costs for all modes and categories. With regard to the activities of the study, TRT (already involved in previous studies) is responsible for: developing estimates of the external costs related to congestion for all transport modes, developing estimates of infrastructure costs for rail mode and with regard to all categories of external costs elaborating the analysis of six case studies on intermodal freight terminals, and supporting data collection, as country expert for Italy, France, Poland, Latvia and Lithuania. For more information, check our previous study on Sustainable Transport Infrastructure Charging and Internalisation of Transport Externalities
- Analysis of the external logistics of the new metallurgical complex in Piombino The analysis, developed on behalf of Metinvest Adria S.P.A., aimed to assess the impact of the external logistics of the new Piombino steel complex. The logistics operations concern the handling of bulk materials and finished steel products (coils and steel plate packaging) from the production site to the external network and vice versa. These handling operations will involve the railway line from the new complex to the Fiorentina station in Piombino, the junction of the existing railway network, the road network serving the area under study and the port area for relations by sea. The analysis was carried out considering two different delivery options of raw material to the industrial site: Option 1 (Basic), according to which the largest share of the volumes are delivered to the new complex by truck and train; Option 2 (Alternative), according to which 80 per cent of the total quantity is delivered to the site by ship. Furthermore, in the analysis of external transport by rail from the plant to the Fiorentina railway station in Piombino, two different study options were considered, which differ substantially in terms of the route taken to the external network. The current demand for both modes of transport considered was then reconstructed, the demand induced by the production site was estimated, and the infrastructures capacity was verified. As far as logistics between the port and the new complex are concerned, the number of vehicles that can be handled during daily operating hours was identified together with a check on rail capacity for an optimal evaluation of solutions. To supplement the analysis, the study included the dimensioning of checkpoints for vehicle control, loading, weighing and document operations, as well as an estimate of the number of locomotives required to manoeuvre the estimated trains.
- Update of the study on the “Costs and Benefits of the Urban Mobility Transition” The Costs and Benefits of the sustainable urban mobility transition study was carried in 2021 by TRT with the purpose of assessing the impacts of different sustainable urban mobility scenarios in European cities while quantifying the costs and benefits of this transition in 2030 and 2050. The current study consists in an update and improvement of the previous analysis, aiming to: Refine the input data, the intervention levels and targets of the policy measures of the transition scenarios and their timeline of implementation. Improve and enlarge the policy measures applied to the scenarios Run a new modelling simulation to quantify the expected costs and benefits of the sustainable urban mobility transition in European cities by 2030 and by 2050. Draft specific policy recommendations for practitioners. Provide a set of relevant datasets for the development of an interactive tool The calculation is based on an improvement and extension of the MOMOS model, which allows to assess the impacts of different mobility transition scenarios. The quantification of results is applied to 12 city prototypes (representing more than 780 cities in EU27), considering different dimensions (small, medium, and large cities) and geographic areas (southern, central/western, northern, and eastern Europe). The project will consider three potential scenarios, based on a combination of policy measures taken from key EU initiatives and related to the specific emphasis of each scenario. The available measures are of a different nature and comprehensively cover the range of options that cities currently have available to promote the transition to sustainable urban mobility, belonging to eight different policy groups: Shared Mobility; Innovative mobility services; Vehicle fleet & Charging Infrastructure; Transport Infrastructure; Transport avoidance and behaviour; Pricing Schemes; Traffic management and control; urban logistics. The outputs of the study will consist in a series of indicators from three domains, estimated at base year 2022 as well as at future years 2030 and 2050: transport (modal split, car ownership), environment (CO2 and air pollutant emissions, fatalities), and economic (city costs, revenues, user and freight operator costs, and externalities). Also, building on the results for the 12 city prototypes and on a policy effectiveness comparison of the different groups of policy measures, a series of recommendations focused on mobility practitioners will be provided. For more information: Previous contract
- Study on cross-border investment needs and climate adaptation of the TEN-T network The effective implementation of the TEN-T policy, with the completion of the core network and the extended network by 2030 and 2040, is key to creating a competitive industry, expanding the labour market, promoting growth and jobs and improve the daily lives of European citizens. It is therefore important to ensure sufficient investment for the completion of the TEN-T network. While it is important to complete the TEN-T, it is equally important to ensure that the infrastructure resists the threats of extreme events resulting from climate change, which will continue to increase in frequency, intensity, duration and spatial extent in the coming decades. The objectives of this study are: 1) identify the investments necessary to make the TEN-T resilient to climate change, 2) identify the investments necessary to remove the cross-border bottlenecks of the TEN-T and ensure its completion. In the study conducted together with M-FIVE (DE), VUB (BE) and ISL (DE), TRT is responsible for: Analyse and quantify the investments necessary for the completion of the TEN-T network until 2040, with particular focus on 43 cross-border projects and 33 national projects. Carry out an assessment of the economic and transport impacts resulting from the non-completion of cross-border projects with the support of two European-scale models TRUST and ASTRA. Analyse the role of CEF (Connecting Europe Facility) funds as a stimulus to the implementation of cross-border projects.
- New hospital in piacenza: transport study and cost-benefit analysis for the design of the feasibility study for the new location in area 5 TRT Trasporti e Territorio was commissioned by the Local Health Unit (AUSL) of Piacenza to provide technical support to the design group led by Policreo Srl, with the in-depth studies on the Transport Study and the Cost-Benefit Analysis developed within the Feasibility Study, (drawn up in accordance with art. 14 of Presidential Decree No. 207/2010), of the New Hospital of Piacenza related to area 5 (AL 9), located in the urban sector within the urban ring road, between Corso Europa and Strada Farnesiana. The study is divided into three main activities: the first is about the mobility and parking system related to the current hospital location, analysing in detail the system of roads, parking and public-private accessibility of the area. the second is about the functionality of the road infrastructures serving the new hospital in Piacenza, assessing the impact of the private mobility system, in terms of road infrastructures and the parking system; the third explores cost-benefit analysis issues, comparing the new project of the hospital with the option of maintaining and upgrading the existing hospital. The cost-benefit analysis estimates the project’s contribution to improving the social-economic well-being of the community, i.e. it estimates whether the social-economic advantages, or benefits, outweigh the disadvantages, or social costs. Related projects: Transport study and cost-benefit analysis of the new hospital in Piacenza
- Data analysis for the project of electric vehicles in Latvia Objectives of the study The study had several objectives. First, assessing and analysing the situation regarding electric mobility in Latvia, considering the trend of the share of electric cars in the fleet and the infrastructural endowment of charging facilities, also assessing their geographical distribution. Then, verifying the state-of-the-art and the potential of hydrogen cars as well as the conditions that could facilitate their penetration into the fleet. Then, developing scenarios for the growth of electric mobility and, based on those, quantifying the need for electric infrastructures and the resulting environmental benefits. Some results of the study The study showed that the registration of electric vehicles (mainly passenger cars) has grown at a high rate in recent years, but the share of these vehicles in the fleet remains limited. The provision of public charging infrastructure appears consistent with needs in all Latvian regions. The role of public administrations as pioneers for the deployment of electric vehicles is relevant. Regarding hydrogen cars, the analysis showed that they currently represent a negligible share of the fleet, with significant numbers in only a few countries. Given also the attitude of manufacturers, it seems preferable at the moment for public intervention to focus on the electric mode. Future scenarios of electric vehicle penetration were defined as projections based on European-scale studies, considering at what extent the observed trend so far has been more or less consistent to the predictions of these studies. In general, the scenarios suggest that in the short to medium term it will be mainly electric cars that will enter the fleet, while in the long term the highest shares of electric penetration will be achieved for commercial vehicles. From an emissions point of view, electrification of the fleet will provide a contribution, but the improvement of the efficiency of conventional vehicles can be even more relevant.
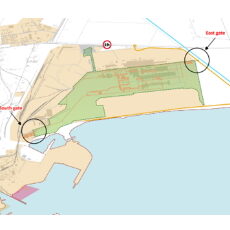
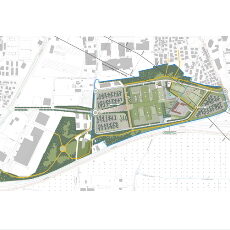
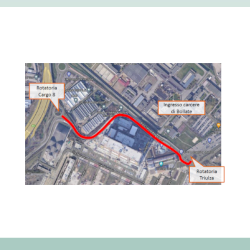
- Due diligence of the documentation supporting the road project for the new Galeazzi hospital, Milan TRT was commissioned to carry out a verification of the demand data used for the Arexpo-MIND project in Milan (redevelopment of the area that hosted the Expo Milano 2015 event) for the area of the new Galeazzi-Sant’Ambrogio hospital, the parking demand and supply, and the viability of the new hospital. The study, focused on the analysis of the documentation made available by the client (taken from the environmental impact studies of the PII Post Expo, which is part of the Arexpo-MIND area’s project, from the annexed Mobility Report of the urban planning project as well as from other internal documents). Data from the official documents were compared with alternative sources, including data collected by TRT in previous studies involving hospital facilities and the ITE 10th edition Trip Generation manual. The official documents were analysed to reconstruct the expected mobility demand and the resulting parking demand. This information was then compared with data from other hospital facilities (one hospital located in an urban area and a second one in a suburban area), with an estimate of the trips conducted by TRT on the basis of data from the Galeazzi hospital shared by the client, and with the estimate of the generating coefficients deduced from the Trip Generation manual. The comparison was carried out using specific indicators that made it possible to compare different hospitals, using the number of total and peak hour trips, peak hour factor, trips per hospital bed, and the ratio of trips with total population involved. A similar approach was followed for the analysis of parking demand and consequent supply, analysing available documentation, identifying the overall supply of dedicated and public parking, in order to compare it with other realities known to TRT through previous studies. Lastly, the access road layout of the new hospital was analysed, verifying the adequacy of the dimensions, the provisional shape of the accesses at the Cargo 8 and Cargo 10 gates (the name remaining from the management of the Expo 2015 area) and the definitive one, taking into account the interference of ordinary traffic with the emergency traffic directed to the emergency room, also proposing a different configuration in the use of the accesses.