- Evaluation of Regulation (EU) No 913/2010 concerning a European rail network for competitive freight The evaluation support study covered all the provisions of the Regulation, all the European countries participating in a Rail Freight Corridor (RFC) and addressed the period from the establishment of the RFCs until 2020. The key overall challenge addressed by the Regulation is the need to improve the competitiveness of rail freight compared to other transport modes. The starting point of the Regulation is that the quality of the rail freight capacity provided by the infrastructure managers to the operators of international rail freight services needs to improve in order to make it happens. The study identified the impact of the Regulation by comparing the actual developments in the rail freight sector, i.e. with the Regulation in place, with respect to a baseline situation describing the likely developments that would have occurred without this policy intervention. The study also took into account the activities related to the RFCs going beyond the provisions of the Regulation, addressing for instance technical and operational interoperability along the RFCs. Furthermore, the study covered the activities of the rail sector undertaken in the period of analysis and contributing to the objectives of the Regulation. Practically, the study examined the relevance, effectiveness, efficiency, coherence and EU added value of the Regulation. The analysis was based on data collected from a range of primary and secondary sources and direct input from concerned stakeholders, collected using interviews and surveys with national authorities, the rail industry and the Commission’s open public consultation. The study has found that the Regulation has been implemented as far as the designation, the governance and the investment and management of the RFCs are concerned. The concerned stakeholders have fulfilled the provisions of the Regulation in a formal sense and within their actual scope. Viewed on its own, however, the Regulation has had a relatively limited impact in achieving the general, specific and operational objectives and has not led to a broad adoption of the tools, which have produced the intended effects only to a limited extent. TRT acted as leader of the study team built in partnership with M-Five (DE), MC-Vienna (AT) and TEPR (UK). TRT was responsible for (i) the design of the evaluation, (ii) the definition of an evaluation baseline, (iii) the analysis of the stakeholders consultation, (iv) the analysis of the effectiveness and efficiency of the Regulation and (v) the estimation of costs and benefits from the implementation. For more information Evaluation of EU regulation on TEN-T rail freight corridors, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication
- Evaluation of the White Paper ‘Roadmap to a single European transport area – towards a competitive and resource efficient transport system’ The 2011 Transport White Paper “Roadmap to a Single European Transport Area – Towards a competitive and resource efficient transport system” is the document with which the European Commission has outlined the strategy on the future EU transport system and which defines the political agenda for the next decades. The main objectives of the strategy are (i) reduce carbon dioxide emissions in transport to a level that is 60 % below that of 1990; (ii) reduce the transport sector’s dependence on oil; (iii) reduce congestion growth. The strategy is articulated through 40 action points and 132 initiatives aimed at achieving 10 operational targets at different time horizons (2030 and 2050). TRT, member of the consortium led by Ricardo NL and participated by M-Five, E3Modelling and TEPR is responsible for carrying out the mid-term evaluation of the effectiveness of the strategy in order to support the European Commission in identifying any proposals for revising the document. The purpose of the evaluation is to provide a robust evidence-based assessment of the White Paper and the actions following from it since its adoption in 2011. It examines the effectiveness, efficiency, coherence, relevance and EU added value of the White Paper in line with the Better Regulation Guidelines. The evaluation looks at the identified needs for transport policy, the objectives and goals set in the White Paper, the proposed initiatives, reached outcomes and their results, as well as the overall impact of the strategy since it was put in place. The results of the evaluation are intended to inform subsequent decisions of the Commission on possible priorities for the future agenda of EU transport policy. For more information Evaluation of the White Paper ‘Roadmap to a single European transport area – towards a competitive and resource efficient transport system’. Final report, March 2021
- Data gathering and analysis of the impacts of cabotage restrictions on combined transport road legs: support study for the evaluation of Regulation 2020/1055 (Mobility Package 1) Regulation 2020/1055 will allow Member States to apply the so-called cabotage restrictions to road legs of international combined transport operations if those road legs do not cross a border. The objective of the study was to provide the Commission with an analysis on the market impacts of the new restrictions. To that end, TRT conducted a survey among major combined transport organisers and terminal operators, covering all modal combinations and a wide range of Member States. The survey focused on the collection of data and information on combined transport road legs, and on the compliance strategies and impacts foreseen by the respondents. Based on the results of the survey, the study evaluated the quantitative impacts of cabotage restrictions on the European combined transport market, including estimates of the expected change in combined transport volumes, market share, modal shift and other transport activity indicators. According to the results, the rail-road segment would suffer more than the other modes considered (short sea shipping and inland navigation) mainly because of the tighter competition of the road only carriage. Relevance of the various compliance measures for CTOs (% of CT operations concerned by each measure) For more information Mobility Package 1 and impacts on combined transport sector, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication
- Nantes Debat Publique – Nantes Atlantique airport, traffic forecasts due diligence On January 2018, the French Prime Minister announced the decision to abandon the project for the construction of the new airport of Notre‐Dame‐des‐Landes and develop the existing Nantes‐Atlantique airport under the management of the Direction Générale de l’Aviation Civile (DGAC). The development of the Nantes‐Atlantic airport by 2040 was subject to prior consultation of the Commission Nationale du Débat Publique (CNDP), in order to inform in a transparent way the participants and discuss mobility needs, protection issues populations, environmental issues, socio‐economic impacts as well as territorial integration of the project. This consultation was envisaged to gather the opinions, stakeholder expectations and proposals for the development of the existing airport, and the options studied by the DGAC to meet needs in short (2025), medium (2030) and long (2040) terms. The objective of the analysis was to assess the solidity of the traffic forecast, taking into account the stakeholders’ opinions that evaluated the projections either underestimating the traffic potential or overestimating it due to taxation, stabilisation of the economic growth and climate change related regulations. The analysis of the traffic forecast was based on documents and studies related provided by the CNDP. Additional documentation was gathered in relation to air transport market development and transport demand projections at different geographical levels. The study identified the following factors as potentially influencing air traffic growth at the airport in the future. Operating airlines and networks. The penetration of low cost airlines in the air market of the region significantly supported the development of the airport traffic during the past. Relationship between airlines networks, travellers profile and socioeconomic context of the region. The network, especially for the international segment, is reflected by the profile of the travellers identified according to the surveys carried out. Competition with other French airports, although it was found low due the small size of the closest airport (Rennes) and negligible interaction with other comparable regional airports. Competition with high-speed trains and long-distance buses. The extensions of the TGV network might divert some air demand at 2030 (LGV Bretagne‐Pays de la Loire) and 2050 (Ligne nouvelle Ouest Bretagne Pays de la Loire). Policies for internalisation of external costs, because the French Government announced an environmental tax levied on airlines flying out of the country. The political scenario (i.e., Brexit) and macro‐economic (e.g., increase the oil price). The study found that the forecast of 2019 did not overestimate the development of the airport at 2030. At 2030‐2050, the growth seem less likely to happen, because the offer of connections could reach the saturation. For more information, please check Debat public website
- Airfreight transport in Italy, Cluster Cargo Aereo study The Cluster Cargo Aereo is a trade association of stakeholders operating in the air cargo market (forwarders, airlines, handlers). Its mission is to provide research, studies and statistics to promote an understanding of the sector and its challenges to relevant stakeholders. After its first study, released in 2019 and focusing on the supply of airfreight services (benchmarking of national and European airports competitiveness), the Cluster commissioned TRT a new study to better understand the airfreight demand and users preferences. TRT was committed to analyse the type of commodities and industrial sectors making the most use of airfreight services, identifying the factors that drive companies to modal and airport choice, including foreign terminals. The analysis was carried out through two main activities: a desk research, i.e. a statistical analysis of airfreight traffic flows (quantities/values) in the last 10 years and with respect to the most relevant types of commodities; a field research, namely a survey to a selection of relevant companies (export oriented manufacturers, freight forwarders, etc.) to gain insights on key research questions. With this study, TRT provided not only an up-to-date analysis of the national airfreight market, but also identified strategic actions for market development, particularly with respect to the sector-specific logistic needs coming from the survey. A particular focus was also devoted to Covid-19 emergency and to the related impacts on the airfreight sector. After the first study, presented in 2019 and focused on transport supply (competitiveness of national and European airports), and the second study on air freight transport demand of 2020, the Cluster has commissioned to TRT a new study in order to better understand the perception of the air cargo service in Italy. Therefore, TRT has realized a survey to the main manufacturing companies, integrated by an in-depth survey to the shipment companies, whose results have been introduced during the 5th Convention of the Air Cargo Observatory, where there was an audience of 200 stakeholders and companies of the sector. For more information (only available in italian) Airfreight transport in Italy, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication Digital conference for the presentation of the Cluster Cargo Aereo study. Milan, 26 October 2020. Download the presentation News (only available in italian) Press review by FEDESPEDI. Link Agroalimentare, ecommerce e aviocamionato: le tre scommesse del cargo aereo italiano. Aircargoitaly, 26 October 2020. Link Cluster Cargo Aereo e TRT – Secondo Studio Osservatorio Cargo Aereo. Fedespedi, 26 October 2020. Link La seconda edizione dell’Osservatorio cargo aereo: strategicità e potenzialità del trasporto aereo merci. Il giornale della logistica, 9 November 2020. Link La seconda edizione dell’Osservatorio cargo aereo: quando le merci volano. Il giornale della logistica, Dicembre 2020. Link
- Statistical sample survey on the international freight transport TRT has been again commissioned by the Banca d’Italia (Italian Central Bank) to carry out a four-year survey on the international freight transport, in order to: identify the unit costs of different transport modes for imports and exports; identify the components of ancillary costs; show in a matrix the abroad goods exchange; define the market share held by Italian actors in the maritime, air and rail transport sectors; estimate the turnover made by Italian ship-owners abroad. The surveys and analyzes carried out are used by the Banca d’Italia to estimate the Balance of Payments in Italy. As part of a consolidated partnership of more than twenty years, the activity constitutes the continuation of similar investigations conducted by TRT for Banca d’Italia since 1998. For more information (only available in italian) Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2023, June 2024. Link Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2022, June 2023. Link Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2021, June 2022. Link Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2020, June 2021. Link Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2019, June 2020. Link Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2018, June 2019. Link Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2017, June 2018. Link Survey on International Merchandise Transport 2016, July 2017. Link Italy’s international freight transport 2015, October 2016. Link The survey on the costs of international freight transport in Italy, September 2014. Link
- TRIMODE PROJECT: DEVELOPING FOR THE EUROPEAN COMMISSION A EUROPE-WIDE TRANSPORT MODEL INTEGRATED WITH ENERGY AND ECONOMY TRIMODE (TRansport Integrated MODel of Europe) has been developed to support policy assessment at the European level. Thanks to its modular structure a large variety of policy scenarios can be analysed and a wide set of impacts can be estimated. The overall TRIMODE integrated modelling system comprises several components belonging to three main blocks: a Transport network model, an Economy model and an Energy model. The geographical coverage of TRIMODE includes the EU countries; all Candidate and Potential candidate countries; UK, Iceland, Norway and Switzerland; other external zones. The zoning system is based on NUTS 3 zones. Within EU, sub-NUTS 3 zones are used where necessary, reaching a total of 1732 zones. The TRIMODE model covers the period between the year 2010 (base year) until the year 2050, providing results at 5 years steps The model was developed over the years 2016 to 2020 on behalf of the European Commission by the consortium led by TRT Trasporti e Territorio and composed by PTV AG, E3MLab, MDS Transmodal and M-Five as key partners and ISI Fraunhofer, BHL and INRIX as subcontractors. The TRIMODE component models are developed in VISUM and GAMS with all additional coding outside these tools handled by PYTHON. These models are implemented within a single software platform. A web-based user interface allows to set up, run and analyse model results. Project flyer – Download THE TRIMODE INTEGRATED MODEL FOR EUROPE Presented at the European Transport Conference (ETC) 2017, the article provides an overview of the TRIMODE model and its applications, with some details on the passenger demand model and the network model. – Download TRIMODE FREIGHT & LOGISTICS MODEL OF EUROPE Presented at the European Transport Conference (ETC) 2017, the article describes TRIMODE’s freight demand model, specifying how links between economic transactions and freight transport flows are managed. – Download LONG-DISTANCE, MULTI-MODAL FREIGHT IN A CONTINENTAL TRANSPORTATION MODEL Presented at the Transportation Research Board (TRB) 2018 (and selected for publication in the Transportation Research Record), the article explains how two key characteristics of freight transport – multimodality and logistics – are modelled in TRIMODE – Download TRIMODE: INTEGRATED TRANSPORT MODEL FOR EUROPE Presented at the Transportation Research Board (TRB) 2018 (and selected for publication in the Transportation Research Record), the article explains how two key characteristics of freight transport – multimodality and logistics – are modelled in TRIMODE. – Download ENERGY AND FLEET MODELLING WITHIN THE TRIMODE INTEGRATED TRANSPORT MODEL FRAMEWORK FOR EUROPE Presented at the EURO Working Group on Transportation Meeting (EWGT) 2018, the article introduces TRIMODE’s energy and fleet model and explains its link to transport demand and the network model. – Download
- HiReach, a project funded by the Horizon 2020 EU research program, addressed the specific mobility needs of segments of the population who are vulnerable to transport poverty and social exclusion Context and overall objectives of the project HiReach addressed the specific mobility needs of those segments of the population vulnerable to transport poverty and social exclusion such as people with temporarily or permanent reduced mobility, children, young and elderly people, women, migrants, ethnic minorities, low income, unemployed and people living in isolated and deprived areas. The project also analysed geographical and spatial elements affecting transport poverty to figure out inclusive mobility options that can properly work in urban-peripheral, peri-urban, rural, and remote or deprived territories. By combining different attributes of available transport concepts and bottom-up initiatives with smart operational schemes and IT applications, HiReach was aimed at the creation of viable business models for small scale, modular and easily replicable mobility services that can be provided at affordable prices or with minimum subsidies, targeting low-density and transport poor segments of the population. The HiReach mechanism for exploring, generating and testing inclusive mobility solutions was based on the creative work of startups and innovative entrepreneurs, but also on social innovation through the direct involvement of different social groups as co-owners of the proposed solutions. The overall ambition was to generate project results in strict linkage with developers and final users. Fieldwork activities have been conducted in 6 European study regions: Counties of Esslingen and Göppingen (Baden-Württemberg, DE), Naxos and Small Cyclades (GR), Inner Area Southern Salento (Puglia Region, IT), Guarda (PT), Buzau (RO), North and South-East Luxembourg. TRT was the project coordinator, leading a 9-partner international consortium. Summary of the project work The first analytical phase of the project explored travel behaviour and social habits of targeted vulnerable groups while assessing their travel demand and mobility needs. An extensive desk research across the EU Member States condensed available data, recent trends and scientific literature associated with transport poverty by targeting spatial specificities, mobility socio-economic landscape(s) as well as visible and hidden mobility needs and attitudes. This step required also the (re)-elaboration of the concept of transport poverty including a complex assessment of inequality and disadvantage, distinguishing between transportation-related disadvantage, social disadvantage and social exclusion. A cornerstone of the HiReach approach was the micro-analysis conducted on the field in six different countries. A set of 47 interviews with experts and stakeholders and the direct involvement of 166 vulnerable users through different focus group sessions served as validation of desk research activities and mobilization of local communities as co-owners of the solutions. In particular, TRT conducted fielwork activities in the Southern Salento area, focusing on the transport challenges of women and people with reduced mobility. A visual and descriptive representation of the identified needs and attitudes, featuring also mixed vulnerability characteristics and traits, was transposed into the elaboration of 6 Personas (see HiReach Insight Package). The following exploratory phase critically assessed the limits and drawbacks of the current supply of public […]
- HARMONY, a project funded by the Horizon 2020 EU research program, applies an holistic approach for providing innovative spatial & transport planning tools to metropolitan and regional authorities, in order to support decision-making and lead a sustainable transition to a new mobility era The main objective of the HARMONY project was to develop a new generation of harmonised spatial and multimodal transport planning tools, modeling comprehensively the dynamics of the changing transport sector and spatial organisation, and enabling metropolitan area authorities to lead the transition to a low carbon new mobility era in a sustainable manner. The main activities of the project were related to: Designing and develop a model suite (the HARMONY MS), integrating land-use models (strategic/long-term), people and freight activity-based models (tactical/mid-term), and multimodal network models (operational/short-term) allowing for vertical planning. Identify new mobility services, concepts and technologies for people and freight for urban, suburban, and regional transport and their business models. Implementing demonstrations with electric AVs, robots, and drones for freight delivery to understand in real-life their requirements. Recommending updates for spatial and transport strategies and SUMPs to deal with mobility transition to decarbonise the transport sector. Applying and validating the model suite on six EU metropolitan areas: Rotterdam(NL), Oxfordshire(UK), Turin(IT), Athens(GR), Trikala(GR), Upper Silesian-Zaglebie Metropolis(PL). The consortium, coordinated by the University College of London, consisted of 21 partners. TRT led the activities related to spatial and transport strategies and SUMPs, and it was involved in the technical activities to design and develop the modelling suite. Furthermore, TRT experts supported the application in the metropolitan area of Turin (IT). HARMONY Model Suite The HARMONY Model Suite has been designed and implemented to enable end-users such as planners, decision makers, researchers and transport operators/providers to couple/link independent models and analyse a portfolio of regional and urban interventions for both passenger and freight mobility, including policies and capital investments, land-use configurations, economic and sociodemographic assumptions, travel demand management strategies and new mobility service concepts. The conceptual architecture of the HARMONY model suite allows to integrate new and existing sub-models with a multi-scale approach, consisting in the Strategic Level (Long-term), the Tactical Level (Mid-Term) and the Operational Level (Short-term). The Strategic Level is mainly composed of regional economic, demographic forecasting, land-use, spatial freight interaction and long-term mobility choice models. The Tactical level is made of a fully agent-based passenger and freight demand model, representing passenger and freight agents’ choices. The Operational Level is representing the transport supply at network level, with demand interactions at high granularity. The Moby App Within the HARMONY project, a new approach for travel demand data collection has been used: a free smartphone application, the MobyApp, was developed for Android and iOS. Downloading the application, the survey participants need only to start the tracking of their trips and activities, and the whole travel diary is tracked by the application. Moreover, a few complementary questionnaires are included in the application, to collect additional information on transport behaviours. The travel survey was performed in Turin and Oxfordshire: […]
- CIVITAS REVEAL, Horizon 2020 project. Adding Urban Vehicle Access Regulations (UVARs) to the standard range of urban mobility transition approaches of cities across Europe ReVeAL is a “Research and Innovation Action” Horizon 2020 project financed by the European Commission. Its overreaching mission is to enable cities to optimise urban space and transport network usage through the selection as well as the implementation of new and integrated packages of UVAR (Urban Vehicle Access Regulation) measures. During the project, six pilot cities representing different sizes and challenges that are common to many other European cities, developed, implemented, tested and evaluated a set of UVAR measures. Cities were Helmond (NL), Jerusalem (IL), London (UK), Padova (IT), Vitoria-Gasteiz (ES) and Bielefeld (DE). The ReVeAL key output is a toolkit that help cities develop good practice UVARs, to help take urban road space from motorised vehicles and give them to people and sustainable mobility. The Toolkit consists of: A Decision Support Tool: 15 questions on the city’s goals and the area being considered for the UVAR, which gives a prioritisation of the building blocks (measures) that might be appropriate for your city. Fact Sheets on each Building Block: The factsheets include the definition of the building block, aspects relevant to timing, phasing and upscaling, time window options, complementary measure and enforcement options, equity issues and future considerations. There are also links to the other building blocks that might be relevant to use with each building block. Links to ReVeAL Guidance: The ReVeAL guidance covers aspects that are broader than a single building block such as the cross-cutting themes, and/or go into more detail on implementational issues than the factsheets allow. The different aspects are linked from the factsheets where relevant, as well as available in an online document. TRT was leading the “Monitoring and evaluation” work package with the aim of designing the evaluation framework, monitoring the implementation processes, as well as evaluating and assessing the impacts in the six pilot cities. TRT was also “pilot coordinators for the actions implemented in London and Padova. TRT experts were also involved development of the tool content and guidance, both as “transition area mentor” for mobility concepts and as “measure field leader” in the field of pricing measures. Finally, TRT was responsible for the technical development of the online Tool. For more information, Official website of the project. It contains an overview of the main elements of the project, the presentation of the 6 pilot cities and other useful resourches.
- CIVITAS ELEVATE, Horizon 2020 project – Increasing the Europe-wide impact of the CIVITAS projects CIVITAS ELEVATE is part of the CIVITAS initiative, a network of cities dedicated to cleaner, better transport in Europe and beyond that has implemented over 800 measures and urban transport solutions in more than 80 living lab cities Europe-wide. The knowledge gathered through these practical experiences is supported by a number of research and innovation projects looking at ways of building more resource efficient and competitive transport. CIVITAS ELEVATE’s scope was to increase the Europe-wide impact of the CIVITAS 2020 and other ongoing projects on urban mobility policy making. The project aimed at advancing the CIVITAS community to a higher level of knowledge, exchange, impact, and sustainability while guaranteeing essential high-quality support. It aimed to enrich the current CIVITAS generation and to feed future EU initiatives while building a European mobility community able to navigate transition. The CIVITAS ELEVATE project, active from April 2019 until April 2023, was carried out by a 6-partner consortium that includes M21 (leader), DTV, ICLEI, INOVA+, Breda University of Applied Sciences, and TRT. TRT was responsible of the evaluation and advancing knowledge activities, providing guidance and support to the stakeholders from across CIVITAS 2020. This enhanced the knowledge that the CIVITAS initiative has been building year after year, to improve urban mobility policy making and planning. TRT is also part of the new CIVITAS Coordination and support action MUSE
- Financial and economic analysis of the new metro line Afragola AV-Napoli and of a moving walkways at Colli Aminei station The project consists of an evaluation of two transport infrastructure projects: the new metro line Afragola-Napoli (LAN) and of a moving walkways at the Colli Aminei metro station (CAM). Respectively, these projects have been planned by the regional administration to connect the Afragola high-speed rail station with Naples inner city, and to improve the accessibility of the (sloping) Colli Aminei metro station. Based on a detailed traffic analysis, TRT carried out a financial and economic evaluation (cost benefit analysis) of the projects, considering on the one hand the project investment and operating costs, and on the other hand the impacts expected from the induced modal shift (lower road traffic levels, travel time savings, reduction of traffic externalities, etc.). The evaluation took into consideration different project layouts of LAN and CAM, contributing to identify the best alternative from a cost-benefit point of view. As provided by the national guidelines on transport project evaluation, a risk analysis was also developed including a qualitative risk analysis, a quantitative risk analysis, a sensitivity analysis.
- Corridor Munich-Verona – Study and analysis of the forecasted passenger traffic flows and the related offers of long-distance trains based on the future infrastructure This study was a modelling application targeted at forecasting future rail passenger demand on the Verona – Munich rail corridor. The opening of the Brenner Basis Tunnel (BBT) is expected by the year 2030. Its effect will be to save more than one hour from rail travel time between Munich and Verona. The full completion of infrastructure should provide additional time savings by the year 2040. This study, using modelling tools, aimed at forecasting the additional rail passenger demand onto the corridor as effect of new rail supply in order to provide inputs for the design of long-distance rail passenger services on the corridor. Four future scenarios were explored. All scenarios shared the same demographic and economic assumptions influencing the modification of the overall transport demand in the area. Then, each scenario considered a specific configuration of passenger rail services on the Corridor, especially in terms of frequencies and stops. The forecasts were based on the results of the two models: the TRUST model used by TRT dealt with long-distance origin-destination pairs at NUTS3 level, while the regional demand was simulated in more spatial detail by means of the VMÖ 2025+ model used by the Austrian company TRAFFIX. The project was managed by EBP Schweiz AG. For more information, please check BBT Brenner Base Tunnel website
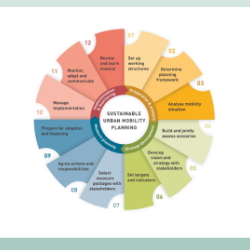
- Implementation and monitoring of the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan of the city of Parma During the year 2019 the Master Mobility Plan coordinated the strategies of the SUMP implementation through the formation of “thematic tables” participated by external experts and by members the Mobility Sector of Parma Municipality. The “thematic tables” included 4 main areas: cycling, urban goods logistics, public transport and ITS. Furthermore the activities of the Master Mobility Plan were oriented towards the development of the first steps for the implementation of the urban area Low Emission Zone (LEZ). The effort was to present the LEZ as a permanent easy to apply and understand measure aimed at overcoming the logic of temporary and emergency initiatives to improve air quality. The assignment also provided for the coordination of the monitoring activities of the SUMP: These activities consisted in the collection and systemization of mobility trends data in Parma over the past 2-3 years and included a field surveys with traffic counts on the urban radials, on the main intersections and on cycling mobility. TRT was also responsible of the drafting of the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan and the General Urban Traffic Plan of the city of Parma.
- Evaluation of noise differentiated track access charges schemes: Support study to the evaluation of Implementing Regulation 2015/429 The Regulation 2015/429 establishes rules for Noise Differentiated Track Access Charge (NDTAC) schemes. The purpose of the study is to provide insight on the performance of the Regulation and its impacts in the EU. To that end, it answers 19 evaluation questions grouped under the evaluation criteria of effectiveness, efficiency, relevance, sustainability, coherence and EU added value. The primary geographical scope of the evaluation is the three Member States were the Regulation has been applied (AT, DE, NL), along with Switzerland (the first country to create a NDTAC scheme aiming at reducing rail noise by incentivising the retrofitting of noisy wagons with composite brake blocks). The wider EU is also considered, in order to understand the impacts that the NDTAC schemes in these four countries have had in countries that did not implement such schemes. The analysis is based on data collected from a range of primary and secondary sources including data on the freight wagons fleet and direct input from relevant stakeholders collected using interviews and surveys with rail industry, authorities and a public consultation.
- Training course on Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans for five Western Balkan countries TRT was selected by GIZ (the German Cooperation) to design and manage a training course targeted to urban mobility experts, public officials and local practitioners from five different Western Balkan countries (Serbia, Bosnia Herzegovina, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Albania). The training programme was designed as an intense, full-time, one-week long, interactive course (“Boot Camp”). It was held in May 2019 in Podgorica, Montenegro, with the participation of 25 trainees. Participants were experts in the field of traffic, urban or strategic planning, from local self-governances, academia, relevant NGOs or similar. The training course had two main goals: i) to improve the knowledge and to increasing the capacities of the participants, in order to enable them to support a Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMP) development process in line with the ELTIS European guidelines; ii) to select potential candidates for a “regional expert pool” to be established by GIZ in the Balkan countries. in the Balkan countries. Activities performed by TRT included the development of the programme, the drafting of training materials, the management of the sessions on site with two experienced trainers, and the final evaluation of the proficiency of participants.
- Study on Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs) fleet and activity in EU TRT has led an international consortium of experts covering 10 EU Member States with the objective to cover the lack of information and data on LCV fleet and activity in EU-28 The study outputs consist of: DBs on LCVs broken down by fuel type, emission standard and age of the vehicle for 10 Member States (64% of EU-28 fleet) Assess the relationship between annual mileage and age of the vehicle in 5 Member States Estimate fixed (taxes) and operating costs (maintenance, insurance, tools) of LCVs Analyse the LCV uses and the activity sectors in EU Review the legal and fiscal regime of the LCVs in EU-28 [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
- Flex-Rail – Paradigm shifts for railway – Technology uptake strategies for a lean, integrated and flexible railway system Shift2Rail (S2R, shift2rail.org) develops the building blocks for the future rail system, as envisaged in the Multi‐Annual Action Plan (MAAP). However, S2R’s work programmes need to be continuously monitored and updated to ensure that they optimally make use of the potential of new technological innovations and developments rising in the society, other industries and specifically within the rail sector. The Flex‐Rail project has the objective of identifying and assessing technological possibilities and innovative concepts that can shape rail operating and business models, aiming to contribute to the formulation of required paradigm shifts for the rail sector. In this view, Flex-Rail has the vision to target a lean, integrated and flexible railway system to stimulate further innovation of the rail sector and ensure that rail the services can address the future user needs. In particular, the Flex-Rail project addresses the following aspects: forecast the evolution of key fundamental technologies and identification of technical risks and potential blocking points; analysis of possible achievement of future impacts, through the definition and implementation of an impact assessment framework and modelling tool for rail scenario and transition pathways; formulation of technological concepts for a future rail system scenario developed on a participatory process involving the users of the rail system. Also, the scenarios build on the analysis of trends and innovations happening in other transport sectors; assessment of business feasibility and analysis of the current safety requirements. The Flex-Rail project develops an in‐depth overview of the state of the art of ideas and technological trends related to innovations of the transport industry and non‐transport sector technologies. As such, it constitutes a knowledge basis for subsequent activities focussed on (i) the definition of key performance indicators, which are key assessment components, (ii) the identification of gaps and development of future (rail system) transition pathways and (iii) the impact assessment of these transition pathways and scenarios. A dedicate interactive website has been created to explore technological trends an innovations relevant for rail transport(*). On these basis, a dedicated assessment framework has been designed to determine the impact of innovation packages and transition pathways on a number of key performance indicators for rail transport and per System Platform Demonstrator (SPD), as defined in S2R’s MAAP. A gap analysis for each SPD has been developed, considering the fulfilment of user’s requirements of rail and modal competitors and for different market segments. This has allowed to identify potential market segments and rail modal share growth. By evaluating such possible paradigm solutions, with aligning or enabling trends and technologies, future scenarios have been developed and assessed on the basis of an open-innovation process for collecting additional future requirements. Among its activities, Flex-Rail mapped projects, studies, initiatives and experts’ groups outputs related to new technologies and trends within and outside the transport sectors that may directly and indirectly have an influence on the rail transport sector. Mapping such these activities ensured coherence with the worldwide […]
- Study for the definition of sustainable regeneration strategies in Stephenson intermodal urban node (Milano) TRT has lied down the transport strategy supporting the sustainable urban regeneration of Stephenson area coordinate with the surrounding developing district of Expo area. The study encompasses a deep analysis of accessibility and potential impact at socio-economic and demographic scale induced by the introduction of a new rail passenger service into Stephenson area. The strategy include the redefinition of intermodal urban role for Stephenson area by introducing new railway connection and station within the area and the related road connections for increasing the accessibility to the area. This include: Interchange parking area with slot dimensioning Bus line path and stops including planning of new service lines Pedestrian and cycling connection
- Santa Caterina Valfurva – Smart Territory – Autofree The assistance for the implementation of the Santa Caterina Smart Territory strategy is focused on the Santa Caterina car-free project. The activities, which take place in collaboration with Ambiente Italia (leader) and Polinomia, concern four points: Parking policy; Definition of practical interventions on urban furniture; Ski Bus service provision; Strategies for implementing interventions to limit vehicles access to the road to Forni, second largest regional alpine glacier. TRT was in charge of putting in place solutions for vehicle traffic reduction in the tourist resort of Santa Caterina, through the design of public transport services that guarantee access to resident and tourists. Moreover, TRT contributed to the identification of possible solutions for the progressive closure to traffic of the Forni’s road (from Santa Caterina to Forni Glacier), through measures of regulation and/or pricing. Both strategies aim to reduce the traffic that crosses the center of Santa Caterina, increasing the environmental quality and the tourist attractiveness of the town.
- Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (SUMP) and the Urban Traffic Plan (PUT) of the Municipality of Piacenza, complemented/integrated by the Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) The Municipality of Piacenza (102,000 inhabitants approx.) has commissioned TRT Trasporti e Territorio, through a public tender, to draft the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan and the Urban Transport Plan of the city of Piacenza. The drafting of the SUMP of Piacenza was developed in accordance with the ELTIS’ methodology and, at the national level, with the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport (Decree August 4, 2017). The SUMP was launched in October 2018 and it consists of the following activities: updating of the local mobility and planning context; evaluation of the current scenario (diagnostic framework and SWOT analysis) and definition of general and specific objectives and indicators; elaboration of the Plan and quantification of resources, including the identification of alternative scenarios (RS and SP), the ex-ante evaluation (technical, economic and environmental), the quantification of financial resources and the definition of the monitoring system; adoption and approval of the plan. In parallel, a traffic simulation tool was developed for technical, environmental and economic assessment. A crucial element of the Plan’s drafting process was the participatory process, which included: i) a survey aimed at those who live, work and study in Piacenza, with the dual purpose to define the transport demand and to know the needs of those who move daily across the city; ii) thematic and territorial focus groups; iii) informal evenings to explain the Plan to residents; iv) a final conference. The Plan was subjected to Strategic Environmental Assessment, adopted with the Municipal Council Resolution n.2020 / 20 – of 24/01/2020 and approved by the City Council Resolution n.57 of 28/12/2020. Tavola SP_05, Scenario di Piano – Ciclabilità For more information Documents available on comune.piacenza.it (only available in italian) “Sustainable Mobility Planning in Piacenza, Italy”. Case study published on Eltis Platform Related projects Monitoring Report of the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan of the Municipality of Piacenza [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
- Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (SUMP) of Bergamo (Italy) and related SEA With 120,000 residents, Bergamo is the fourth largest city in Lombardy. According to the origin-destination survey carried out by Regione Lombardia in 2014, 366,000 journeys daily affect the municipal territory. The drafting of the SUMP of Bergamo guaranteed consistency with the methodology suggested by the European Commission (www.eltis.org) and with the guidelines issued by the Italian Ministry of Transports (Decree 4 August 2017). Started in July 2018, the work has been organised in four phases:: background analysis of the mobility-related framework and its environmental, social and economic impact in Bergamo; evaluation of the current scenario (diagnostic framework and SWOT analysis) and subsequent definition of the general and specific objectives system as well as measurement indicators; elaboration of the SUMP, including the identification of alternative scenarios, the selection of the related policies and measures, the preparation of a monitoring plan for the ex post evaluation of the plan; acceptance and approval process. The plan has been prepared with the support of a traffic simulation model thus allowing for a detailed technical, environmental and economic evaluation. A tool for strategic evaluation (MOMOS, entirely developed by TRT) has been also used. A fundamental element of the SUMP has been the participatory process, which has included a survey on mobility habits addressed to those who live, work and study in Bergamo and four thematic focus groups. The sustainability of the SUMP has been supported by a Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) and an assessment of the effects of the Plan for the naturalistic Site of Community Importance (SCI) named «Boschi dell’Astino e dell’Allegrezza». The SUMP of Bergamo has been accepted by the City Council on 16/05/2019 and eventually approved om 05/07/2022. For more information Documents available on comune.bergamo.it (only available in italian) “Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan for Bergamo and its functional area”. Case study published on Eltis Platform
- Overview of existing pricing components that influence the competitiveness between road and rail freight transport The Alpine regions are particularly sensitive to negative environmental and social impacts caused by the road traffic flow of freight and passenger transport through the Alps. To tackle this challenge, the harmonisation and implementation of modal shift policies is of utmost relevance. EUSALP Action Group 4 on Mobility (AG4) has commissioned to TRT Trasporti e Territorio a study to support its strategy in designing a proper mix of modal shift policies. TRT provided an overall analysis of existing policy-induced pricing components affecting the competitiveness between road and rail freight transport in and through the Alps. The objectives of the study were: To collect detailed information on policy-induced pricing components that influence road and rail transport cost; To develop a comparative illustration of them for supporting political discussion and communication; To provide preliminary recommendations to improve the instrument mix for balancing the transport modal split in the Alpine Region. [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
- Isola della Scala Intermodal Terminal– Feasibility study TRT has carried out an analysis to assess the feasibility for implementing an intermodal terminal in the Municipality if Isola della Scala. This has included the definition of the requirements for both rail and road logistics areas as well as the actual mode of operation of the terminal area. In particular, the assessment has included: The road accessibility to the terminal areas within the surrounding road network The rail accessibility to the terminal areas by the existing railway line aside the terminal and the operation mode for manoeuvring the rolling stocks for routing them on the network An estimation of both logistics and storage areas based on daily terminal operations of intermodal transport units The study included the impact assessment of terminal operations on road traffic, in particularly it has been considered a daily flow of 30 couple of train of 750m (mainly made by semitrailer and swap bodies) An estimation of the investments costs to set up the intermodal terminal, including the related costs for adapting the existing road and rail network, has also been made
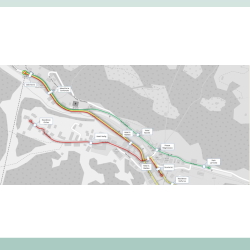
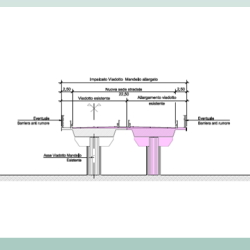
- Technical and economic feasibilty assessment. Upgrading measures for existing road and new road sections for the IV Stretch From Vaglio industrial area to the junction with S.P. Oppido S.S. 96 The project is part of the broader plan for the Salerno – Potenza – Bari Route, which was included in the First Program of Strategic Infrastructures approved by the Interministerial Committee for Economic Planning (CIPE) with the resolution n°121/2001. More in detail the object of the study is a portion of the IV Stretch “Zona industriale Vaglio – SS96 BIS – Inizio Variante di Gravina”, that is supposed to be 20 km long with a C1 section, as classified by the standards imposed by the D.M. 5/11/2001, and includes: A newly built stretch from S.S.407 «Basentana» to SP123, North of Tolve, in which a tunnel is planned Upgrading works for S.P.123 from North of Tolve to the junction with S.S.96 bis, near Oppido Lucano. The objective of the Technical Economic Feasibility Study is to find a design solution compatible with the financial resources allocated in the tender documents. For this assessment, TRT Trasporti e Territorio, in collaboration with GPI Ingegneria, is in charge for developing a traffic study, with the support of PTV Visum software, and a cost-benefit analysis. The modelling activities include: Current state network build-up Model parameters updating O/D demand matrices estimation and correction through mathematical correction procedure Validation of assigned vehicle flows with up-to-date traffic counts; Development of project scenarios to assess and compare their performances.
- COG-LO – COGnitive Logistics Operations through secure, dynamic and ad-hoc collaborative networks The main goal of COG-LO, an innovative project on ICT logistics solutions funded by the European Programme Horizon 2020, was to create the framework and tools to implement cognitive and collaborative ICT solutions on future logistics processes, embracing many contexts and environments. By exploiting COG-LO, it was possible to achieve several benefits, such as: increase the load factor, reduce the cross-border parcel delivery costs, reduce the ratio between distance covered by the logistic vehicles and the number of pickups, implement quick adaptive response management to dynamic customer requirements. The project outcomes were validated in three different pilots, covering multi-modality, inter-country deliveries and urban logistics operations. The international partnership involved 14 public and private actors working both in transportation and ICT fields across eight European countries. TRT leaded WP2 (Cognitive logistics framework), capitalizing on its vast experience on freight transport and logistics research projects. It also brought its long experience in the field of quantitative analysis, strategic planning, KPIs assessment by supporting the technological requirements analysis in one of the pilots developed along the project (the EKOL case on intra-terminal operations and multimodality solutions). [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
- Modal shift in European transport: a way forward The study, developed for the TRAN committee of the European Parliament for the Year of Multimodality (2018), provides a comprehensive analysis of the progress and potential of modal shift in the EU from road to more sustainable transport modes, with respect to the policy objectives set in the 2011 White Paper on transport. The study focuses both on passenger and freight transport, highlighting the main barriers and factors that are hampering a more effective modal shift at EU level, providing policy recommendations for the way forward. The analysis carried out highlights that, at EU level, a modal shift from road to more sustainable transport means (rail, inland waterways, public transport) is taking place at a lower pace, compared to the objectives previously set. The relevant measures proposed, besides broadly confirming the actions so far undertaken, include the increase of investments on multimodal projects, the improvement of multimodal access and connectivity of all the EU regions and to enhance the use of ITS technologies. [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
- Specific contract for long-term quantitative assessment of policy scenarios for the EU transport system Since 2016, TRT holds a framework contract for the simulation of long-term scenarios relating to the evolution of the transport system up to 2050 in EU 27 Member States. Scenarios and their variants are assessed with the use of European scale simulation models by TRT and E3Modelling. The modelling tools are: TRUST, for the quantification of traffic impacts on road and rail networks and of specific emissions on the European territory; PRIMES-TREMOVE, for the quantification of the evolution of the vehicle fleet of different transport modes and of the related energy consumption starting from changes in costs and/or legislation on technologies; GEM-E3, for the quantification of macroeconomic impacts. Studies carried out under the framework contract concern the development of baselines, scenarios and variants focusing on transport, energy and macroeconomic systems and providing results at EU member state level. Within the Framework Contract a new Reference Scenario 2020 which takes into account the expected medium-term impact of the COVID-19 outbreak has been produced.
- Identification and collection of a set of indicators for the description of the urban sustainable mobility in European cities The SUMI project provided technical support for the identification and the collection of a set of sustainable urban mobility indicators in 50 European large and small urban areas. Main project activities were related to: providing rigorous and consistent methodologies for acquisition, harmonisation and analysis of data for the calculation of indicators; this included the definition of a «mentor» for each indicator, i.e. a reference experts capable to sort out all related technical issues; giving technical support to the urban areas and systematically collecting their hands-on experiences; appointed «urban area coaches» had the responsibility to establish direct links between the project consortium and the urban areas and help city administrations to gather the needed data; carrying on consultation, capacity building and dissemination actions addressed to subjects both inside and outside of the project; preparing realistic, harmonised and sound recommendations to the Commission for further improvement and extension of the indicator set; definition of an online benchmarking tool, available for European and non-European cities, aimed at comparing the indicators of each urban area with reference average values. TRT has been a key partner of the project, with direct responsibility in the coordination of data acquisition and technical assistance to the local experts, being «mentor» for four different mobility indicators. In addition, TRT experts have been «urban area coaches » for cities in Italy. The SUMI indicator set For more information: Webpage of the SUMI project on the European Commission portal. It contains the indicator set, the guidelines for the calculation of values and the benchmarking tool for the comparison of results Entire SUMI indicator set (.zip file) General harmonized guidelines for calculating the indicators (.pdf file) E-course to support cities with the application of the SUMI indicator set. Registration needed, free of charge
- Sustainable mobility territorial system within the MIBACT Salento Arco Ionico project The study is part of a wider project focused on the promotion and valorisation of tourism and cultural heritage in 12 municipalities located along the jonian coast of the Province of Lecce. The project is funded by the Italian Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities and Tourism (MIBACT). TRT developed a wider area cycling network to connect the towns and points of interest in the inner territory with the coastline and interlink two main long distance cycle routes crossing the area: the national Apulian Aqueduct Cycle Route and the regional «Three Seas» Cycle Route. The new plan identified each cycling segment primarily on existing rural roads. Apart for verifiyng and describing the current status and characteristics of the different itineraries (level of difficoulty, POIs, etc.), the plan detailed the needed infrastructural interventions to improve safety and quality along the networks, including punctual elements like water points and signage. TRT has also developed a scheme for the promotion of the network as cycle tourism destination. Thematic routes and itineraries (e.g. wine route, industrial heritage, natural landscapes) have been associated to services and nodes activated and managed by local companies of the tourist sector and cycling associations.
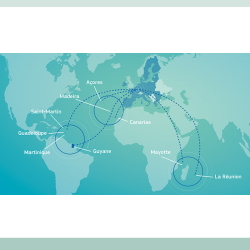
- Study on the physical accessibility of the Outermost Regions of France, Spain and Portugal The objective of the study was to develop a list of transport projects to improve the connectivity of the nine Outermost Regions of France, Spain and Portugal. The study aimed to identify the physical disadvantages, bottlenecks and missing links of the Outermost Regions. This comprehensive analysis was needed for the TEN-T policy to ensure connectivity to all European regions by 2050. The study provided a comprehensive information base of the observed transport conditions of the Outermost regions and a proposition of well-justified actions to improve the overall physical connectivity. In general, the study: identified existing transport links between the EU Member States and the Outermost Regions as well as among and between the Outermost Regions, including regional hubs; identified existing transport links between the Outermost Regions and their neighbouring countries, including regional hubs; developed an assessment of insufficient, missing and promising links; identified key investment needs regarding maritime and air transport; developed an evaluation how to strengthen the Motorway of the Sea policy and its funding; provided recommendations and a list of projects including the sources of funding. This study analysed the observed state of the transport connectivity of (i) Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Martinique, Réunion, Saint-Martin, Mayotte (France), (ii) the Azores and Madeira (Portugal) and the Canary Islands (Spain). These Outermost Regions strongly rely on air and maritime transport connections for accessing to basic goods and services, as well as for their regional economic development. The study found that, in general, the Outermost Regions are well connected with their mainland, both in terms of air and maritime transport. On the other hand, the connectivity with neighbouring regions and countries remains limited. Developing regional connectivity increases territorial cooperation and stimulates regional economic development. Therefore, policy recommendations have suggested to stimulate the level of regional integration, by optimising conditions for operators to provide regional connections through more liberal traffic rights and balanced taxation. In addition, policy recommendations on territorial cohesion aimed at improving the mobility of the residents of the Outermost Regions, as well as the conditions for transport of goods. The recommendations to support general connectivity needs focussed on the development of resilient transport infrastructures and funding options to accelerate the development of the TEN-T in the Outermost Regions.
- Financial and economic evaluation of the shore-side electrification project (cold ironing) in the new cruise terminal in La Spezia By electrifying ships hoteling activities, the La Spezia port authority aims to prevent diesel combustion from berthing vessels and avoid exhaust emissions and noise in the port areas. The objective of this project is thus to assess the welfare implications of the shore-side electrification project (cold ironing) and evaluate the feasibility of such infrastructure investment from a socio-economic point of view. Following a cost-benefit analysis approach and based on first-hand information on port traffic flows and infrastructure costs, the analysis estimates the evolution over time of both health benefits and investment and operation costs, providing a monetary quantification of the net social benefits obtained from the electrification of the cruise terminal. Taking into account relevant developments in the maritime and energy sector, such as the diffusion of natural LNG-fuelled cruise vessels and of renewables in the national energy mix, the evaluation work also provides a comprehensive assessment of the convenience of maritime transport electrification as compared to alternative policy options, and a sound case study about more sustainable approach to coastal policy and infrastructure spending.
- Eltis portal management & development The European Local Transport Information Service (Eltis) is the EU platform facilitating the exchange of information and best practices in the field of urban mobility. Expanding its services during years, nowadays it has became an Urban Mobility Observatory, providing broader services, including training materials and support tools with special focus on mutual learning. Eltis also organises the annual SUMP (Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan) Conference. The main TRT activities within this project are: Update and further development of the portal, developing new contents. Chair the ‘Coordinating Group’ meetings for the SUMPs Platform, bringing together representatives from relevant on-going EU-supported actions aiming at a) Exchange information and lessons learnt, b) Identify and exploit synergies, c) Agree on common views to inform the further development of the SUMP concept and tools. Deliver training on SUMPs, delivering national training events, Helping to bring in new cities that have not previously considered the SUMP concept.
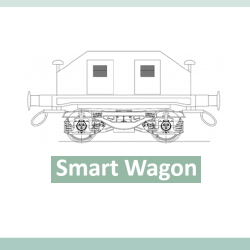
- Automatic Rail Freight Transport System – Analysis of Transport Costs The study developed the feasibility analysis of an innovative and automatic rail freight transport system and elaborated a business plan to assess its economic and financial sustainability. The aim of introducing automatic vehicles for rail freight transport is that of enhancing the internal efficiency of the production system (e.g., in intermodal terminals and logistic centres), by reducing the operating costs and vehicles manoeuvring. Also, the use of automatic vehicles allows to optimise the shipment of cargos from intermodal terminals and logistic centres to transport networks to which they are connected. Further to this, the advantage of using automatic vehicles is twofold. First, automatic vehicles support higher safety levels of the operations avoiding internal collisions (i.e., vehicle-to-vehicle communication and knowledge of the relative position). Second, they reduce the environmental impact, optimising manoeuvring and needs of energy and fuel. The analysis developed an estimation of the operating costs of three scenarios, considering rail-road intermodal transport of semi-trailers, and compared them against the “as-is” situation as follows: wagon towed by a manoeuvring bogie equipped with a traditional coupling system; automatic manoeuvring wagon equipped with a traditional coupling system; automatic manoeuvring wagon equipped with an automatic coupling system. The estimation of the costs shows that there exists a competitive advantage for transporting by rail. With respect to road transport, the difference of cost of transporting by rail increases for longer trips and if a higher level of automation is introduced. The most important advantage of the Smart Wagon system, compared to conventional transport systems, can be obtained when specific conditions hold, namely in contexts such that the demand of freight transport is weak and spread. For example, within ports characterized by a multiplicity of connected internal terminals, the Smart Wagon system would allow to develop transport solutions that merge the demand generated in each internal terminal and share the final destination. Some aspects deserve consideration before implementing an automatic manoeuvring wagon system. First, the cost of feeder legs, which is often a critical cost component for choosing intermodal transport (i.e., the magnitude of the cost is proportional to the length of the trip). Second, with respect to transporting only via road, one should take into account the longer time of the trip, due to two modal shifts (i.e., road-rail and viceversa) and additional waiting times before the train run.
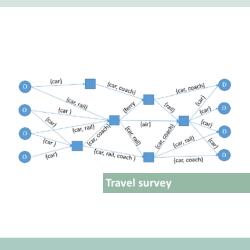
- EU survey on issues related to transport and mobility Nowadays, a reliable analysis of the transport system which allow to monitor the achievement of goals set by the European policy require the availability of updated mobility data. In line with this concept, in 2013 (and again in 2018) the European Commission launched a study involving the design of a questionnaire for a survey that investigate the mobility habits of people at European level. The survey involves 1000 individuals for each of the 28 European countries. In addition to traditional socio-demographic data and daily mobility habits, the survey deeply investigates: the role of long distance trips by mode and by purpose; the tendency to make multimodal trips; the awareness of the opportunities offered by mobile applications and innovative ICT solutions. These studies, both coordinated by TRT and implemented by IPSOS, follow the same methodological approach. This guarantees continuity in data collection allowing for data comparability, definition of trends and monitoring the impact of transport policies.
- The Impact Assessment study, developed for the European Commission, aims to identify and assess the impacts of policy measures on facilitating the deployment of multimodal ITS services By enabling communication between vehicles, infrastructure and other road users, Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems (C-ITS) can greatly improve safety and efficiency in road transport. Here is a look at some of the most recent developments in C-ITS and how quickly the technology could change the way we drive and interact with each other in traffic. The wide-scale deployment of Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems could contribute to delivering several Commission’s objectives for transport, such as those on safety, reduced congestion, enhanced mobility and environmental performance. Together with Ricardo Energy&Environment, TRT supported the Directorate for Mobility and Transport of the European Commission in three different studies over a six year period. In 2020-2021 for the development of an Impact Assessment Support Study for the revision of the Intelligent Transport Systems Directive (2010/40/EU) to support the EC with evidence-based analysis. In 2017-2018 developing the legal framework required to support the widespread deployment of C-ITS services in Europe by 2019: a set of policy options and deployment scenarios were assessed with the European scale modelling tools ASTRA and TRUST for the analysis and comparison of the impacts in terms of economic, environmental and social indicators. In 2015 for the preparation of the Communication strategy and the Action plan for the deployment of C-ITS in Europe, providing the analysis of costs and potential benefits based on different scenarios. To support the analysis, the ASTRA and TRUST models are applied to provide quantitative indicators to evaluate the impacts of various policy options and deployment scenarios. For more information Final report of 2015 study Final report of 2017-2018 study
- Odometer tampering – measures to prevent it (Research for TRAN Committee) The study, commissioned by the TRAN Committee of the EU Parliament, examined the phenomenon of odometer tampering in the EU and proposed concrete actions to tackle it. Despite the EU legislation has addressed the issue in the “Roadworthiness Package”, a major gap has been identified in the long timeframe occurring between the vehicle’s registration and the first Periodical Technical Inspection, as well as the lack of sufficient cooperation and data exchange on odometer readings between EU Member States (MS). The implementation of a EU-wide data exchange system between EU MS on odometer readings could help competent authorities to detect fraudsters (as shown by the Slovakian and the Dutch bilateral cooperation, making use of the EUCARIS platform). The study also explored the best practices developed in Belgium and the Netherlands, where the problem was nearly eradicated in the last years. In both countries the percentage of unauthorised manipulations dropped below 1%. Furthermore, the study highlighted that odometers are still inadequately protected against cybersecurity threats. Potential IT solutions to combat the phenomenon have been suggested. [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
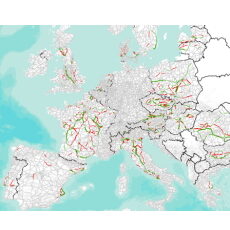
- CEDR’s TEN-T (Roads) 2017 Performance Report The 2017 TEN-T (Roads) Performance report is the fifth biannual report issued by the Conference of European Directors of Roads (CEDR) on the performance of the TEN-T road network within the participating countries. Biennial CEDR reports offer a coherent set of data with which to monitor trends and identify changes in the performance of the TEN-T road network since the year 2009. As such, these reports are a particularly useful source of information for individual National Road Authorities, regulatory bodies and others for benchmarking purposes and for setting national performance targets. More specifically, the CEDR reporting framework is based on a common simple Location Referencing Model and a consistent set of performance indicators based on common data definitions and on data provided directly by National Road Administrations. A web map is developed to display the GIS layer of CEDR’s logical network, in conformity with CEDR’s Location Referencing Model, and to allow for the visualisation of thematic maps showing road performance indicators at link level (e.g. road type, number of lanes, etc.) and for different years. An online tool is developed for the collection and visualization of CEDR Strategic Key Performance Indicators. For more information, please check the project website – cedr.eu
- Transport Market Study: Quantification of modal shift potential on the Rail Freight Corridor Rhine-Alpine The study, coordinated by TRT and involving relevant partners across Europe, aimed to quantify the potential modal shift to rail thanks to the improvement in transport performance on the Rail Freight Corridor Rhine-Alpine. More specifically, the objective of the study was to investigate the possibility to introduce: heavier and longer trains, faster trains (less stops), more reliable trains. The work was structured by three consecutive activities: analysis of the freight transport demand, quantification of the cost savings in relation to heavier, faster and more reliable trains, quantification of modal shift potential. For more information The Transport Market Study summary report is available for download here
- Sustainable Transport Infrastructure Charging and Internalisation of Transport Externalities The objective of the study was to assess the extent to which the “user pays” and the “polluter pays” principles were implemented. This allowed the European Commission to take stock of the progress of Member States towards the goal of full internalisation of external and infrastructure costs of transport and to identify options for further internalisation. The scope of the study involved all external costs, all transport modes and, geographically, EU28 plus Norway, Switzerland, USA (2 States), Canada (2 provinces) and Japan. To realise the general objective and address the scope of the study information has been collected extensively about: infrastructure costs (i.e., investment, renewal and operating), transport-related charges, earmarking of fiscal revenues and compensations paid by the users. The analyses carried out in this study showed that the transport taxes and charges levied in the EU Member States are in general insufficient to fully internalise the external and infrastructure costs of transport. For most vehicle categories, only 15% to 25% of the external and infrastructure costs are covered by tax/charge revenues. The cost coverage ratio for passenger cars was found higher (about 50%), which was mainly because of the relatively high fuel and vehicle tax levels applied in (some of) the EU Member States for these vehicles. For inland waterways and maritime transport, much lower cost coverage ratios were found (i.e., 6% and 4%, respectively), reflecting the limited tax/charge burden levied on these modes in the EU. Even if one excludes fixed infrastructure costs from the analyses, the taxes and charges did not cover the external and variable infrastructure costs for most vehicle categories. High-speed trains are an exception, as for these trains the current taxes and charges did cover all external and variable infrastructure costs. This finding has been supported by the results of the analyses of the marginal social cost (MSC) coverage ratios. Despite the limitations of this analyses, it provides a first indication that there was a lack of charging in accordance with the MSC principle in the EU28. The revenues from transport taxes and charges in the EU28 were partly earmarked for expenditure for transport infrastructure. However, significant differences did exist between modes. For road transport, about 10% of the taxes/charges are earmarked, while for rail transport this is about 85%. For the other modes, only fragmented data on earmarking was identified, showing that (at least part of) the (air)port charges are earmarked to cover infrastructure expenditures. Although taxes and charges are efficient policy instruments to reduce the external costs of transport, the study recognize that other types of policy instruments and non-pricing policies (e.g., command-and-control measures and subsidies) may effectively complement tax and charge schemes, for example by providing EU-wide harmonised incentives to invest in certain reduction technologies. With regard to the activities of the study, TRT was responsible to (i) develop estimations of the external costs related to congestion for all transport modes (quantitatively for road), (ii) elaborate estimations of the infrastructure costs […]