- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
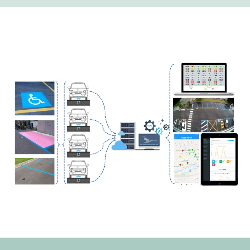
- Evaluation of internal traffic access and parking in the areas of the major polyclinic hospital This study addresses issues related to the reorganisation and management of vehicles parking within the areas of the Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico in the city centre of Milan. The area, currently occupied by construction sites for the new buildings, is characterised by very limited parking spaces and it is affected by frequent phenomena of irregular parking that affect its proper and safe use for the various functions, particularly those related to emergencies. The study analyses in detail the current demand for mobility through: the administration of a questionnaire to employees concerning individual travel, analysis of vehicles and bicycle/pedestrian input/output flows from the area and an in-situ analysis campaign of the supply and demand for parking. Based on the solid reconstruction of the current state, innovative solutions were proposed with regard to parking management, through the implementation of an innovative access control and parking management system. This system is characterised by a high technological content based on the control of both access (through a number plate reading system) and individual parking spaces (through the installation of special sensors on the ground). The new system will be able to control both access and parking vehicles, allowing the automatic detection of any abuses in terms of access and parking. ]
- CIVITAS MUSE – Coordination and Support Action for the CIVITAS Initiative The scope of CIVITAS MUSE is to support the CIVITAS community to increase its impact on urban mobility policy making and advance it to a higher level of knowledge, exchange, impact and sustainability, while guaranteeing essential high-quality support. Their main objectives include: to act as a destination for knowledge developed by the CIVITAS Community over the past twenty years To expand and strengthen relationships between cities and stakeholders at all levels To support the enrichment of the wider urban mobility community by providing learning opportunities To represent CIVITAS on the international stage TRT is responsible of the activities related to projects monitoring and evaluation, as well as for the development of policy recommendations. More specifically, the key objectives of TRT work are: Monitor results and implementation activities across CIVITAS and urban mobility projects with reference to what is new and emerging from the CIVITAS Community on urban mobility innovations and policy making. Enhance, consolidate, and bring to the next level the substantial body of knowledge that has and is continuously being produced by urban mobility projects, to improve its accessibility to practitioners. Provide a common realistic, user-friendly and effective evaluation framework as the reference point for mobility measures and concepts, supporting projects in its implementation to harmonise evaluation activities. Provide focused policy support to the CIVITAS Community, informed by Policy Groups contributing to Green Deal objectives, elaborating policy building blocks and content for MUSE learning and communications. For more information, check the previous Coordination and Support Action for the CIVITAS Initiative, CIVITAS Elevate
- Modelling European cities’ pathways to zero-emission urban mobility by 2030 through the development of potential transition scenarios This study modelled European cities’ pathways to zero-emission urban mobility by 2030 through the development of potential transition scenarios. Each scenario is built on different set of sustainable policy measures, whose impacts is quantified through a series of indicators as output results. The assessment is realized through MOMOS a quantitative tool which allows to simulate and quantify in a simplified way the impacts of potential mobility transition scenarios in cities. Four potential scenarios, each one with a different focus and a specific combination of policy measures, have been simulated and applied to five real European cities: Brussels, Madrid, Milan, Greater Manchester, and Warsaw. An in-depth data collection defined and reproduced the city characteristics at the base year, including socio-demographic aspects as well as mobility features. The main output of the study consisted in the calculation of the CO2 emissions reduction associated to each scenario. Besides that, a series of core indicators have also been calculated for the 2030 horizon. These included: modal split, public and private fleet electrification, car ownership, road safety, and air pollutants emissions. In addition, multi-criteria cost effectiveness analysis estimated costs and benefits associated to the four transition scenarios. Such analysis was based on four components: (implementation and maintenance) costs of the policy measures, environmental benefits, users’ transport costs and travel time, and revenues for the public administration and service providers. For more information: Clean cities website on the (E)Mission zero study, including technical reports and factsheet results. Briefing of the (E)Mission zero study Interactive tool to explore results of the (E)Mission zero study
- Formazione e Capacity Building per i Piani di Mobilità Urbana Sostenibile (PUMS) nei Paesi dell’UE TRT, supported by a consortium of six companies (DTV Consultants, TREDIT, TIS, Stratec, Goudappel, and Eurocities), has been appointed by the European Investment Bank (EIB) to provide SUMP Training and Capacity Building activities in multiple EU countries The primary goal of the project is to enhance the expertise of urban and regional transport planners, as well as newcomers, focusing on Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMPs) and offering centralized support for their implementation at the local and regional levels. The project entails a comprehensive program encompassing almost 30 training sessions and workshops in less than 2 years, covering SUMPs, National SUMP Support Programmes (NSSP), and Urban Mobility Indicators (UMI) monitoring and reporting mechanisms. The project aims to improve the technical and policy expertise of urban transport planners regarding SUMPs and facilitate their implementation at city or regional levels. It targets local training for TEN-T urban nodes, Cities Mission cities, and small/medium-sized EU cities, alongside capacity-building workshops to assist in establishing NSSPs at the national/regional levels. This initiative is crucial for implementing the Commission Recommendation on NSSPs, bridging capacity gaps in smaller cities, and ensuring national engagement and support. Aligned with the New EU Urban Mobility Framework, the training sessions focus on various SUMP aspects, including governance, legislation, funding, monitoring, evaluation, guidelines, methodology, education, and knowledge exchange through NSSPs. The training approach blends fundamental SUMP knowledge with the latest mobility, technology, and societal developments. The ultimate goal of the project is to strengthen SUMP implementation and governance across Europe by addressing key aspects of modern mobility planning, including monitoring tools, legal frameworks, and financial commitment, while tailoring activities based on Member States’ specific needs and interests. The SUMP training and NSSP workshops are delivered by 4 key experts: Tom Rye, Christiaan Kwantes, Kristina Gaučė, and Aljaž Plevnik. In addition, they are supported by a pool of Non-Key Experts with a vast experience in the different fields of the urban mobility domain. The SUMP trainings cover a wide range of topics: CORE MODULES Basics of SUMP methodology and practice The link between Strategic Plans, Programming, Pipeline and project preparation Urban nodes and the interface between local and strategic transport ELECTIVE MODULES Organisational and institutional aspects Multimodal plan scenario building in SUMPs Indicators, targets and monitoring Citizen/Stakeholder engagement and communication SUMPs for small and medium-sized cities Demand and Accessibility analysis through the SUMP Transport decarbonisation Environmental aspects Climate change adaptation and resilience Collective passenger transport Active modes and micromobility Freight and logistics Demand management Spatial planning Road safety and street design Inclusive and accessible mobility The NSSP workshops encompass several aspects, including the introduction of NSSP concepts, EC guidance, guest speakers, Q&A sessions, breakout group discussions, systemic barriers, national legislations, SUMP financial support, National SUMP platforms, SUMP guidance, and monitoring and evaluation at the national level. The first phase of the project lasted from September 2024 and was completed in June 2025, which saw the organisation of 12 training […]
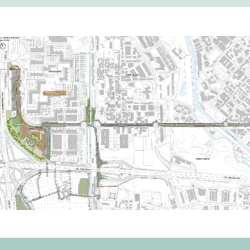
- Integrated Planning Programme “PII1 -Milanofiori Sud” in the Municipality of Rozzano: Mobility Study The project addresses and offers solutions to the mobility impacts generated by the future development of the urban area PII1 – Milanofiori Sud in the Municipality of Rozzano (MI). TRT was part of the multidisciplinary team led by Policreo and Studio Nonis. TRT was involved in the definition of the mobility infrastructures and related impacts. The main activities carried out by TRT in the development of the area concerned: the selection of a suitable mobility scenario (transport and infrastructure), characterised by a strong connotation of sustainability; the development of a transport study that, through solid quantitative analyses and modelling simulations, defines the performance characteristics and accessibility level of the transport scheme selected for the area. TRT has actively contributed to the functional reorganisation of the M2 Assago-Milanofiori-Forum stop, which will represent a new multimodal interchange hub with an annexed cycle station equipped to serve intermodal users. TRT also supported the project team in defining the new cycle path that runs along Viale Gran San Bernardo – Viale Monte Amiata – Viale Isonzo and will connect the metro stop with the tram line 15 stop in Via Curiel. Related projects – City of Rozzano, mobility solutions for Città Nuova
- Update of the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (SUMP) of Parma (Italy) The Municipality of Parma has entrusted TRT Trasporti e Territorio with the update of the current Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (SUMP) of the city, which has been in effect since March 2017 and was also drafted by TRT. The update of the SUMP is significant because: it references the EU guidelines developed within the Eltis project (latest version from 2019), as well as the Minister of Transport’s DM 397/2017 and 396/2019 «Guidelines for Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans», which were not yet issued at the time of the current SUMP; it follows the preparation of the «First Monitoring of the SUMP» (prepared by TRT and approved by the City Council in 2021), which assessed the ongoing achievement of objectives and targets set in the current SUMP; it takes place after the pandemic period (Covid-19), during and after which there have been significant changes in the mobility demand characteristics; moreover, important amendments have been introduced in the Road Code; it must be consistent and support the EU mission «100 climate-neutral and smart cities by 2030», to which the city of Parma has been admitted as one of the nine in Italy, with the goal of achieving climate neutrality by 2030. The activity will unfold in the following methodological steps: background analysis of the framework regarding the Parma’s mobility system and its impacts; analysis, processing, and synthesis of numerical information regarding mobility demand; evaluation of the current scenario (diagnostic framework) through a SWOT analysis; identification of strategies and alternative scenarios for the SUMP, as well as their detailed design; development of a participatory process to extend the sharing and acceptability of measures promoted by the future SUMP; evaluation of scenarios through the application of a multimodal transportation model (VISUM); estimation of investment and management costs for the Plan interventions, and finally design of monitoring activities. Regarding the participation activities, these will accompany different phases of SUMP development, involving citizens and stakeholders through public and thematic meetings, as well as the administration of an online survey directed at the entire community. Related projects: TRT was commissioned in 2019 to coordinate the implementation and monitoring of Parma’s SUMP and was also responsible of the drafting of the General Urban Traffic Plan of the city of Parma. TRT was also responsible of the drafting of the previuos Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan.
- Air cargo in Italy – Survey to companies The Cluster Cargo Aereo represents the main stakeholder of the market of the air cargo in Italy (shippers, carriers, handlers), with 400 companies that occupy approximately 40.000 direct dependent. The function of the Cluster is to provide research, studies and statistics and to offer insights for the operators of the sector through the project «Osservatorio Cargo Aereo» born in 2018. After the first study, presented in 2019 and focused on transport supply (competitiveness of national and European airports), and the second study on air freight transport demand of 2020, the Cluster has commissioned to TRT a new study in order to better understand the perception of the air cargo service in Italy. Therefore, TRT has realized a survey to the main manufacturing companies, integrated by an in-depth survey to the shipment companies, whose results have been introduced during the 5th Convention of the Air Cargo Observatory, where there was an audience of 200 stakeholders and companies of the sector. The results made it possible to identify the determining factors for the modal choice, the degree of satisfaction of the Italian airport system, the main criticalities, the potentialities of development of the air cargo in Italy regarding to some trends of market and the strategies that can be put in field in order to favor the development of the belonging row.
- Drafting of the executive design including the elements of the definitive project necessary for the Services Conference of two parts of the VENTO cycle route between Piacenza, Fossadello and Cremona TRTIngegneria was commissioned by AIPO to draw up the executive design of two sections of the VENTO cycle path: the Piacenza-Fossadello priority lot and the Fossadello-Cremona lot E1. The second mentioned lot is financed by funds linked to the National Recovery and Resilience Plan. Starting from the Technical-Economic Feasibility Project developed at an interregional level, TRTingegneria develops the executive project of the lots indicated above, in particular the in-depth study of the detailed aspects, by means of a chorography of the framework, the plan of the project insertion both on aerial photos and on CTR, the list and analysis of prices with the incidence of labour, the metric computation, the economic framework, the report on the excavated soil and rocks and the descriptive-performance specifications of the work. As for the specialised reports, TRTingegneria develops the geological and geotechnical report in addition to the hydrological and hydraulic report, the environmental report, the preventive check of archaeological interest, the technical report of the electrical systems, the interference resolution and their planimetry. On the urban planning side, landscape and historical/cultural constraints are analysed, as well as interferences with the Natura 2000 Network and the drainage and irrigation system. Similarly, the technical maps of the municipal regulatory plans (or similar instruments) will be analysed to verify the project’s inclusion. Finally, TRTingeneria develops the road design of the cycle track, with detailed plans on planimetric survey, with details of intersections, longitudinal profile, current and typological sections. Road construction details, signage, parking areas, water collection system and electrical installations are also included.
- Data analysis for the project of electric vehicles in Latvia Objectives of the study The study had several objectives. First, assessing and analysing the situation regarding electric mobility in Latvia, considering the trend of the share of electric cars in the fleet and the infrastructural endowment of charging facilities, also assessing their geographical distribution. Then, verifying the state-of-the-art and the potential of hydrogen cars as well as the conditions that could facilitate their penetration into the fleet. Then, developing scenarios for the growth of electric mobility and, based on those, quantifying the need for electric infrastructures and the resulting environmental benefits. Some results of the study The study showed that the registration of electric vehicles (mainly passenger cars) has grown at a high rate in recent years, but the share of these vehicles in the fleet remains limited. The provision of public charging infrastructure appears consistent with needs in all Latvian regions. The role of public administrations as pioneers for the deployment of electric vehicles is relevant. Regarding hydrogen cars, the analysis showed that they currently represent a negligible share of the fleet, with significant numbers in only a few countries. Given also the attitude of manufacturers, it seems preferable at the moment for public intervention to focus on the electric mode. Future scenarios of electric vehicle penetration were defined as projections based on European-scale studies, considering at what extent the observed trend so far has been more or less consistent to the predictions of these studies. In general, the scenarios suggest that in the short to medium term it will be mainly electric cars that will enter the fleet, while in the long term the highest shares of electric penetration will be achieved for commercial vehicles. From an emissions point of view, electrification of the fleet will provide a contribution, but the improvement of the efficiency of conventional vehicles can be even more relevant.