- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
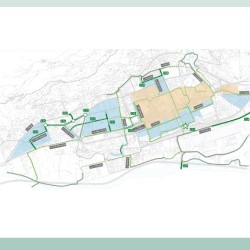
- Update of the General Urban Traffic Plan (PGTU) of Aosta The study concerned the update of the Aosta General Urban Traffic Plan (PGTU) already prepared by TRT Trasporti e Territorio about 10 years ago as part of the Metis Consortium. The city of Aosta (about 35,000 inhabitants) concentrates one fourth of the Aosta Valley regional population and plays an important role in regional mobility thanks to its services and economic activities. The activity was launched in November 2019 and it consisted of the following activities: the update of the key mobility factors – demographic and socio-economic structure, transport networks and services supply, mobility demand, environmental and social impacts; the analysis of the on-going planning tools, including an assessment of the state of implementation of the measures included in the previous PGTU (2011); the identification of the urban mobility system’s strengths and weaknesses in order to define the set of strategies and interventions to be included in the new PGTU; the design of the Reference and the Planning scenarios with measures related to: road network and its regulation, public transport system, cycling network, parking system, mobility management, electric mobility, urban logistics and ITS systems; the definition of detailed interventions for specific locations – the Arch of Augustus area, the new university complex area, the railway station area – both from urban planning and from mobility system points of view. The PGTU was approved by the Municipality Council on February 23rd, 2022, with official act no. 23.
- Technical support in the drafting of the Territorial Plan of the Province of Piacenza (Piano Territoriale di Area Vasta) TRT has been commissioned by the Province of Piacenza to provide technical support in the drafting of the Territorial Plan of the Province (PTAV) in line with the new Regional Planning Law No. 24/2017. Project activities included the definition and evaluation of alternative mobility and transport scenarios within the time frame of the Territorial Plan of Piacenza Province. In this context, the main tasks concerned: the update of the knowledge framework of the mobility and transport system in the Province of Piacenza; the development of a reference scenario and two alternative evolving scenarios. The first, tendential, includes interventions planned and not implemented by the current Territorial Plan (PTCP). The second scenario is based on a selection of interventions and measures that respond to the ASI (Avoid, Shift, Improve) strategy, including measures to manage mobility demand and in favour of alternative modes to motorized private vehicles; the evaluation of alternative scenarios, both from a transport and environmental perspective, was also carried out with the support of the traffic simulation model at the 2032 horizon; the provision of technical support to the Public Administration in the interaction with the stakeholders; the providing of technical contribution in the drafting of intermediate and final reports. The final document includes four preliminary modelling tests to identify the best route alternative for the so-called “median road“ of the province.. A further test concerned the complex interconnection system between motorways A21, A1 and State Road SS9. The intervention includes: a new connection between the Rottofreno tollgate on the A21 and the Basso Lodigiano tollgate on the A1, the downgrading of the Piacenza section of the A21, a new bridge over the Po river as a variant to the SS9. The evaluation of these alternatives included transport, environmental and territorial aspects, also thanks to the support of Politecnica. For more information visit the official website – Only available in italian
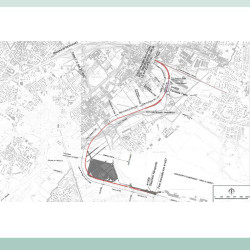
- City of Bergamo – New railway station in the strategic urban context of the new exhibition center As part of the transformation area “Fiera Nuova-Boccaleone Park” – At_e / s29 – UMI 2, to be implemented in the strategic urban context of the “New Exhibition Center” of the Municipality of Bergamo, TRT has provided transport consultancy specialized for the feasibility study for the construction of a railway station along the new Bergamo – Airport railway line. TRT led the study alongside a team of railway design experts (GVG Engineering) in the development in the development of the plans, profiles and railway sections for the new railway station. The new station will be located in an intermediate position, on the edge of the Bergamo Exhibition Center, ensuring a direct connection from the city station and the Bergamo Orio al Serio Airport. The station will be in a viaduct, ensuring the east-west permeability of both the road network and the cycle-pedestrian connections as well as providing a new interchange parking hub serving the airport the urban area and the exhibition center.
- New Hospital of Piacenza: Contributed to the feasibility study through an in-depth transport system analysis and a Cost-Benefit Analysis TRT Trasporti e Territorio was commissioned by the Local Health Unit of Piacenza to provide technical support for the project of the New Hospital of Piacenza, as part of a consortium led by Policreo Srl. TRT contributed to the feasibility study through an in-depth transport system analysis and a Cost-Benefit Analysis. The activities were divided into three main topics: the first topic concerned the mobility system of the current hospital complex, analysing in detail the road system, the public and private accessibility of the area and the hospital parking area; the second theme assessed the functionality of the road and parking infrastructures serving the new hospital area and estimated the impacts on the private mobility system. The transport analyses concerned the private and public modes as well as cycling and the parking systems. The analysis was conducted through the application of a sophisticated and dynamic traffic micro-simulation tool that provided a series of quantitative parameters (average speed, delays, etc..) functional to assess vehicular flows; The third one was related to the cost-benefit analysis. The analysis was developed comparing the scenario with the new hospital with the scenario where the existing hospital is upgraded/renovated. The cost-benefit analysis estimated the project’s contribution to social welfare, comparing the socio-economic costs of the two scenarios (investment, maintenance, etc.) with the corresponding benefits (health benefits, improved transport accessibility, availability of recreational and green spaces).
- Implementing a multimodal transport network model of the Rail Baltica Corridor and appraisal of the passenger and freight transport activity onto the Corridor Rail Baltica Global Project is the Baltic part of a rail transport infrastructure project with a goal to integrate the Baltic States in the European rail network. The expected core outcome is a fully interoperable railway line of more than 870 km in length meant for both passenger and freight transport as part of TEN-T Core Network (North Sea – Baltic Corridor). A first phase of the study, carried out in 2021-22 consisted of two main activities. The first activity was the implementation of a multimodal transport network model of the Rail Baltica Corridor covering in some detail (NUTS3 or even sub-NUTS3 zones) the area of the three Baltic countries (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania) and of neighbouring regions of Finland and Poland plus the rest of Europe and world regions in a progressively more aggregated fashion. The transport model is a four-stage model, dealing with the estimation of generated demand, distribution, mode split and assignment to a multimodal network. The model covers both passenger and freight activity of interest for the planned rail infrastructure. All transport modes competing with rail are represented. Different rail services are explicitly modelled both for passenger (including Night-Train services) and for freight. Supporting the implementation of the model, a Stated Preference surveys was carried out to estimate parameters for the passenger demand model. The second activity of the first part of the study was the application of the model to estimate the passenger and freight demand onto the corridor in several future time thresholds, corresponding to different stages of the implementation of the infrastructure, and under three scenarios: a “do-nothing” scenario without the new infrastructure. a “Base scenario” with the new infrastructure. an alternative scenarios where alternative assumptions are made regarding intermodal rail transport services and the application of measures related to the EC Green Deal transport policy is considered. The application of the model provided several outputs ranging from aggregated statistics to link-based traffic and including impact indicators on energy consumption and emissions. The model was delivered along with the outcomes of the study and a training course focused on the use of the model was held for staff of Rail Baltica AS. This first phase of study was carried out by TRT with the support of PTV (DE), MDS Transmodal (UK), CSE COE (LV). TRT was the coordinator of the study and was responsible for developing the demand model (passenger and freight) as well as the Stated Preference survey. In a second phase (2024), some aspects of the model have been revised in order to improve the level of detail of the analysis and make the interaction with the model easier. In particular, the number of zones has been increased so that zones do not include more than one (non-urban) regional station. Following the revisions implemented, at the end of the second phase the model is recalibrated. The activities of […]
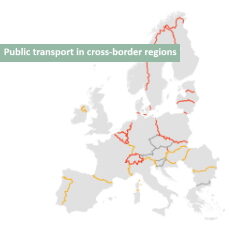
- Study on “Providing public transport in cross-border regions. Mapping of existing services and related legal obstacles” In the EU it is widely acknowledged that border and cross-border regions need particular attention. About 30% of the EU population live in regions close to internal border. Despite the single market, cross-border activities still face bottlenecks hampering businesses and citizens. Cross-border transport is one central means to facilitate cross-border activities. Despite the importance of cross-border public transport to link regions across borders, to date, no European-wide and comprehensive inventory of cross-border public transport (CBPT) services exists. Thus, even the actual number of services is impossible to estimate. In view of this role of CBPT, this study: provides a comprehensive inventory of existing CBPT services along the internal borders of the European Economic Area and a sound and profound analysis thereof; develops an inventory of obstacles to the implementation of CBPT and further analyse them and possible solutions; identifies best practices with relevant case studies and develop a toolbox to support planners and implementers. Within the project TRT is responsible for: the analysis of cross-border rail transport services; the development of a web viewer to map existing services for all transport modes; the analysis of 3 case studies on the business models of cross-border public transport services.
- User-friendly information tool on urban and regional vehicle access regulation schemes UVAR-BOX is the EU project which has been established to tackle fragmented or unavailable information on up-to-date and relevant UVARs (Urban Vehicle Access Regulations) policies in European cities. The 24-month project successfully ended in 2023 and developed the Datex II standard for UVARs and a tool, the UVAR-BOX, to facilitate the input of UVAR data into the Datex II standard, which can be read automatically by navigation systems and mobile applications available to European drivers. UVAR policies pursue various objectives such as improving air quality, livability and reducing congestion. The project aimed to harmonize and disseminate information on UVAR policies in fleet management tools and navigation devices. Its widespread application and use will support both road users to plan journeys across the EU, and local authorities and Member States to set up standardized communication procedures in line with European regulations on the dissemination of mobility-related information (ITS directive and single digital gateway). TRT, as part of a large consortium, had the role of Italian Country Coach to support Italian public administrations in this digitization process. For more information Project brochure – Link Country Coaches web page – Website DATEX II: the standard for traffic and mobility information – Video
- Study on exploring the possible employment implications of connected and automated driving The European Commission has commissioned a study focused on getting a better understanding of the impacts on work and employment in the transport sector resulting from the introduction of vehicles with connected and autonomous driving (CAD). The study is aimed at supporting the development of adequate policies to promptly mitigate any negative impacts. Part of a consortium led by Ecorys (NL) and participated by M-Five (DE), VTT (FI), SEURECO (FR), ERTICO, IRU and UITP, TRT is in charge of the design and development of 4 explorative scenarios that consider different levels of penetration of CAD vehicles for the evaluation of the consequent employment repercussions. The evaluation of the impacts is supported by two modelling tools on a European scale ASTRA and NEMESIS. Scenarios’ creation is supported by the Scenario Model. Developed by TRT in System Dynamics, the Scenario Model considers the main drivers on both the supply and demand sides, which influence the uptake of autonomous driving vehicles. The elements on the supply side concern the technology and the conditions of use of CAD; the elements on the demand side concern requirements, preferences and constraints that guide the choice of modes and means of transport. In addition to supply and demand, a third important aspect considered by the model is the regulation introduced by authorities concerning the use of CAD vehicles in different environments. For more information: The Main Report and its annexes are available for download; A brochure of the report is available too; The findings were also presented during a conference in September 2020, where stakeholders in road transport discussed a potential social roadmap for automation.
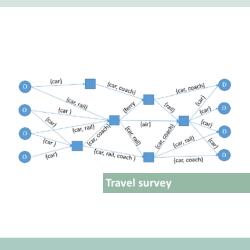
- A survey in 20 European cities on behalf of the JRC of the European Commission to explore the impacts of COVID-19 outbreak on urban transport The Covid-19 crisis triggered major changes in users’ mobility preferences in light of health risks and restrictions, as well as changes in terms of different working patterns and economic activity that have impacted on the demand of urban mobility. The study was aimed at collecting data through a survey in 20 EU cities, in order to understand individuals’ urban mobility patterns in light of the changes introduced by the Covid-19 pandemic. In specific, the exercise analysed how the health crisis impacted on elements like: mode choice, transport costs, trip purposes, frequency of movements, external factors driving the transport choice. The impact of disruptive elements, such as teleworking was also explored. TRT was responsible for the research, which was managed by IPSOS. The 20 cities were distributed in 11 EU countries; they included large metropolitan areas as well as medium cities with different levels of diffusion of the Covid-19 virus, different role of public transport and bike and different level of road congestion. The survey involved 500 individuals in each city. Two different methodologies were used to collect responses: a CAWI questionnaire and a CATI questionnaire. The combination of the two methods ensured an affordable and representative sample.