- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
- Shift2Sustain: Driving Behavioural Change in Mobility Towards Sustainability Shift2Sustain project started in November 2025, and brings together 17 partners, including 7 pilot cities. The purpose of the project is to promote the adoption of Mobility Management Plans (MMP) for public and private actors, by developing a guidance and testing mobility solutions in the pilot cities. The first objective of the project is the generation of a database of information on existing Mobility Management Plans (MMP) and Mobility Management Schemes (MMS). This work is needed to analyze the state-of-art in Europe and highlight which measures had positive outcomes and why. The analysis is carried out through a desk research and a stakeholder consultation for different countries. Furthermore, S2S aims to implement 7 pilot tests about MMP and MMM solutions in each city participating in the consortium: Oeiras (PT), Turin (IT), Gdansk (PL), Zagreb (HR), Izmir (TR), Sarajevo (BA) and Copenhagen (DK). These actions will be mapped with indicators and expected impacts calculated before and after the projects, to quantitatively and qualitatively assess the results of such pilots. Together with the pilots, it will be developed a digital toolkit composed of a digital serious game and a behavioral gamification app for community involvement. The app will be developed by an external startup, selected after a market consultation. The games are adaptable for the various location and measures implemented, facilitating, enhancing and tracking the implementation of MMM. Thanks to the analysis of the results, a guideline with the lessons learned and policy recommendations will be produced, with the aim to develop mobility training plans, focusing on MMP and MMM. The trainings will be launched through an online course called “Learn2Shift”, a program which provides practical and professional skills. Finally, the consortium will provide technical dissemination of the project contents through events and scientific publication, as well as through the engagement with relevant EU stakeholders.
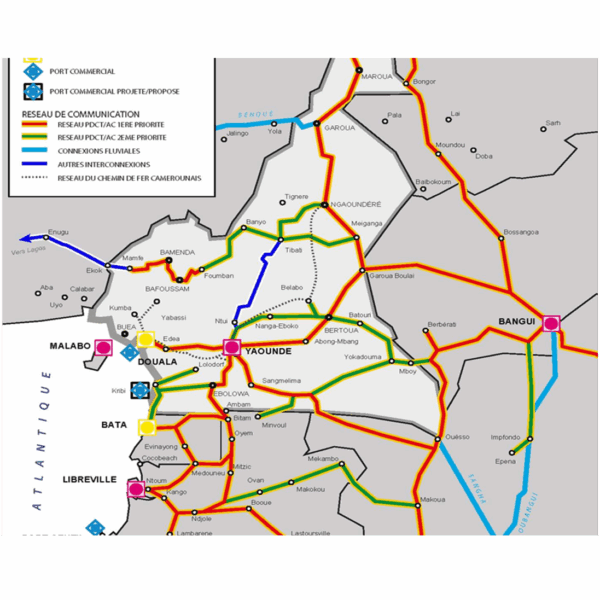
- Development of Cameroon’s National Logistics Strategy and Action Plan for the period 2025-2035 TRT Trasporti e Territorio, with its team of logistics experts, is involved in developing a national logistics strategy for Cameroon and an action plan for the years 2025 to 2035. The activity is divided into two main areas: •Activity 1: develop the strategy and action plan in line with various sectoral development strategies, such as urban mobility plans, regional development plans, river and intermodal transport strategies, etc.. •Activity 2: develop terms of reference for the main priority activities recommended by the national logistics strategy and carry out a feasibility study for the formation of a National Transport and Logistics Coordination Council (CNCTL) in Cameroon. Among the activities listed, TRT is specifically responsible and leader for assessing the infrastructure requirements and logistical services needed, as well as the measures to be taken to improve their performance.
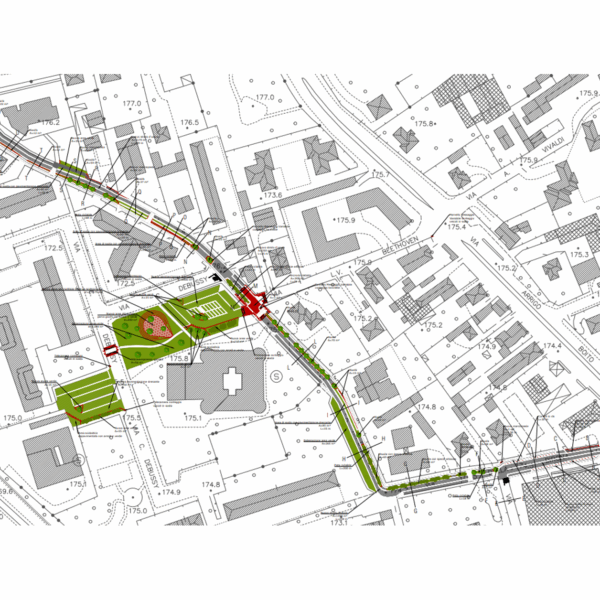
- Drafting of a Technical and Economic Feasibility Study (PFTE) for a cycle path along Via della Birona in Monza TRTIngegneria was commissioned by architect Andrea Nonni to assist in the preparation of project design documents for the Municipality of Monza’s participation in the Lombardy Region’s ‘Strade Verdi’ (Green Roads) tender. Specifically, the contribution is required for the drafting of the PFTE (Preliminary Technical Project) of a cycle path along Via della Birona in Monza, Italy and the related works for its inclusion in the areas in front of the entrance to the nursery and primary schools in Via Debussy. The project involved the construction of a one-way cycle path along the entire length of Via della Birona, divided into two sections (one one-way northbound in the southern part and one southbound in the northern part of Via Beethoven). The infrastructure integration work included: • the renovation of the car park along Via della Birona, with the use of draining paving and devices for groundwater filtration; • the implementation of speed reduction measures along Via della Birona and Via Debussy, through the construction of a speed bump at the intersection with Via Beethoven and a raised crossing on Via Debussy; • the construction of new paving for the parking areas in front of schools that allows rainwater to filter through, including a filter tank; • green spaces with plants capable of filtering atmospheric pollutants, accompanied by a playground, pedestrian areas serving schools to improve their accessibility, together with bicycle parking facilities (racks), benches and other street furniture.
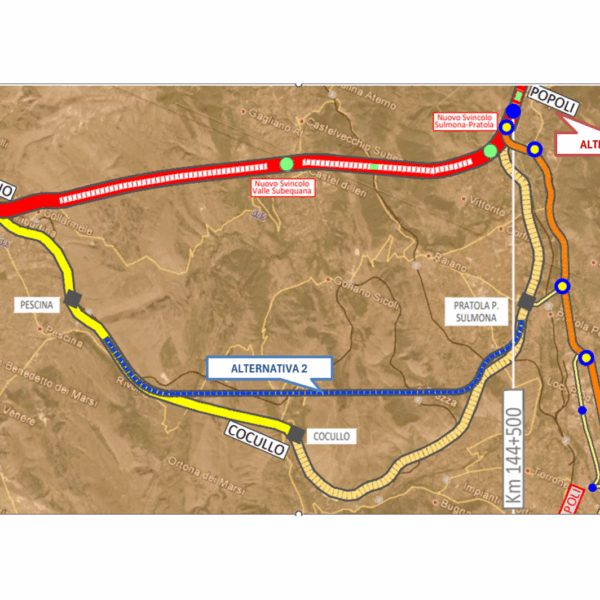
- Comparative analysis of costs and savings of two alternative routes As part of the feasibility study for the structural and functional upgrade of the A25 motorway, with particular attention to the section known as the “Cerchio-Popoli Variant,” TRT was tasked with preparing a comparative analysis of the costs and savings between two possible route alternatives. The currently operational highway section between Cerchio and Popoli presents significant infrastructure challenges related to both the age of the structures and the morphological conditions of the terrain it crosses. In this context, Strada dei Parchi S.p.A. and Italferr have submitted design modification proposals aimed at improving the safety, functionality, and sustainability of the infrastructure. Alternative 1 envisions the construction of three new tunnels, two viaducts, and new junctions, along with the demolition of the existing section between Cucullo, Pratola Peligna, and Sulmona. The new route would extend from the municipality of Cerchio to Popoli and would save approximately 17 km compared to the current situation. Alternative 2 envisions the construction of a new tunnel and the simultaneous demolition of the same existing section between Cucullo, Pratola Peligna, and Sulmona. This solution would save approximately 7.5 km compared to the current situation. For Alternatives 1 and 2, costs and savings were estimated over a 34-year timeframe, including the four years of construction of Alternative 1 (the first to enter into operation) and the 30 years of operation from its opening date. Based on the demand data provided by the traffic study (carried out by Plinomia Srl, and including accidents’ costs estimation as well), three growth scenarios were defined: Precautionary, Optimistic, and Pessimistic. For each scenario, the construction and maintenance costs of the works, the residual value taking into account the useful life of the various components, the time savings, the environmental benefits, and the accident costs of the two alternatives were compared.
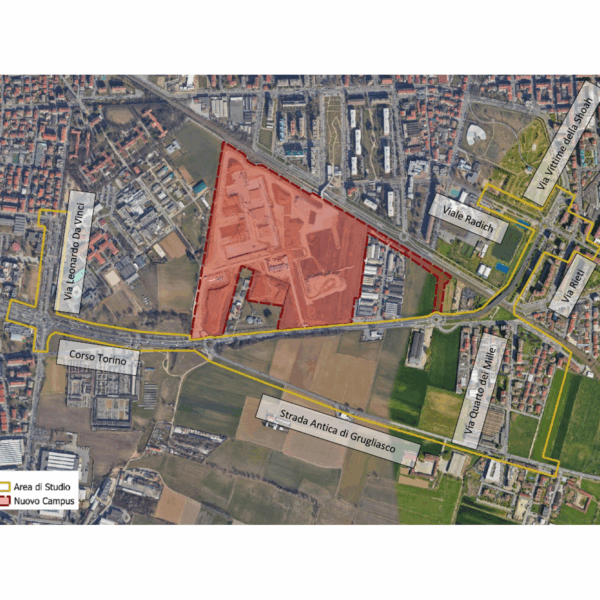
- Assessment of the impact on traffic of the opening of the new campus of the University of Turin, ‘Città delle Scienze e dell’Ambiente’ (City of Science and Environment), located in Grugliasco, Metropolitan City of Turin TRT was chosen by Zona Ovest di Torino srl to provide modelling support in defining the impact of the new campus of the University of Turin, ‘Città delle Scienze e dell’Ambiente’ (City of Science and Environment), in the municipality of Grugliasco. The new campus includes facilities for the Chemistry and Biology Departments, spaces for research, teaching and ancillary services for students, covering a total of approximately 90.000 m2 and is expected to double the university population (from the current 5,000 to approximately 10,000). The study begins with the VISUM model developed by TRT on behalf of Zona Ovest and the Municipality of Grugliasco as part of the support assignment for the evaluation of the PGTU, further refining its calibration through a traffic detection campaign. The macroscopic model was used for the municipal-scale assessment of the opening of the new campus, while the local impact assessment was carried out using a dynamic microscopic simulation model in the VISSIM environment. The study took into account various data sources, in addition to ad hoc surveys, of a demographic and statistical nature on the student population and university staff involved in the transfer (keeping teachers separate from researchers, research fellows, scholarship holders, technical and administrative staff, etc.) as well as information on the current travel habits of people who already gravitate towards Grugliasco (where the veterinary, agrovet, agricultural and “agrinnova” facilities are located), including modes of transport, weekly campus attendance, the number of years students are behind in their studies, and the location of their domicile or residence. The analyses carried out have made it possible to identify the configuration and adaptation measures for the road network that are most effective in mitigating the impact of the opening of the university campus.
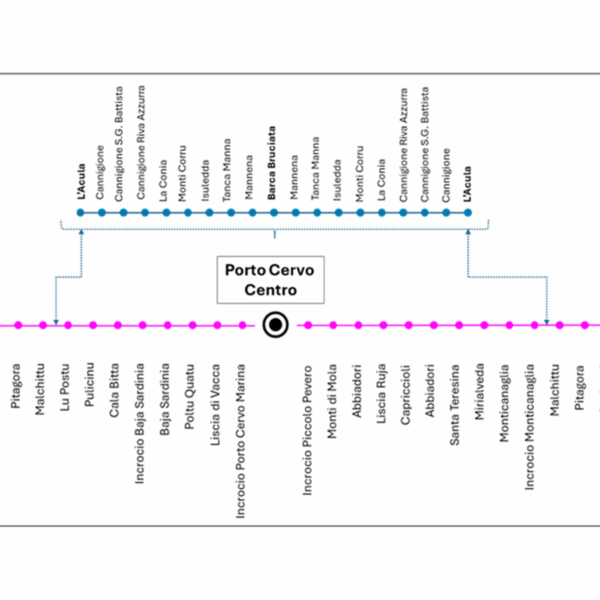
- Design and technical assistance for the award of the Local Public Transport service of the Municipality of Arzachena The Municipality of Arzachena entrusted TRT with the service of “Design and technical assistance for the award of the Local Public Transport service of the Municipality of Arzachena”. The assignment involves activities aimed at the design and assistance for the awarding of the Local Public Transport (LPT) service contract for the Municipality of Arzachena. The work is structured into three main phases: •Preliminary territorial and transport analysis, aimed at understanding the territorial dynamics and the characteristics of the existing service; •Planning and design of the public transport service, consisting of the definition of the characteristics of the proposed public transport service; •Technical assistance to the procedures for the selection and award of the service, consisting of technical support to the Municipality for the preparation of the tender documents and for all phases of the award procedure. The first phase of analysis aims to reconstruct the current framework of local mobility, considering the settlement, demographic and tourist characteristics of the municipal area, as well as analysing transport demand through specific investigations. The second phase is based on the results of the knowledge framework reconstruction to develop a new transport offer configuration, consistent with the mobility needs of the different user groups, both in summer (tourists) and winter (residents), distinguishing between annual service, seasonal summer service and any flexible services. The activities also include technical assistance to the Municipality of Arzachena in the preparation of the special tender specifications, the tender rules and the service contract scheme. To date, TRT has completed the preliminary territorial and transport analysis.
- Development of a transport model to analyse Bergamo students’ travel and analysis of Bergamo functional urban area TRT has been commissioned by the Bergamo Public Transport Agency to conduct two analyses supporting the redefinition of the province’s extra-urban public transport service: •The development of a traffic model with demand assignment for high school students •An analysis of the urban functions of Bergamo’s FUA (Functional Urban Area). The first task has been carried out using the VISUM software, applying an origin-destination matrix of the student population, for which both the municipality of origin and the school destination are known, as well as the GTFS (General Transit Feed Specification) files from various bus operators. To support this part, the information basis has been validated by cross-checking the GTFS timetables with the tabular schedules published by the operators, ensuring the correct reconstruction of service for a typical weekday in winter. Key service indicators were identified, such as bus-km for both the average day and peak-hour periods. Following demand assignment, additional indicators were calculated, including average travel time, boardings and alightings per stop, seat-km offered, and passenger-km or passengers per hour. A complementary analysis considered the comparison between regular weekday service and school-day weekday service. Different scenarios were developed and discussed with the client. The second activity covered by the contract involves drafting a technical-methodological report to assess whether the current delimitation of the capital city’s urban area is appropriate. Various methods and tools used or codified at national and international levels will be analyzed (e.g., the 2001 provincial resolution, the ISTAT methodology based on the OECD-Eurostat approach). For this purpose, origin-destination data from the Lombardy Region was used, along with ISTAT databases and regional and local Open Data. This information was collected in a GIS environment to identify different territorial areas.
- UVAR4US – Using Urban Vehicle Access Regulations for Reshaping Urban Space The UVAR4US project, coordinated by RiSE (Research Institutes of Sweden) with TRT among its partners, is funded under the Driving Urban Transitions (DUT) partnership within the Horizon Europe programme. The project explores how Urban Vehicle Access Regulations (UVARs) can help create cleaner, more liveable, and people-friendly cities in line with the 15-minute city vision — where daily needs are within a short walk or cycle. UVAR4US studies how access regulations affect mobility, the use of public space, and car dependency. By breaking UVARs down into key “building blocks”, the project identifies how different approaches can be combined to fit local urban contexts and community preferences. An open knowledge base will share examples of existing UVARs and their impact on mobility and urban life. A participation framework will highlight how citizen involvement and transparent decision-making contribute to successful policies. These resources will feed into the UVAR4US Toolkit — a practical set of tools to help cities design and evaluate UVAR strategies that support the 15-minute City model. Four Living Lab cities, each preparing to implement new access regulations, will test and refine the project’s tools and methods in real-life conditions. Why it matters Cities across Europe struggle with congestion, air pollution, and limited public space. UVAR4US aims to show how smarter vehicle access management can reduce car dependency, encourage walking, cycling, and public transport, and improve overall urban quality of life. Participating countries Belgium, Germany, Greece, Italy, Spain, Sweden. Funded project partners Cluster Viooikonomias Kai Perivallontos Dytikis Makedonias, Helsingborgs kommun, Living Prospects Ypiresies Anaptyxis & Perivallontos Etaireia Periorismenis Efthynis, Rupprecht Consult-forschung & Beratung GmbH, TRT Trasporti E Territorio Srl, Universiteit Gent
- Municipality of Fermo, Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan Following a tender procedure, the Municipality of Fermo entrusted TRT, together with local experts, with drafting the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan (PUMS) and the related Preliminary Environmental Report – Screening procedure for Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA).The drafting of the PUMS is structured in three phases. The first phase is related to the definition of guidelines, including the knowledge framework of the mobility system and the SWOT analysis, leading to the formulation of objectives and strategies. The planning-programming framework was defined at regional, provincial, and local levels, along with the territorial and socio-economic context of the planning area, the supply of transport networks and services, mobility demand, and the social (accidents) and environmental impacts generated by the mobility system. The second phase includes the drafting of the preliminary PUMS report, which builds on the knowledge framework to identify planning scenarios and related actions. This document allows the initiation of the SEA screening procedure, providing the essential information to assess the environmental impact of the Plan. In parallel with the first and during the second phase, a participation process was developed involving local stakeholders: initially to identify the critical issues of the mobility system and later to critically review the system of actions forming the Plan’s scenario. The feedback received helped refine the definition of scenarios based on comments and suggestions. The third phase is the drafting of the final Plan document, which includes not only the contents of the second phase but also the results of the MOMOS model application, as well as cost estimates and target indicators.