- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
- Modal shift in European transport: a way forward The study, developed for the TRAN committee of the European Parliament for the Year of Multimodality (2018), provides a comprehensive analysis of the progress and potential of modal shift in the EU from road to more sustainable transport modes, with respect to the policy objectives set in the 2011 White Paper on transport. The study focuses both on passenger and freight transport, highlighting the main barriers and factors that are hampering a more effective modal shift at EU level, providing policy recommendations for the way forward. The analysis carried out highlights that, at EU level, a modal shift from road to more sustainable transport means (rail, inland waterways, public transport) is taking place at a lower pace, compared to the objectives previously set. The relevant measures proposed, besides broadly confirming the actions so far undertaken, include the increase of investments on multimodal projects, the improvement of multimodal access and connectivity of all the EU regions and to enhance the use of ITS technologies. [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
- Identification and collection of a set of indicators for the description of the urban sustainable mobility in European cities The SUMI project provided technical support for the identification and the collection of a set of sustainable urban mobility indicators in 50 European large and small urban areas. Main project activities were related to: providing rigorous and consistent methodologies for acquisition, harmonisation and analysis of data for the calculation of indicators; this included the definition of a «mentor» for each indicator, i.e. a reference experts capable to sort out all related technical issues; giving technical support to the urban areas and systematically collecting their hands-on experiences; appointed «urban area coaches» had the responsibility to establish direct links between the project consortium and the urban areas and help city administrations to gather the needed data; carrying on consultation, capacity building and dissemination actions addressed to subjects both inside and outside of the project; preparing realistic, harmonised and sound recommendations to the Commission for further improvement and extension of the indicator set; definition of an online benchmarking tool, available for European and non-European cities, aimed at comparing the indicators of each urban area with reference average values. TRT has been a key partner of the project, with direct responsibility in the coordination of data acquisition and technical assistance to the local experts, being «mentor» for four different mobility indicators. In addition, TRT experts have been «urban area coaches » for cities in Italy. The SUMI indicator set For more information: Webpage of the SUMI project on the European Commission portal. It contains the indicator set, the guidelines for the calculation of values and the benchmarking tool for the comparison of results Entire SUMI indicator set (.zip file) General harmonized guidelines for calculating the indicators (.pdf file) E-course to support cities with the application of the SUMI indicator set. Registration needed, free of charge
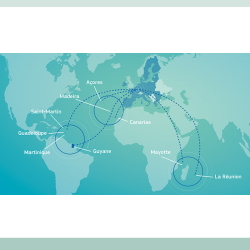
- Study on the physical accessibility of the Outermost Regions of France, Spain and Portugal The objective of the study was to develop a list of transport projects to improve the connectivity of the nine Outermost Regions of France, Spain and Portugal. The study aimed to identify the physical disadvantages, bottlenecks and missing links of the Outermost Regions. This comprehensive analysis was needed for the TEN-T policy to ensure connectivity to all European regions by 2050. The study provided a comprehensive information base of the observed transport conditions of the Outermost regions and a proposition of well-justified actions to improve the overall physical connectivity. In general, the study: identified existing transport links between the EU Member States and the Outermost Regions as well as among and between the Outermost Regions, including regional hubs; identified existing transport links between the Outermost Regions and their neighbouring countries, including regional hubs; developed an assessment of insufficient, missing and promising links; identified key investment needs regarding maritime and air transport; developed an evaluation how to strengthen the Motorway of the Sea policy and its funding; provided recommendations and a list of projects including the sources of funding. This study analysed the observed state of the transport connectivity of (i) Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Martinique, Réunion, Saint-Martin, Mayotte (France), (ii) the Azores and Madeira (Portugal) and the Canary Islands (Spain). These Outermost Regions strongly rely on air and maritime transport connections for accessing to basic goods and services, as well as for their regional economic development. The study found that, in general, the Outermost Regions are well connected with their mainland, both in terms of air and maritime transport. On the other hand, the connectivity with neighbouring regions and countries remains limited. Developing regional connectivity increases territorial cooperation and stimulates regional economic development. Therefore, policy recommendations have suggested to stimulate the level of regional integration, by optimising conditions for operators to provide regional connections through more liberal traffic rights and balanced taxation. In addition, policy recommendations on territorial cohesion aimed at improving the mobility of the residents of the Outermost Regions, as well as the conditions for transport of goods. The recommendations to support general connectivity needs focussed on the development of resilient transport infrastructures and funding options to accelerate the development of the TEN-T in the Outermost Regions.
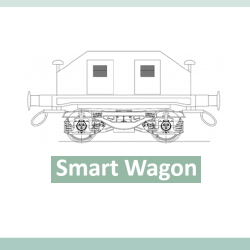
- Automatic Rail Freight Transport System – Analysis of Transport Costs The study developed the feasibility analysis of an innovative and automatic rail freight transport system and elaborated a business plan to assess its economic and financial sustainability. The aim of introducing automatic vehicles for rail freight transport is that of enhancing the internal efficiency of the production system (e.g., in intermodal terminals and logistic centres), by reducing the operating costs and vehicles manoeuvring. Also, the use of automatic vehicles allows to optimise the shipment of cargos from intermodal terminals and logistic centres to transport networks to which they are connected. Further to this, the advantage of using automatic vehicles is twofold. First, automatic vehicles support higher safety levels of the operations avoiding internal collisions (i.e., vehicle-to-vehicle communication and knowledge of the relative position). Second, they reduce the environmental impact, optimising manoeuvring and needs of energy and fuel. The analysis developed an estimation of the operating costs of three scenarios, considering rail-road intermodal transport of semi-trailers, and compared them against the “as-is” situation as follows: wagon towed by a manoeuvring bogie equipped with a traditional coupling system; automatic manoeuvring wagon equipped with a traditional coupling system; automatic manoeuvring wagon equipped with an automatic coupling system. The estimation of the costs shows that there exists a competitive advantage for transporting by rail. With respect to road transport, the difference of cost of transporting by rail increases for longer trips and if a higher level of automation is introduced. The most important advantage of the Smart Wagon system, compared to conventional transport systems, can be obtained when specific conditions hold, namely in contexts such that the demand of freight transport is weak and spread. For example, within ports characterized by a multiplicity of connected internal terminals, the Smart Wagon system would allow to develop transport solutions that merge the demand generated in each internal terminal and share the final destination. Some aspects deserve consideration before implementing an automatic manoeuvring wagon system. First, the cost of feeder legs, which is often a critical cost component for choosing intermodal transport (i.e., the magnitude of the cost is proportional to the length of the trip). Second, with respect to transporting only via road, one should take into account the longer time of the trip, due to two modal shifts (i.e., road-rail and viceversa) and additional waiting times before the train run.
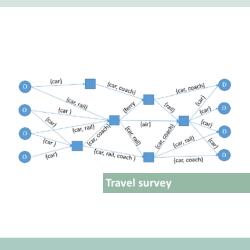
- EU survey on issues related to transport and mobility Nowadays, a reliable analysis of the transport system which allow to monitor the achievement of goals set by the European policy require the availability of updated mobility data. In line with this concept, in 2013 (and again in 2018) the European Commission launched a study involving the design of a questionnaire for a survey that investigate the mobility habits of people at European level. The survey involves 1000 individuals for each of the 28 European countries. In addition to traditional socio-demographic data and daily mobility habits, the survey deeply investigates: the role of long distance trips by mode and by purpose; the tendency to make multimodal trips; the awareness of the opportunities offered by mobile applications and innovative ICT solutions. These studies, both coordinated by TRT and implemented by IPSOS, follow the same methodological approach. This guarantees continuity in data collection allowing for data comparability, definition of trends and monitoring the impact of transport policies.
- Odometer tampering – measures to prevent it (Research for TRAN Committee) The study, commissioned by the TRAN Committee of the EU Parliament, examined the phenomenon of odometer tampering in the EU and proposed concrete actions to tackle it. Despite the EU legislation has addressed the issue in the “Roadworthiness Package”, a major gap has been identified in the long timeframe occurring between the vehicle’s registration and the first Periodical Technical Inspection, as well as the lack of sufficient cooperation and data exchange on odometer readings between EU Member States (MS). The implementation of a EU-wide data exchange system between EU MS on odometer readings could help competent authorities to detect fraudsters (as shown by the Slovakian and the Dutch bilateral cooperation, making use of the EUCARIS platform). The study also explored the best practices developed in Belgium and the Netherlands, where the problem was nearly eradicated in the last years. In both countries the percentage of unauthorised manipulations dropped below 1%. Furthermore, the study highlighted that odometers are still inadequately protected against cybersecurity threats. Potential IT solutions to combat the phenomenon have been suggested. [tw_button icon=”” link=”https://www.trt.it/archivio-progetti/” size=”small” rounded=”false” style=”flat” hover=”default” color=”#223468″ target=”_self”]Projects[/tw_button]
- CEDR’s TEN-T (Roads) 2017 Performance Report The 2017 TEN-T (Roads) Performance report is the fifth biannual report issued by the Conference of European Directors of Roads (CEDR) on the performance of the TEN-T road network within the participating countries. Biennial CEDR reports offer a coherent set of data with which to monitor trends and identify changes in the performance of the TEN-T road network since the year 2009. As such, these reports are a particularly useful source of information for individual National Road Authorities, regulatory bodies and others for benchmarking purposes and for setting national performance targets. More specifically, the CEDR reporting framework is based on a common simple Location Referencing Model and a consistent set of performance indicators based on common data definitions and on data provided directly by National Road Administrations. A web map is developed to display the GIS layer of CEDR’s logical network, in conformity with CEDR’s Location Referencing Model, and to allow for the visualisation of thematic maps showing road performance indicators at link level (e.g. road type, number of lanes, etc.) and for different years. An online tool is developed for the collection and visualization of CEDR Strategic Key Performance Indicators. For more information, please check the project website – cedr.eu
- Transport Market Study: Quantification of modal shift potential on the Rail Freight Corridor Rhine-Alpine The study, coordinated by TRT and involving relevant partners across Europe, aimed to quantify the potential modal shift to rail thanks to the improvement in transport performance on the Rail Freight Corridor Rhine-Alpine. More specifically, the objective of the study was to investigate the possibility to introduce: heavier and longer trains, faster trains (less stops), more reliable trains. The work was structured by three consecutive activities: analysis of the freight transport demand, quantification of the cost savings in relation to heavier, faster and more reliable trains, quantification of modal shift potential. For more information The Transport Market Study summary report is available for download here
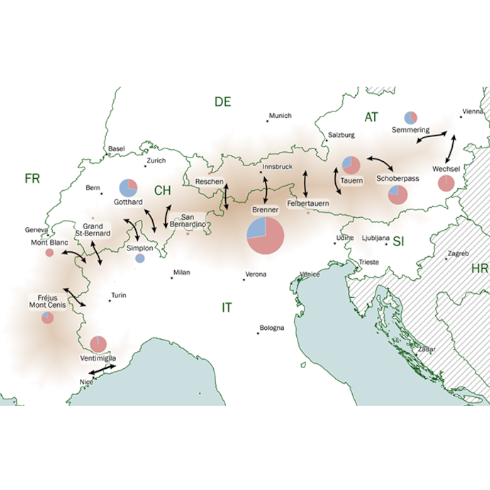
- Transalpine Observatory – Data collection and analysis of freight flows across the Alps The objective of the Observatory is to collect and make available the information for the EU-CH Terrestrial Transport Committee implementing and managing the Agreement on Terrestrial Transport between the European Union and Switzerland on 21 June 1999. As a part of the Consortium, TRT has collected, verified and analysed data on road, rail and combined transport activities through the Alps for Italian side. The types of collected data involved information on traffic, infrastructure, vehicles, transported goods, market operators, costs and environmental impacts. All data have been compared for the period 2020-2023 regarding the borders with France, Switzerland and Austria. One of the main interest of the project has been the evaluation in time of the modal split across the Alps useful for the reduction of transport’s environmental impact. TRT has also worked on designing and updating the cost model on road and combined transport, Unaccompanied (UCT) Accompanied (ACT) and Motorway Of the Sea (MoS), adoptable also for other spatial contests.