- All
- African projects
- assessment
- assessment selected projects
- Assessment selected projects 2
- Assessment selected projects 3
- Assessment selected projects 4
- ASTRA
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Electric mobility and ITS
- MOMOS
- planning
- planning selected projects
- planning selected projects 2
- planning selected projects 3
- planning selected projects 4
- planning selected projects 5
- projects
- Railways projects
- research
- research selected projects
- research selected projects 2
- research selected projects 3
- studies
- studies selected projects 1
- studies selected projects 2
- studies selected projects 3
- studies selected projects 4
- studies selected projects 5
- TRTingegneria
- TRUST
- urban mobility
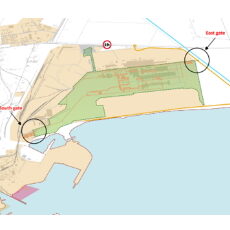
- Analysis of the external logistics of the new metallurgical complex in Piombino The analysis, developed on behalf of Metinvest Adria S.P.A., aimed to assess the impact of the external logistics of the new Piombino steel complex. The logistics operations concern the handling of bulk materials and finished steel products (coils and steel plate packaging) from the production site to the external network and vice versa. These handling operations will involve the railway line from the new complex to the Fiorentina station in Piombino, the junction of the existing railway network, the road network serving the area under study and the port area for relations by sea. The analysis was carried out considering two different delivery options of raw material to the industrial site: Option 1 (Basic), according to which the largest share of the volumes are delivered to the new complex by truck and train; Option 2 (Alternative), according to which 80 per cent of the total quantity is delivered to the site by ship. Furthermore, in the analysis of external transport by rail from the plant to the Fiorentina railway station in Piombino, two different study options were considered, which differ substantially in terms of the route taken to the external network. The current demand for both modes of transport considered was then reconstructed, the demand induced by the production site was estimated, and the infrastructures capacity was verified. As far as logistics between the port and the new complex are concerned, the number of vehicles that can be handled during daily operating hours was identified together with a check on rail capacity for an optimal evaluation of solutions. To supplement the analysis, the study included the dimensioning of checkpoints for vehicle control, loading, weighing and document operations, as well as an estimate of the number of locomotives required to manoeuvre the estimated trains.
- Scoping and Feasibility Study for a European Transport Market Study Client: RailNetEurope (RNE) RailNetEurope (in short, RNE), commissioned the consortium formed by TRT (lead) and HaCon a scoping and feasibility study for the development of a freight transport market study at the European level (European Transport Market Study, or ETMS). The need to investigate the technical characteristics, and the potential use cases of such a study stems from the scarce diffusion and lack of application of the Transport Market Studies made by individual European Rail Freight Corridors (RFCs) in the past. A European-level study would overcome the drawbacks identified with previous studies and would concretely support the necessity of optimising and coordinating efforts aimed at increasing the modal share of rail freight transport, in line with EU policy targets. The research process underlying the feasibility study was first grounded on a thorough analysis of existing RFCs’ Transport Market Studies, aimed at identifying the respective contents and structure, as well as the data sources and databases employed; further, the employment of EU-scale models was assessed with respect to the purposes of simulation and forecasting, and a wide stakeholder consultation strategy was activated, bringing i.a. infrastructure managers, railway undertakings, associations, port terminals, and members of the Rail Freight Corridors to the table. The project delivered a feasibility study with an accurate assessment of the actual possibility of making a Transport Market Study at the European scale, based on both the availability of necessary data and analytical tools, as well as the need to adequately and efficiently respond to the requests brought up by stakeholders. Specifically, several options for realising the study have been evaluated, accompanied by the definition of required analytical tools and methodologies. Based on the best solution, the main components of the actual study have been set, and guidelines for its realization have been redacted. For more information: RailNetEurope istitutional websire Dedicated page for Rail Freight Corridors
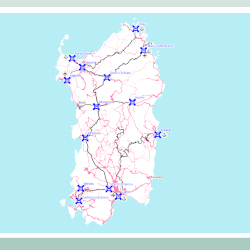
- Consultancy assignment for specialist transport engineering activities related to the “Pre-feasibility study for a regional railway network in Sardinia” on behalf of Uniontrasporti TRT collaborated with GVG Engineering on an in-depth study on the current railway network in Sardinia, defining its characteristics and potential, for a study requested by Uniontrasporti. TRT analyzed the current railway network in terms of extension and technical characteristics of both the Rete Ferroviaria Italiana (RFI, main Italian railway infrastructure manager) and secondary narrow-gauge (ARST) networks; the analysis of services offered; the analysis of production nodes and tourist demand; the definition of the needs of the local population to favor the accessibility of inner areas and support regional economic development; the definition of requirements; and the identification of modal interchange points between passenger services. This was accompanied by an analysis of the interventions planned on networks according to the Economy and Finance Document 2022 (“Documento Economia e Finanza” of Italian government), the Framework Agreement between the Region of Sardinia and RFI, the RFI 2022 Business Plan, regional planning instruments, and the three-year plan of works of ARST. The services description was based on an analysis of the timetables published on institutional websites of individual organizations. The analysis focused also on tourist services, such as the Green Train (“Trenino Verde”, a touristic service on dismissed rail lines), and urban services, above all MetroCagliari and MetroSassari. This analysis led to the identification of interchange nodes, which were described in terms of the services present. The demand analysis completes the definition of the knowledge framework, identifying the main municipalities in terms of population and employees, tourist demand over the years and identifying the most attractive municipalities. Eventually, the definition of needs analyses the information gathered during several meetings held with local stakeholders, trying to define the priorities of the territory. The study is completed by the description of possible project interventions, constraints and criticalities of the network, which TRT supported in defining.
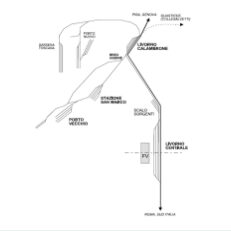
- Feasibility study and preliminary design of the railway network of the Northern Tyrrhenian sea port system TRT, with Vega Engineering, was in charge of the feasibility project for the development of railway network of the ports of Livorno and Piombino. The objective of the work is to quantify the transport demand observed in the past, with reference to the movement of goods and passengers and, at the same time, to estimate the future freight flows, also using the transport simulation model –TRUST, developed by TRTv that works at European scale. The project proposals envisage the improvement of the capacity of the existing terminals and their progressive adaptation to international standards. On the basis of the proposed project alternatives, a specific study was made of the railway capacity of the system in terms of the number of trains that can be operated by the two ports, verifying that the long-term demand forecasts can be met by the planned planning schemes, while also maintaining residual capacity . The transport performance of the railway system, together with the design characteristics (costs, construction times, etc.), constitute the database that has allowed the development of a Multicriteria Analysis that has compared the different design alternatives. A Cost Benefit Analysis was conducted, to assess the advantages and disadvantages of the project for the community.
- Impact assessment on measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail The impact assessment study is intended to provide evidence-based support for developing a new initiative implementing: Action 19: Measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including – if necessary – through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail Action 24: EU 2021 Rail Corridor Initiative – Revise the Rail Freight Corridor Regulation of the European Commission’s Smart Mobility Strategy (COM/2020/789 final) for achieving the objectives of the EU Green Deal (COM/2019/640 final). In the Green Deal and the Strategy vision for the future EU transport system, a substantial part of the 75% of inland freight carried today by road should shift onto rail and inland waterways. Moreover, rail freight traffic is projected to increase by 50% by 2030 and double by 2050; by 2030, rail and waterborne-based intermodal transport will be able to compete on equal footing with road-only transport in the EU.
- Analysis accompanying the Impact Assessment for the revision of Directive 92/106/EEC (Combined Transport Directive) The project aims to provide a robust evidence-based analysis to develop an impact assessment on the possible revision of the Combined Transport Directive. The objective of the revision is to increase the share of rail, SSS and IWW in the EU freight transport, reducing GHG emissions as well as other transport externalities such as congestion and accidents. The impact assessment should inform the specific measures to be included and the level of ambition of the revised Directive, including the following tasks: Task 1: analysis of the main problems and policy objectives identified by the Commission Task 2: Assessment of the policy measures according to their legal, political and technical feasibility Task 3: Analysis of the baseline scenario, including both the status-quo and the likely evolution of the problem drivers Task 4: Assessment of the economic, social and environmental impacts of each policy option Task 5 and 6: comparison of options and selection of the preferred policy options TRT is involved mainly in Task 3 and 4, providing among others EU scale modelling (ASTRA) for estimations of key variables (transport activity, modal share, fuel consumption, emissions, etc.) for the baseline and policy scenarios, and tailored cost models to quantify the economic impacts of the proposed measures and combination of measures.
- Implementing a multimodal transport network model of the Rail Baltica Corridor and appraisal of the passenger and freight transport activity onto the Corridor Rail Baltica Global Project is the Baltic part of a rail transport infrastructure project with a goal to integrate the Baltic States in the European rail network. The expected core outcome is a fully interoperable railway line of more than 870 km in length meant for both passenger and freight transport as part of TEN-T Core Network (North Sea – Baltic Corridor). A first phase of the study, carried out in 2021-22 consisted of two main activities. The first activity was the implementation of a multimodal transport network model of the Rail Baltica Corridor covering in some detail (NUTS3 or even sub-NUTS3 zones) the area of the three Baltic countries (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania) and of neighbouring regions of Finland and Poland plus the rest of Europe and world regions in a progressively more aggregated fashion. The transport model is a four-stage model, dealing with the estimation of generated demand, distribution, mode split and assignment to a multimodal network. The model covers both passenger and freight activity of interest for the planned rail infrastructure. All transport modes competing with rail are represented. Different rail services are explicitly modelled both for passenger (including Night-Train services) and for freight. Supporting the implementation of the model, a Stated Preference surveys was carried out to estimate parameters for the passenger demand model. The second activity of the first part of the study was the application of the model to estimate the passenger and freight demand onto the corridor in several future time thresholds, corresponding to different stages of the implementation of the infrastructure, and under three scenarios: a “do-nothing” scenario without the new infrastructure. a “Base scenario” with the new infrastructure. an alternative scenarios where alternative assumptions are made regarding intermodal rail transport services and the application of measures related to the EC Green Deal transport policy is considered. The application of the model provided several outputs ranging from aggregated statistics to link-based traffic and including impact indicators on energy consumption and emissions. The model was delivered along with the outcomes of the study and a training course focused on the use of the model was held for staff of Rail Baltica AS. This first phase of study was carried out by TRT with the support of PTV (DE), MDS Transmodal (UK), CSE COE (LV). TRT was the coordinator of the study and was responsible for developing the demand model (passenger and freight) as well as the Stated Preference survey. In a second phase (2024), some aspects of the model have been revised in order to improve the level of detail of the analysis and make the interaction with the model easier. In particular, the number of zones has been increased so that zones do not include more than one (non-urban) regional station. Following the revisions implemented, at the end of the second phase the model is recalibrated. The activities of […]
- Evaluation of Regulation (EU) No 913/2010 concerning a European rail network for competitive freight The evaluation support study covered all the provisions of the Regulation, all the European countries participating in a Rail Freight Corridor (RFC) and addressed the period from the establishment of the RFCs until 2020. The key overall challenge addressed by the Regulation is the need to improve the competitiveness of rail freight compared to other transport modes. The starting point of the Regulation is that the quality of the rail freight capacity provided by the infrastructure managers to the operators of international rail freight services needs to improve in order to make it happens. The study identified the impact of the Regulation by comparing the actual developments in the rail freight sector, i.e. with the Regulation in place, with respect to a baseline situation describing the likely developments that would have occurred without this policy intervention. The study also took into account the activities related to the RFCs going beyond the provisions of the Regulation, addressing for instance technical and operational interoperability along the RFCs. Furthermore, the study covered the activities of the rail sector undertaken in the period of analysis and contributing to the objectives of the Regulation. Practically, the study examined the relevance, effectiveness, efficiency, coherence and EU added value of the Regulation. The analysis was based on data collected from a range of primary and secondary sources and direct input from concerned stakeholders, collected using interviews and surveys with national authorities, the rail industry and the Commission’s open public consultation. The study has found that the Regulation has been implemented as far as the designation, the governance and the investment and management of the RFCs are concerned. The concerned stakeholders have fulfilled the provisions of the Regulation in a formal sense and within their actual scope. Viewed on its own, however, the Regulation has had a relatively limited impact in achieving the general, specific and operational objectives and has not led to a broad adoption of the tools, which have produced the intended effects only to a limited extent. TRT acted as leader of the study team built in partnership with M-Five (DE), MC-Vienna (AT) and TEPR (UK). TRT was responsible for (i) the design of the evaluation, (ii) the definition of an evaluation baseline, (iii) the analysis of the stakeholders consultation, (iv) the analysis of the effectiveness and efficiency of the Regulation and (v) the estimation of costs and benefits from the implementation. For more information Evaluation of EU regulation on TEN-T rail freight corridors, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication
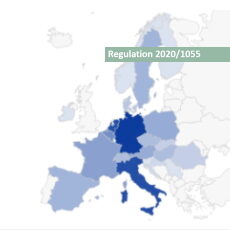
- Data gathering and analysis of the impacts of cabotage restrictions on combined transport road legs: support study for the evaluation of Regulation 2020/1055 (Mobility Package 1) Regulation 2020/1055 will allow Member States to apply the so-called cabotage restrictions to road legs of international combined transport operations if those road legs do not cross a border. The objective of the study was to provide the Commission with an analysis on the market impacts of the new restrictions. To that end, TRT conducted a survey among major combined transport organisers and terminal operators, covering all modal combinations and a wide range of Member States. The survey focused on the collection of data and information on combined transport road legs, and on the compliance strategies and impacts foreseen by the respondents. Based on the results of the survey, the study evaluated the quantitative impacts of cabotage restrictions on the European combined transport market, including estimates of the expected change in combined transport volumes, market share, modal shift and other transport activity indicators. According to the results, the rail-road segment would suffer more than the other modes considered (short sea shipping and inland navigation) mainly because of the tighter competition of the road only carriage. Relevance of the various compliance measures for CTOs (% of CT operations concerned by each measure) For more information Mobility Package 1 and impacts on combined transport sector, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication