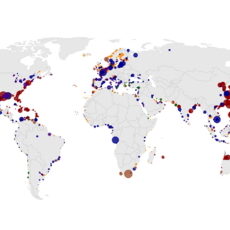
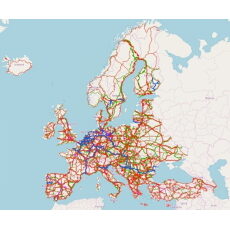
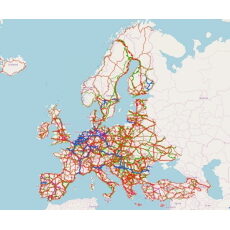
Since its first developments TRUST has been successfully used in several studies on behalf of European Commission and other European institutions
- Study on cross-border investment needs and climate adaptation of the TEN-T network The effective implementation of the TEN-T policy, with the completion of the core network and the extended network by 2030 and 2040, is key to creating a competitive industry, expanding the labour market, promoting growth and jobs and improve the daily lives of European citizens. It is therefore important to ensure sufficient investment for the completion of the TEN-T network. While it is important to complete the TEN-T, it is equally important to ensure that the infrastructure resists the threats of extreme events resulting from climate change, which will continue to increase in frequency, intensity, duration and spatial extent in the coming decades. The objectives of this study are: 1) identify the investments necessary to make the TEN-T resilient to climate change, 2) identify the investments necessary to remove the cross-border bottlenecks of the TEN-T and ensure its completion. In the study conducted together with M-FIVE (DE), VUB (BE) and ISL (DE), TRT is responsible for: Analyse and quantify the investments necessary for the completion of the TEN-T network until 2040, with particular focus on 43 cross-border projects and 33 national projects. Carry out an assessment of the economic and transport impacts resulting from the non-completion of cross-border projects with the support of two European-scale models TRUST and ASTRA. Analyse the role of CEF (Connecting Europe Facility) funds as a stimulus to the implementation of cross-border projects.
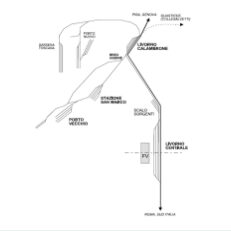
- Feasibility study and preliminary design of the railway network of the Northern Tyrrhenian sea port system TRT, with Vega Engineering, was in charge of the feasibility project for the development of railway network of the ports of Livorno and Piombino. The objective of the work is to quantify the transport demand observed in the past, with reference to the movement of goods and passengers and, at the same time, to estimate the future freight flows, also using the transport simulation model –TRUST, developed by TRTv that works at European scale. The project proposals envisage the improvement of the capacity of the existing terminals and their progressive adaptation to international standards. On the basis of the proposed project alternatives, a specific study was made of the railway capacity of the system in terms of the number of trains that can be operated by the two ports, verifying that the long-term demand forecasts can be met by the planned planning schemes, while also maintaining residual capacity . The transport performance of the railway system, together with the design characteristics (costs, construction times, etc.), constitute the database that has allowed the development of a Multicriteria Analysis that has compared the different design alternatives. A Cost Benefit Analysis was conducted, to assess the advantages and disadvantages of the project for the community.
- Impact assessment on measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail The impact assessment study is intended to provide evidence-based support for developing a new initiative implementing: Action 19: Measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including – if necessary – through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail Action 24: EU 2021 Rail Corridor Initiative – Revise the Rail Freight Corridor Regulation of the European Commission’s Smart Mobility Strategy (COM/2020/789 final) for achieving the objectives of the EU Green Deal (COM/2019/640 final). In the Green Deal and the Strategy vision for the future EU transport system, a substantial part of the 75% of inland freight carried today by road should shift onto rail and inland waterways. Moreover, rail freight traffic is projected to increase by 50% by 2030 and double by 2050; by 2030, rail and waterborne-based intermodal transport will be able to compete on equal footing with road-only transport in the EU.
- Impact assessment support study for the new proposal addressing the development of multimodal digital mobility services and a cost-benefit analysis for the revision of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/1926 on multimodal travel information services Maximising multimodality and intermodality in passenger mobility is a key element in reducing transport’s contribution to climate change while ensuring that transport systems operate efficiently, both within Member States and also across the EU’s internal borders. Multimodal digital mobility services (MDMS) are, in turn, crucial to foster multimodality as they promote comparability, transparency, and the selling of products across operators and modes. MDMS bring direct benefits to users: they help people to navigate and access an increasingly complex and diverse range of transport offerings, including a range of shared mobility services, as well as to understand the role and benefits of active modes, that will help them meet their mobility needs in different, more sustainable ways. This can also help to increase accessibility more generally, and so help to reduce social exclusion, by enabling those most in need to access the mobility services that enable them to participate more fully in society. Services that support multimodal transport also help to make transport more efficient and sustainable by increasing the utilisation of the various transport services, improving their operation, and nudging users towards the more sustainable options. The study is crucial in informing the scope and focus of the actions that are necessary at the EU level to ensure that MDMS can fully contribute to the aims of the Smart Mobility Strategy and the Green Deal and, more importantly, bring their associated benefits to users and the environment.
- Analysis accompanying the Impact Assessment for the revision of Directive 92/106/EEC (Combined Transport Directive) The project aims to provide a robust evidence-based analysis to develop an impact assessment on the possible revision of the Combined Transport Directive. The objective of the revision is to increase the share of rail, SSS and IWW in the EU freight transport, reducing GHG emissions as well as other transport externalities such as congestion and accidents. The impact assessment should inform the specific measures to be included and the level of ambition of the revised Directive, including the following tasks: Task 1: analysis of the main problems and policy objectives identified by the Commission Task 2: Assessment of the policy measures according to their legal, political and technical feasibility Task 3: Analysis of the baseline scenario, including both the status-quo and the likely evolution of the problem drivers Task 4: Assessment of the economic, social and environmental impacts of each policy option Task 5 and 6: comparison of options and selection of the preferred policy options TRT is involved mainly in Task 3 and 4, providing among others EU scale modelling (ASTRA) for estimations of key variables (transport activity, modal share, fuel consumption, emissions, etc.) for the baseline and policy scenarios, and tailored cost models to quantify the economic impacts of the proposed measures and combination of measures.
- Impact assessment for the revision of regulation (eu) n° 1315/2013 on union guide-lines for the development of the trans-european transport network The European Union with the Green Deal (proposal EC COM(2019) 640 final) has agreed to implement the Paris Climate Agreement leading the EU towards climate neutrality in 2050. In a more detailed communication in 2020 the European Commission proposed to step-up the climate policy ambition for 2030 and reduce GHG emissions of the EU by 55% compared to 1990 (EC COM(2020) 562). For the transport sector the EC published a new smart and sustainable mobility strategy in December 2020 (EC COM(2020) 789) presenting the strategic policy framework that would deliver the GHG reductions required by the transport sector for 2030 and until 2050. As part of this highly dynamic policy framework the EC has foreseen the revision of several existing transport regulations. The revision of the TEN-T guidelines is one of the major transport related policies besides the revision of the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure and the Intelligent Transport System directives and the planned revision of the Rail Freight Corridors regulation. This study carries out the analysis accompanying the impact assessment for the revision of Regulation (EU) N° 1315/2013 on Union Guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network. Supported by two European scale modelling tools ASTRA and TRUST, the study provides the assessment of three alternative policy options in terms of their transport, economic, social and environmental impacts and identifies the most promising one. The report is available on the website of the “Publications Office of the European Union” at this link.
- Corridor Munich-Verona – Study and analysis of the forecasted passenger traffic flows and the related offers of long-distance trains based on the future infrastructure This study was a modelling application targeted at forecasting future rail passenger demand on the Verona – Munich rail corridor. The opening of the Brenner Basis Tunnel (BBT) is expected by the year 2030. Its effect will be to save more than one hour from rail travel time between Munich and Verona. The full completion of infrastructure should provide additional time savings by the year 2040. This study, using modelling tools, aimed at forecasting the additional rail passenger demand onto the corridor as effect of new rail supply in order to provide inputs for the design of long-distance rail passenger services on the corridor. Four future scenarios were explored. All scenarios shared the same demographic and economic assumptions influencing the modification of the overall transport demand in the area. Then, each scenario considered a specific configuration of passenger rail services on the Corridor, especially in terms of frequencies and stops. The forecasts were based on the results of the two models: the TRUST model used by TRT dealt with long-distance origin-destination pairs at NUTS3 level, while the regional demand was simulated in more spatial detail by means of the VMÖ 2025+ model used by the Austrian company TRAFFIX. The project was managed by EBP Schweiz AG. For more information, please check BBT Brenner Base Tunnel website
- Economic modelling exercise in support of the multi-modal transport market studies for nine core network corridors The objective of the study is to provide transport and economic modelling support to the nine “Studies on the TEN-T Core Network Corridors and support of the European Coordinators”. Such transport and economic modelling support: Is based on the methodology of the “The impact of TEN-T completion of growth, jobs and the environment” study, Makes reference to the Baseline Scenario of the TEN-T Growth Study; Adopts the same approach for each of the nine corridors. The transport and economic modelling results estimate the impact on travel time and modal shift for macro sections of the different TEN-T corridors and on growth, jobs and decarbonisation by country along the corridors and for EU28, EU15, EU13.
- Specific contract for long-term quantitative assessment of policy scenarios for the EU transport system Since 2016, TRT holds a framework contract for the simulation of long-term scenarios relating to the evolution of the transport system up to 2050 in EU 27 Member States. Scenarios and their variants are assessed with the use of European scale simulation models by TRT and E3Modelling. The modelling tools are: TRUST, for the quantification of traffic impacts on road and rail networks and of specific emissions on the European territory; PRIMES-TREMOVE, for the quantification of the evolution of the vehicle fleet of different transport modes and of the related energy consumption starting from changes in costs and/or legislation on technologies; GEM-E3, for the quantification of macroeconomic impacts. Studies carried out under the framework contract concern the development of baselines, scenarios and variants focusing on transport, energy and macroeconomic systems and providing results at EU member state level. Within the Framework Contract a new Reference Scenario 2020 which takes into account the expected medium-term impact of the COVID-19 outbreak has been produced.
- The Impact Assessment study, developed for the European Commission, aims to identify and assess the impacts of policy measures on facilitating the deployment of multimodal ITS services By enabling communication between vehicles, infrastructure and other road users, Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems (C-ITS) can greatly improve safety and efficiency in road transport. Here is a look at some of the most recent developments in C-ITS and how quickly the technology could change the way we drive and interact with each other in traffic. The wide-scale deployment of Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems could contribute to delivering several Commission’s objectives for transport, such as those on safety, reduced congestion, enhanced mobility and environmental performance. Together with Ricardo Energy&Environment, TRT supported the Directorate for Mobility and Transport of the European Commission in three different studies over a six year period. In 2020-2021 for the development of an Impact Assessment Support Study for the revision of the Intelligent Transport Systems Directive (2010/40/EU) to support the EC with evidence-based analysis. In 2017-2018 developing the legal framework required to support the widespread deployment of C-ITS services in Europe by 2019: a set of policy options and deployment scenarios were assessed with the European scale modelling tools ASTRA and TRUST for the analysis and comparison of the impacts in terms of economic, environmental and social indicators. In 2015 for the preparation of the Communication strategy and the Action plan for the deployment of C-ITS in Europe, providing the analysis of costs and potential benefits based on different scenarios. To support the analysis, the ASTRA and TRUST models are applied to provide quantitative indicators to evaluate the impacts of various policy options and deployment scenarios. For more information Final report of 2015 study Final report of 2017-2018 study
- Sustainable Transport Infrastructure Charging and Internalisation of Transport Externalities The objective of the study was to assess the extent to which the “user pays” and the “polluter pays” principles were implemented. This allowed the European Commission to take stock of the progress of Member States towards the goal of full internalisation of external and infrastructure costs of transport and to identify options for further internalisation. The scope of the study involved all external costs, all transport modes and, geographically, EU28 plus Norway, Switzerland, USA (2 States), Canada (2 provinces) and Japan. To realise the general objective and address the scope of the study information has been collected extensively about: infrastructure costs (i.e., investment, renewal and operating), transport-related charges, earmarking of fiscal revenues and compensations paid by the users. The analyses carried out in this study showed that the transport taxes and charges levied in the EU Member States are in general insufficient to fully internalise the external and infrastructure costs of transport. For most vehicle categories, only 15% to 25% of the external and infrastructure costs are covered by tax/charge revenues. The cost coverage ratio for passenger cars was found higher (about 50%), which was mainly because of the relatively high fuel and vehicle tax levels applied in (some of) the EU Member States for these vehicles. For inland waterways and maritime transport, much lower cost coverage ratios were found (i.e., 6% and 4%, respectively), reflecting the limited tax/charge burden levied on these modes in the EU. Even if one excludes fixed infrastructure costs from the analyses, the taxes and charges did not cover the external and variable infrastructure costs for most vehicle categories. High-speed trains are an exception, as for these trains the current taxes and charges did cover all external and variable infrastructure costs. This finding has been supported by the results of the analyses of the marginal social cost (MSC) coverage ratios. Despite the limitations of this analyses, it provides a first indication that there was a lack of charging in accordance with the MSC principle in the EU28. The revenues from transport taxes and charges in the EU28 were partly earmarked for expenditure for transport infrastructure. However, significant differences did exist between modes. For road transport, about 10% of the taxes/charges are earmarked, while for rail transport this is about 85%. For the other modes, only fragmented data on earmarking was identified, showing that (at least part of) the (air)port charges are earmarked to cover infrastructure expenditures. Although taxes and charges are efficient policy instruments to reduce the external costs of transport, the study recognize that other types of policy instruments and non-pricing policies (e.g., command-and-control measures and subsidies) may effectively complement tax and charge schemes, for example by providing EU-wide harmonised incentives to invest in certain reduction technologies. With regard to the activities of the study, TRT was responsible to (i) develop estimations of the external costs related to congestion for all transport modes (quantitatively for road), (ii) elaborate estimations of the infrastructure costs […]
- The impact of TEN-T completion on growth, jobs and the environment The objective of the study is to quantify the impact of the TEN-T core network implementation until 2030 – as well as the impact of each of the nine core network corridors separately – on European Union growth, jobs and the environment. The assessment is done with the support of two European scale modelling tools ASTRA and TRUST. ASTRA is a System Dynamics model used for assessing the wider economic impacts like indirect and induced changes in employment or value added and economic growth due to the TEN-T investments. TRUST is a transport network model allowing for the assignment of OD matrices at the NUTS3 level for passenger and freight demand which is used to provide the transport quantitative inputs to ASTRA. A set of major economic, environmental and transport indicators is provided for the assessment at EU level as well as at the level of Member States for the base year 2015 and the time horizons 2020, 2025 and 2030. The quantitative indicators are accompanied by qualitative arguments where required to elaborate on the quality of jobs created and the typology of jobs. For more information The impact of TEN-T completion on growth, jobs and the environment. Go to the publication
- Impact assessment accompanying the revision of Eurovignette Directive for Heavy Goods Vehicles charging The “Eurovignette” Directive provides a detailed legal framework for charging heavy goods vehicles (HGVs) for the use of certain roads. Following ex-post evaluations of the current legislative framework, the Commission intends to assess the potential impacts of options for a possible revision of the legislative act. The impact assessment study will help substantiate the specific problems linked to charging of vehicles and to design policy options in this field. TRT supports the quantitatve assessment of the impacts of the policy options through the use of European scale models ASTRA and TRUST.
- Support Study for the Impact Assessment Accompanying the Revision of the Eurovignette Directive (1999/62/EC) The charging of heavy goods vehicles (HGVs) for the use of road infrastructure in Europe is governed by Directive 1999/62/EC (the “Eurovignette” Directive). The Directive aimed to achieve step-wise harmonisation of vehicle taxes and establishment of fair mechanisms of infrastructure charging. The general objective of the proposed revision of Directive 1999/62/EC is to promote financially and environmentally sustainable and socially equitable (road) transport through wider application of the ‘user pays’ and ‘polluter pays’ principles (fair and efficient pricing). This study supported the DG MOVE experts in evaluating the impact of the new Directive analysing several interventions trough three different models: ASTRA (to estimate the impacts on the transport and economy systems), TRUST (to estimate the impacts on the traffic distribution), PRIMES-TREMOVE (to estimate the trend of the vehicle fleet). The model suite covers the entire transport system (e.g. transport activity represented at Member State level, by origin-destination and at link level, technologies and fuels at Member State level, air pollution emissions at Member State and link level and CO2 emissions at Member State level) and its macro-economic impacts. The modelling is complemented by a literature review and stakeholder consultation. Input from stakeholders is gathered via an online public consultation and a targeted consultation (mainly via interviews, with some written contributions) that gathers more detailed views and factual information on the considered policy options. For more information Support Study for the Impact Assessment Accompanying the Revision of the Eurovignette Directive (1999/62/EC), Final Report
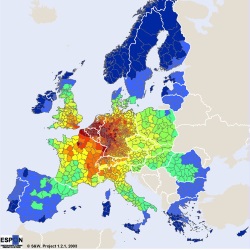
- The ESPON project TRACC (TRansport ACCessibility at regional/local scale and patterns in Europe) The ESPON project TRACC (TRansport ACCessibility at regional/local scale and patterns in Europe) aimed at updating the results of previous studies, extending the range and the spatial resolution of accessibility indicators in response to the most recent policy questions. The TRACC conceptual framework is based on a systematic and comprehensive theoretical consideration of the major dimensions of accessibility, as well as of the most frequently used types of accessibility indicators and extensions of these. TRACC developed a systematic and consistent set of accessibility indicators, differentiated according to three spatial contexts (global, European, regional) and also between travel and freight. At European level, accessibility indicators for travel are further distinguished between traditional and newer ones. At regional level, moreover, a new set of indicators is included focusing on the accessibility to services of general interest, which are among the top priorities in the current policy agenda.