TRT has proven experience in transport project assessment, socio-economic and financial analysis, impact analysis.
The company experts have prepared cost-benefit analysis guides and handbooks on behalf of national and international institutions and have participated in research projects on ex-ante and ex-post evaluation of transport projects and policies.
Project evaluation and impact assessment expertise concerns railway, road and port infrastructure investment projects as well as urban, regional and national mobility and transport plans and transport regulations and policies.
- Application of the TRUST model to support the resilience analysis of the Alpine crossing system The aim of the study was to analyse the resilience of the Alpine crossing system, that is, to evaluate how much the complex of crossings can guarantee an adequate level of service in case of “breakdown” events. For this purpose, the TRUST model, which is a strategic model at European scale, was used to simulate the functioning of the entire range of crossings with respect to the different hypothesized scenarios. The definition of the scenarios considered the fact that, from the point of view of their modelling, it is not the nature of the event that generates a certain variation of the inputs that is significant, but the extent of the variation that is determined in the functioning of the transport system. The scenarios have been translated into variations of one or more input elements of the model itself, namely: availability of some arcs to the modelled vehicle categories, capacity of the road links, travel speed on the links for the modelled vehicle categories. The application of the TRUST model produced, for each scenario, the following results compared to the reference situation:
- Assess the degree of the implementation of the ‘user pays’ and the ‘polluter pays’ principles in the transport field in the EU Member States and other developed countries The objective of the study is to assess the extent to which the “user pays” and the “polluter pays” principles are implemented in the transport field. This allows the European Commission to observe the progress of Member States towards the goal of full internalisation of external and infrastructure costs of transport and to identify options for further internalisation. This study is an update of previous studies published in the years 2019 and 2014. The scope of the current study is extended to cover all external costs, all transport modes and, geographically, EU27 plus UK, Norway, Switzerland, Turkey, Western Balkans, Iceland, USA (2 States), Canada (2 provinces), Japan, Australia, New Zealand. Specific objectives concern: Provide estimations of total, average and marginal infrastructure and external costs for all relevant modes/vehicle categories and countries. Provide a detailed and transparent overview of the transport-related taxes and charges, including their structure and revenues, for all relevant modes/vehicle categories and countries. Assess the application for the different transport modes in the relevant countries of both the user-pays and polluter-pays principles. The update of the Handbook on External costs The objectives of the study are achieved through a comprehensive data collection on infrastructure costs (i.e., investment, renewal and operating), transport charges, earmarking of tax revenues and user charges. Appropriate methodologies are applied to estimate external costs for all modes and categories. With regard to the activities of the study, TRT (already involved in previous studies) is responsible for: developing estimates of the external costs related to congestion for all transport modes, developing estimates of infrastructure costs for rail mode and with regard to all categories of external costs elaborating the analysis of six case studies on intermodal freight terminals, and supporting data collection, as country expert for Italy, France, Poland, Latvia and Lithuania. For more information, check our previous study on Sustainable Transport Infrastructure Charging and Internalisation of Transport Externalities
- Analysis of the external logistics of the new metallurgical complex in Piombino The analysis, developed on behalf of Metinvest Adria S.P.A., aimed to assess the impact of the external logistics of the new Piombino steel complex. The logistics operations concern the handling of bulk materials and finished steel products (coils and steel plate packaging) from the production site to the external network and vice versa. These handling operations will involve the railway line from the new complex to the Fiorentina station in Piombino, the junction of the existing railway network, the road network serving the area under study and the port area for relations by sea. The analysis was carried out considering two different delivery options of raw material to the industrial site: Option 1 (Basic), according to which the largest share of the volumes are delivered to the new complex by truck and train; Option 2 (Alternative), according to which 80 per cent of the total quantity is delivered to the site by ship. Furthermore, in the analysis of external transport by rail from the plant to the Fiorentina railway station in Piombino, two different study options were considered, which differ substantially in terms of the route taken to the external network. The current demand for both modes of transport considered was then reconstructed, the demand induced by the production site was estimated, and the infrastructures capacity was verified. As far as logistics between the port and the new complex are concerned, the number of vehicles that can be handled during daily operating hours was identified together with a check on rail capacity for an optimal evaluation of solutions. To supplement the analysis, the study included the dimensioning of checkpoints for vehicle control, loading, weighing and document operations, as well as an estimate of the number of locomotives required to manoeuvre the estimated trains.
- Update of the study on the “Costs and Benefits of the Urban Mobility Transition” The Costs and Benefits of the sustainable urban mobility transition study was carried in 2021 by TRT with the purpose of assessing the impacts of different sustainable urban mobility scenarios in European cities while quantifying the costs and benefits of this transition in 2030 and 2050. The current study consists in an update and improvement of the previous analysis, aiming to: Refine the input data, the intervention levels and targets of the policy measures of the transition scenarios and their timeline of implementation. Improve and enlarge the policy measures applied to the scenarios Run a new modelling simulation to quantify the expected costs and benefits of the sustainable urban mobility transition in European cities by 2030 and by 2050. Draft specific policy recommendations for practitioners. Provide a set of relevant datasets for the development of an interactive tool The calculation is based on an improvement and extension of the MOMOS model, which allows to assess the impacts of different mobility transition scenarios. The quantification of results is applied to 12 city prototypes (representing more than 780 cities in EU27), considering different dimensions (small, medium, and large cities) and geographic areas (southern, central/western, northern, and eastern Europe). The project will consider three potential scenarios, based on a combination of policy measures taken from key EU initiatives and related to the specific emphasis of each scenario. The available measures are of a different nature and comprehensively cover the range of options that cities currently have available to promote the transition to sustainable urban mobility, belonging to eight different policy groups: Shared Mobility; Innovative mobility services; Vehicle fleet & Charging Infrastructure; Transport Infrastructure; Transport avoidance and behaviour; Pricing Schemes; Traffic management and control; urban logistics. The outputs of the study will consist in a series of indicators from three domains, estimated at base year 2022 as well as at future years 2030 and 2050: transport (modal split, car ownership), environment (CO2 and air pollutant emissions, fatalities), and economic (city costs, revenues, user and freight operator costs, and externalities). Also, building on the results for the 12 city prototypes and on a policy effectiveness comparison of the different groups of policy measures, a series of recommendations focused on mobility practitioners will be provided. For more information: Previous contract
- Study on cross-border investment needs and climate adaptation of the TEN-T network The effective implementation of the TEN-T policy, with the completion of the core network and the extended network by 2030 and 2040, is key to creating a competitive industry, expanding the labour market, promoting growth and jobs and improve the daily lives of European citizens. It is therefore important to ensure sufficient investment for the completion of the TEN-T network. While it is important to complete the TEN-T, it is equally important to ensure that the infrastructure resists the threats of extreme events resulting from climate change, which will continue to increase in frequency, intensity, duration and spatial extent in the coming decades. The objectives of this study are: 1) identify the investments necessary to make the TEN-T resilient to climate change, 2) identify the investments necessary to remove the cross-border bottlenecks of the TEN-T and ensure its completion. In the study conducted together with M-FIVE (DE), VUB (BE) and ISL (DE), TRT is responsible for: Analyse and quantify the investments necessary for the completion of the TEN-T network until 2040, with particular focus on 43 cross-border projects and 33 national projects. Carry out an assessment of the economic and transport impacts resulting from the non-completion of cross-border projects with the support of two European-scale models TRUST and ASTRA. Analyse the role of CEF (Connecting Europe Facility) funds as a stimulus to the implementation of cross-border projects.
- Impact assessment on measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail The impact assessment study is intended to provide evidence-based support for developing a new initiative implementing: Action 19: Measures to better manage and coordinate international rail traffic, including – if necessary – through revised rules for capacity allocation and infrastructure charging in rail Action 24: EU 2021 Rail Corridor Initiative – Revise the Rail Freight Corridor Regulation of the European Commission’s Smart Mobility Strategy (COM/2020/789 final) for achieving the objectives of the EU Green Deal (COM/2019/640 final). In the Green Deal and the Strategy vision for the future EU transport system, a substantial part of the 75% of inland freight carried today by road should shift onto rail and inland waterways. Moreover, rail freight traffic is projected to increase by 50% by 2030 and double by 2050; by 2030, rail and waterborne-based intermodal transport will be able to compete on equal footing with road-only transport in the EU.
- Impact assessment support study for the new proposal addressing the development of multimodal digital mobility services and a cost-benefit analysis for the revision of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/1926 on multimodal travel information services Maximising multimodality and intermodality in passenger mobility is a key element in reducing transport’s contribution to climate change while ensuring that transport systems operate efficiently, both within Member States and also across the EU’s internal borders. Multimodal digital mobility services (MDMS) are, in turn, crucial to foster multimodality as they promote comparability, transparency, and the selling of products across operators and modes. MDMS bring direct benefits to users: they help people to navigate and access an increasingly complex and diverse range of transport offerings, including a range of shared mobility services, as well as to understand the role and benefits of active modes, that will help them meet their mobility needs in different, more sustainable ways. This can also help to increase accessibility more generally, and so help to reduce social exclusion, by enabling those most in need to access the mobility services that enable them to participate more fully in society. Services that support multimodal transport also help to make transport more efficient and sustainable by increasing the utilisation of the various transport services, improving their operation, and nudging users towards the more sustainable options. The study is crucial in informing the scope and focus of the actions that are necessary at the EU level to ensure that MDMS can fully contribute to the aims of the Smart Mobility Strategy and the Green Deal and, more importantly, bring their associated benefits to users and the environment.
- Analysis accompanying the Impact Assessment for the revision of Directive 92/106/EEC (Combined Transport Directive) The project aims to provide a robust evidence-based analysis to develop an impact assessment on the possible revision of the Combined Transport Directive. The objective of the revision is to increase the share of rail, SSS and IWW in the EU freight transport, reducing GHG emissions as well as other transport externalities such as congestion and accidents. The impact assessment should inform the specific measures to be included and the level of ambition of the revised Directive, including the following tasks: Task 1: analysis of the main problems and policy objectives identified by the Commission Task 2: Assessment of the policy measures according to their legal, political and technical feasibility Task 3: Analysis of the baseline scenario, including both the status-quo and the likely evolution of the problem drivers Task 4: Assessment of the economic, social and environmental impacts of each policy option Task 5 and 6: comparison of options and selection of the preferred policy options TRT is involved mainly in Task 3 and 4, providing among others EU scale modelling (ASTRA) for estimations of key variables (transport activity, modal share, fuel consumption, emissions, etc.) for the baseline and policy scenarios, and tailored cost models to quantify the economic impacts of the proposed measures and combination of measures.
- Impact assessment for the revision of regulation (eu) n° 1315/2013 on union guide-lines for the development of the trans-european transport network The European Union with the Green Deal (proposal EC COM(2019) 640 final) has agreed to implement the Paris Climate Agreement leading the EU towards climate neutrality in 2050. In a more detailed communication in 2020 the European Commission proposed to step-up the climate policy ambition for 2030 and reduce GHG emissions of the EU by 55% compared to 1990 (EC COM(2020) 562). For the transport sector the EC published a new smart and sustainable mobility strategy in December 2020 (EC COM(2020) 789) presenting the strategic policy framework that would deliver the GHG reductions required by the transport sector for 2030 and until 2050. As part of this highly dynamic policy framework the EC has foreseen the revision of several existing transport regulations. The revision of the TEN-T guidelines is one of the major transport related policies besides the revision of the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure and the Intelligent Transport System directives and the planned revision of the Rail Freight Corridors regulation. This study carries out the analysis accompanying the impact assessment for the revision of Regulation (EU) N° 1315/2013 on Union Guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network. Supported by two European scale modelling tools ASTRA and TRUST, the study provides the assessment of three alternative policy options in terms of their transport, economic, social and environmental impacts and identifies the most promising one. The report is available on the website of the “Publications Office of the European Union” at this link.
- New hospital in piacenza: transport study and cost-benefit analysis for the design of the feasibility study for the new location in area 5 TRT Trasporti e Territorio was commissioned by the Local Health Unit (AUSL) of Piacenza to provide technical support to the design group led by Policreo Srl, with the in-depth studies on the Transport Study and the Cost-Benefit Analysis developed within the Feasibility Study, (drawn up in accordance with art. 14 of Presidential Decree No. 207/2010), of the New Hospital of Piacenza related to area 5 (AL 9), located in the urban sector within the urban ring road, between Corso Europa and Strada Farnesiana. The study is divided into three main activities: the first is about the mobility and parking system related to the current hospital location, analysing in detail the system of roads, parking and public-private accessibility of the area. the second is about the functionality of the road infrastructures serving the new hospital in Piacenza, assessing the impact of the private mobility system, in terms of road infrastructures and the parking system; the third explores cost-benefit analysis issues, comparing the new project of the hospital with the option of maintaining and upgrading the existing hospital. The cost-benefit analysis estimates the project’s contribution to improving the social-economic well-being of the community, i.e. it estimates whether the social-economic advantages, or benefits, outweigh the disadvantages, or social costs. Related projects: Transport study and cost-benefit analysis of the new hospital in Piacenza
- Study on costs and benefits of the sustainable urban mobility transition The study had the objective to assess the impacts of different sustainable urban mobility transition scenarios, producing a quantitative analysis of their costs and benefits for European cities by 2030 and 2050. The calculation is based on an improvement and extension of the MOMOS model, which allows to calculate the costs and benefits of the transition through a set of indicators. To take into account differences among 779 European cities, the quantification of results has been applied to 12 city prototypes, which considered different dimensions (small, medium, and large cities) and geographic areas (southern, central/western, northern, and eastern Europe). The project considered three potential scenarios, based on a combination of policy measures taken from key EU initiatives: Promote and regulate, based on changing behaviour and promotion; Plan and build, focused on investments in technology and infrastructure; Mixed, which combines policies from the previous two scenarios. The three scenarios were built on specific combinations and applications of policy measures, belonging to six different policy groups: Shared Mobility and Demand Management; Innovative Services; Green Public Transport and Logistics Fleets & Charging Infrastructure; Pricing Schemes; Transport Infrastructure; Traffic management and control. The outputs of the study consisted in a series of indicators from three domains: transport (modal split, car ownership), environment (CO2 emissions, fatalities), and economic (city costs, revenues, and externalities). Also, a policy effectiveness comparison determined the best policy measures, in terms of associated cost/revenues and CO2 reduction, according to different city sizes. For more information: Full results of the study can be explored with this interactive tool. The study’s Full Report can be downloaded here. Additional info can also be found on the EIT Urban Mobility website For more information: New contract Interactive tool to explore results of 2021 study 2021 study’s Full Report EIT Urban Mobility website on 2021 study
- Technical Assistance to Develop a Business Model to Finance and Scale-up E-Mobility in Uruguay Uruguay has an emerging electric vehicle sector, with good growth prospects and a strong policy agenda on fleet electrification. The country has committed to several mitigation measures in the transport sector, such as the introduction of electric vehicles in public transport, of utility electric vehicles and the installation of the first electrical route of Latin America connecting Colonia-Montevideo-Chui. The main objective of this project is to provide a policy and regulatory guide for a smooth transition to e-mobility in Uruguay and help the country to achieve an efficient and sustainable transport decarbonisation, through: Diagnosis of the current infrastructure and regulatory situation of e-mobility; Assessment of the several pilot projects already developed; Identification of desired business models and financing scheme for e-buses and private EVs; Propose a policy and regulatory guide to achieve overall e-mobility expansion targets in a time-line consistent with Uruguayan Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to the Paris Agreement objectives; Propose a consistent and sustainable body of fiscal incentives and subsidies to favour and promote the previous e-mobility targets. The project is carried out by an international consortium led by MRC Consultants and Transaction Advisers (ES) and composed by TRT (IT) and SEG Ingeniería (UY). TRT is specifically involved in the project component related to private e-mobility, as well as in the fiscal impact assessment to proposed measures and policies. The project will provide a set of outputs including: E-bus financing alternative sschemes with estimated cost impact, timeframe, and impact on rolling stock; Assessment of long-term fiscal impact and ways to ensure efficiency and sustainability of alternative schemes; Regulatory and fiscal incentive schemes to sustainably increase use of private e-vehicles; Long-term fiscal impact analysis of incentives and tax revenues from foregone taxes, and elaborate recommendations; Two public workshops and related materials available for knowledge sharing.
- Assessment of infrastructure costs calculation, tolls calculation and variation for heavy goods vehicles in Member States Directive 1999/62/EC and following amendments provide the legal framework for the application of toll charges to heavy vehicles in the EU, stipulating that road infrastructure charging shall be based on the recovery of infrastructure costs and of traffic-related externalities. Before implementing or amending tolling arrangements, Member States must provide the Commission with a detailed description of the new system. As contractor of the FWC, TRT verifies whether the tolling arrangement notified to the Commission fully respects the provisions of the Directive. The methodology applied for the assessment includes: determination of the scope of the tolling scheme notified by the Member State; identification of costs eligible to be recovered through tolls; allocation of infrastructure costs across vehicles categories; calculation of the weighted average tolls and cost recovery rate. In its assessment reports, TRT provides sound and evidence‐based analyses of the methodology used for infrastructure costs calculation, assessment of compliancy with the Directive’s core principles, as well as recommendations for possible modifications and improvements. Thus far TRT has assessed nine cases, including tolling arrangements from Italy, Spain, France, Bulgaria, Poland and Hungary.
- Flex-Rail – Paradigm shifts for railway – Technology uptake strategies for a lean, integrated and flexible railway system Shift2Rail (S2R, shift2rail.org) develops the building blocks for the future rail system, as envisaged in the Multi‐Annual Action Plan (MAAP). However, S2R’s work programmes need to be continuously monitored and updated to ensure that they optimally make use of the potential of new technological innovations and developments rising in the society, other industries and specifically within the rail sector. The Flex‐Rail project has the objective of identifying and assessing technological possibilities and innovative concepts that can shape rail operating and business models, aiming to contribute to the formulation of required paradigm shifts for the rail sector. In this view, Flex-Rail has the vision to target a lean, integrated and flexible railway system to stimulate further innovation of the rail sector and ensure that rail the services can address the future user needs. In particular, the Flex-Rail project addresses the following aspects: forecast the evolution of key fundamental technologies and identification of technical risks and potential blocking points; analysis of possible achievement of future impacts, through the definition and implementation of an impact assessment framework and modelling tool for rail scenario and transition pathways; formulation of technological concepts for a future rail system scenario developed on a participatory process involving the users of the rail system. Also, the scenarios build on the analysis of trends and innovations happening in other transport sectors; assessment of business feasibility and analysis of the current safety requirements. The Flex-Rail project develops an in‐depth overview of the state of the art of ideas and technological trends related to innovations of the transport industry and non‐transport sector technologies. As such, it constitutes a knowledge basis for subsequent activities focussed on (i) the definition of key performance indicators, which are key assessment components, (ii) the identification of gaps and development of future (rail system) transition pathways and (iii) the impact assessment of these transition pathways and scenarios. A dedicate interactive website has been created to explore technological trends an innovations relevant for rail transport(*). On these basis, a dedicated assessment framework has been designed to determine the impact of innovation packages and transition pathways on a number of key performance indicators for rail transport and per System Platform Demonstrator (SPD), as defined in S2R’s MAAP. A gap analysis for each SPD has been developed, considering the fulfilment of user’s requirements of rail and modal competitors and for different market segments. This has allowed to identify potential market segments and rail modal share growth. By evaluating such possible paradigm solutions, with aligning or enabling trends and technologies, future scenarios have been developed and assessed on the basis of an open-innovation process for collecting additional future requirements. Among its activities, Flex-Rail mapped projects, studies, initiatives and experts’ groups outputs related to new technologies and trends within and outside the transport sectors that may directly and indirectly have an influence on the rail transport sector. Mapping such these activities ensured coherence with the worldwide […]
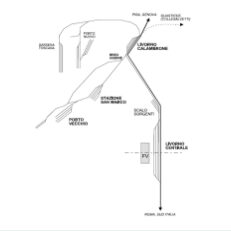
- Feasibility study and preliminary design of the railway network of the Northern Tyrrhenian sea port system TRT, with Vega Engineering, was in charge of the feasibility project for the development of railway network of the ports of Livorno and Piombino. The objective of the work is to quantify the transport demand observed in the past, with reference to the movement of goods and passengers and, at the same time, to estimate the future freight flows, also using the transport simulation model –TRUST, developed by TRTv that works at European scale. The project proposals envisage the improvement of the capacity of the existing terminals and their progressive adaptation to international standards. On the basis of the proposed project alternatives, a specific study was made of the railway capacity of the system in terms of the number of trains that can be operated by the two ports, verifying that the long-term demand forecasts can be met by the planned planning schemes, while also maintaining residual capacity . The transport performance of the railway system, together with the design characteristics (costs, construction times, etc.), constitute the database that has allowed the development of a Multicriteria Analysis that has compared the different design alternatives. A Cost Benefit Analysis was conducted, to assess the advantages and disadvantages of the project for the community.
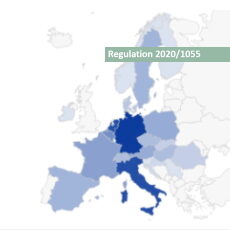
- Data gathering and analysis of the impacts of cabotage restrictions on combined transport road legs: support study for the evaluation of Regulation 2020/1055 (Mobility Package 1) Regulation 2020/1055 will allow Member States to apply the so-called cabotage restrictions to road legs of international combined transport operations if those road legs do not cross a border. The objective of the study was to provide the Commission with an analysis on the market impacts of the new restrictions. To that end, TRT conducted a survey among major combined transport organisers and terminal operators, covering all modal combinations and a wide range of Member States. The survey focused on the collection of data and information on combined transport road legs, and on the compliance strategies and impacts foreseen by the respondents. Based on the results of the survey, the study evaluated the quantitative impacts of cabotage restrictions on the European combined transport market, including estimates of the expected change in combined transport volumes, market share, modal shift and other transport activity indicators. According to the results, the rail-road segment would suffer more than the other modes considered (short sea shipping and inland navigation) mainly because of the tighter competition of the road only carriage. Relevance of the various compliance measures for CTOs (% of CT operations concerned by each measure) For more information Mobility Package 1 and impacts on combined transport sector, the study carried out by TRT. Go to the publication